Aldehydes and ketones are organic compounds that contain the carbonyl functional group (C=O). In this answer, I will provide an overview of some important concepts related to aldehydes and ketones that are relevant for JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course.
- Nomenclature: Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e ending of the parent alkane with -al. Ketones are named by replacing the -e ending of the parent alkane with -one. The position of the carbonyl group is indicated by a number, starting from the end of the chain closest to the carbonyl group.
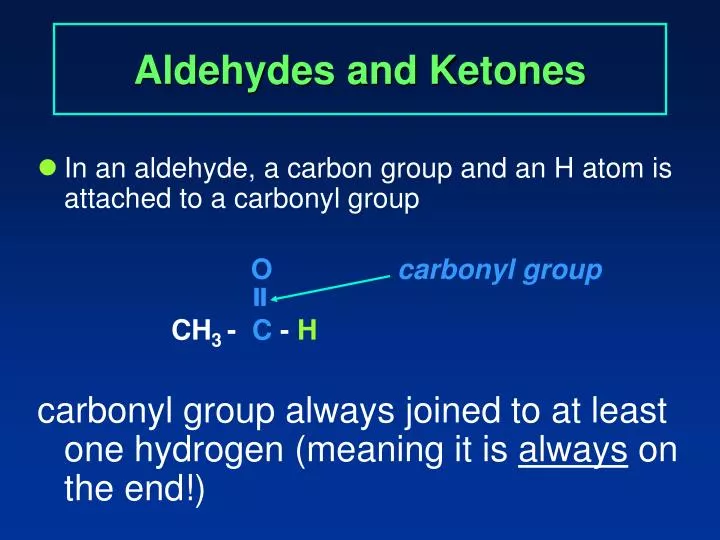
- Structure and properties: Aldehydes have a carbonyl group at the end of the carbon chain, while ketones have a carbonyl group in the middle of the carbon chain. This difference in structure affects their physical and chemical properties. Aldehydes are more reactive than ketones due to the greater polarization of the carbonyl group in aldehydes.
- Preparation: Aldehydes can be prepared by oxidation of primary alcohols using oxidizing agents like potassium permanganate or chromic acid. Ketones can be prepared by oxidation of secondary alcohols using the same oxidizing agents.
- Reactions: Aldehydes and ketones undergo a variety of reactions, including nucleophilic addition, reduction, and oxidation. Some important reactions include:
- Addition of nucleophiles: Aldehydes and ketones can react with nucleophiles (such as Grignard reagents, cyanide ion, or water) to form addition products.
- Reduction: Aldehydes can be reduced to primary alcohols using reducing agents like sodium borohydride or lithium aluminum hydride. Ketones can be reduced to secondary alcohols using the same reducing agents.
- Oxidation: Aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acids using oxidizing agents like potassium permanganate or chromic acid. Ketones are resistant to oxidation under normal conditions.
- Uses: Aldehydes and ketones have many important uses in industry and daily life. Some examples include formaldehyde (used as a disinfectant and in the production of resins), acetone (used as a solvent and in nail polish remover), and benzaldehyde (used in perfumes and flavorings).
Overall, a thorough understanding of the properties and reactions of aldehydes and ketones is essential for success in JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course.
History of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Aldehydes and Ketones
The study of aldehydes and ketones has a long history in organic chemistry, dating back to the early 19th century. One of the first aldehydes to be isolated and studied was formaldehyde, which was first prepared by the Russian chemist Aleksandr Butlerov in 1859.
In the following decades, many other aldehydes and ketones were isolated and their properties were studied. In 1872, the German chemist Hermann Kolbe showed that acetic acid could be prepared from acetaldehyde, providing an important insight into the relationship between aldehydes and carboxylic acids.
In the early 20th century, the development of new techniques for organic synthesis and the discovery of new reactions greatly expanded the field of organic chemistry. The study of aldehydes and ketones continued to be an important area of research, with many new compounds and reactions being discovered.
The importance of aldehydes and ketones in industry and daily life also grew during this time, with the development of new applications for these compounds in the production of plastics, resins, and other materials.
In India, the Joint Entrance Examination (JEE) was first introduced in 2002 as a common entrance examination for admission to engineering programs at the undergraduate level. The JEE (Main+Advanced) examination, which covers topics including aldehydes and ketones, was introduced in 2013 as a two-tier examination system for admission to the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) and other top engineering colleges in India.
Today, the study of aldehydes and ketones continues to be an important area of research and education in organic chemistry, and remains a key topic in the JEE (Main+Advanced) Intermediate Course.
Importance of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Aldehydes and Ketones
The study of aldehydes and ketones is an important part of the JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course, and has a number of practical applications in various fields.
- Industry: Aldehydes and ketones are widely used in industry as intermediates in the production of a variety of chemicals, including solvents, plastics, and pharmaceuticals. Formaldehyde, for example, is used in the production of resins, while acetone is used as a solvent and in the production of plastics.
- Organic synthesis: Aldehydes and ketones are important building blocks in organic synthesis. They can be used to prepare a wide variety of other organic compounds through a range of reactions, including nucleophilic addition, reduction, and oxidation.
- Biological systems: Aldehydes and ketones are also important in biological systems. For example, glucose, a key source of energy for the body, is an aldose (a type of sugar that contains an aldehyde functional group). Ketones are also produced by the body during periods of fasting or low-carbohydrate diets.
- Chemical analysis: Aldehydes and ketones can be used in analytical chemistry for the detection and quantification of various compounds. For example, the Fehling’s test and Tollens’ test are commonly used to detect the presence of aldehydes and ketones in a sample.
- Academic research: The study of aldehydes and ketones is also important in academic research, particularly in the fields of organic chemistry and biochemistry. Many important discoveries in these fields have been made through the synthesis and study of aldehydes and ketones.
Overall, a thorough understanding of aldehydes and ketones is essential for success in many fields, including chemistry, biochemistry, and engineering, making it an important topic in the JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course.
Benefits of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Aldehydes and Ketones
There are several benefits of studying aldehydes and ketones in the JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course.
- Understanding of organic chemistry: Aldehydes and ketones are an important part of organic chemistry, and a thorough understanding of these compounds can help students develop a deeper understanding of the principles of organic chemistry. This can be useful not only in academic research, but also in industry, where a strong background in organic chemistry is often required.
- Preparation for further education: Students who plan to pursue further education in chemistry, biochemistry, or related fields will likely encounter aldehydes and ketones again in their studies. A strong foundation in these compounds gained through the JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course can help prepare students for success in their future studies.
- Preparation for engineering and other technical fields: Aldehydes and ketones are used in a variety of technical fields, including engineering, materials science, and chemical processing. Students who plan to pursue careers in these fields will benefit from a solid understanding of aldehydes and ketones gained through the JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course.
- Practical applications: The study of aldehydes and ketones has a number of practical applications in industry, as mentioned earlier. Students who have a solid understanding of these compounds can be better prepared to work in industry or pursue careers that involve the use of aldehydes and ketones.
- Development of problem-solving skills: The study of aldehydes and ketones involves problem-solving skills, such as predicting the outcome of reactions and understanding reaction mechanisms. These skills can be valuable in many fields, including science, engineering, and technology.
Overall, the JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course in aldehydes and ketones can provide students with a strong foundation in organic chemistry, prepare them for further education and careers in technical fields, and develop important problem-solving skills.
Conclusion of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Aldehydes and Ketones
In conclusion, the JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course in aldehydes and ketones is an important part of the overall curriculum in chemistry. Aldehydes and ketones are versatile organic compounds that have numerous practical applications in industry, biochemistry, and other technical fields. A thorough understanding of aldehydes and ketones can help students develop problem-solving skills, prepare for further education and careers in chemistry and related fields, and gain a deeper understanding of the principles of organic chemistry. Overall, the study of aldehydes and ketones is an essential part of the JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course and provides a solid foundation for success in many fields.
Overview of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Aldehydes and Ketones
The JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course in aldehydes and ketones is designed to provide students with a thorough understanding of these important organic compounds. The course covers a range of topics related to aldehydes and ketones, including their physical and chemical properties, their reactions and mechanisms, and their practical applications in industry, biochemistry, and other fields.
Students in the JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course in aldehydes and ketones will learn about the various reactions that these compounds undergo, including nucleophilic addition reactions, reduction reactions, and oxidation reactions. They will also learn about the different methods used to synthesize aldehydes and ketones, as well as the analytical techniques used to detect and quantify them.
Throughout the course, students will develop important problem-solving skills, including the ability to predict the outcomes of reactions and understand reaction mechanisms. They will also gain a deeper understanding of the principles of organic chemistry and their practical applications in industry and other technical fields.
Overall, the JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course in aldehydes and ketones is an important part of the overall curriculum in chemistry, providing students with a solid foundation in these versatile organic compounds and preparing them for further education and careers in chemistry and related fields.
Types of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Aldehydes and Ketones
The JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course in aldehydes and ketones covers a range of topics related to these important organic compounds. Here are some of the types of topics that may be covered in the course:
- Introduction to aldehydes and ketones: This section of the course provides an overview of aldehydes and ketones, including their physical and chemical properties, nomenclature, and functional groups.
- Synthesis of aldehydes and ketones: This section covers the different methods used to synthesize aldehydes and ketones, including oxidation of alcohols, hydration of alkynes, and Friedel-Crafts acylation.
- Reactions of aldehydes and ketones: This section covers the various reactions that aldehydes and ketones undergo, including nucleophilic addition reactions, reduction reactions, and oxidation reactions.
- Reaction mechanisms: This section covers the mechanisms behind the different reactions of aldehydes and ketones, including the role of carbonyl groups, nucleophiles, and electrophiles.
- Applications of aldehydes and ketones: This section covers the practical applications of aldehydes and ketones in industry, biochemistry, and other fields, including their use in pharmaceuticals, flavorings, and polymers.
- Spectroscopic analysis: This section covers the analytical techniques used to detect and quantify aldehydes and ketones, including UV-Vis spectroscopy, IR spectroscopy, and NMR spectroscopy.
Overall, the JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course in aldehydes and ketones covers a wide range of topics related to these important organic compounds, providing students with a thorough understanding of their properties, reactions, and practical applications.
Application of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Aldehydes and Ketones
The JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course in aldehydes and ketones has many practical applications in various fields. Some of the most common applications include:
- Pharmaceuticals: Aldehydes and ketones are used in the synthesis of a wide range of pharmaceuticals, including antibiotics, analgesics, and antihistamines.
- Flavors and fragrances: Aldehydes and ketones are used in the production of flavors and fragrances, including vanilla, cinnamon, and raspberry.
- Polymers: Aldehydes and ketones are used in the production of various polymers, including nylon and polyester.
- Biochemistry: Aldehydes and ketones are important in many biochemical processes, including the metabolism of carbohydrates.
- Solvents: Some aldehydes and ketones, such as acetone and butanone, are commonly used as solvents in various applications.
- Dyes: Aldehydes and ketones are used in the production of various dyes, including indigo and anthraquinone.
Overall, the study of aldehydes and ketones in the JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course provides students with a solid foundation for further education and careers in chemistry and related fields, as well as a deeper understanding of the practical applications of organic chemistry.
Nomenclature of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Aldehydes and Ketones
The nomenclature of aldehydes and ketones is an important part of the JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course in organic chemistry. Here are the basic rules for naming aldehydes and ketones:
Nomenclature of Aldehydes:
- Identify the longest carbon chain that contains the carbonyl group (C=O).
- Replace the -e suffix of the parent alkane with -al. If the carbonyl group is not on the end of the chain, number the carbon atoms in the chain starting from the end closest to the carbonyl group. Indicate the position of the carbonyl group with a number.
- If the aldehyde is a substituent on a larger molecule, use the prefix “formyl-“.
Examples:
- Methanal (formaldehyde)
- Ethanal (acetaldehyde)
- Propanal (propionaldehyde)
Nomenclature of Ketones:
- Identify the longest carbon chain that contains the carbonyl group (C=O).
- Replace the -e suffix of the parent alkane with -one. If the carbonyl group is not on the end of the chain, number the carbon atoms in the chain starting from the end closest to the carbonyl group. Indicate the position of the carbonyl group with a number.
- If there are two carbonyl groups in the molecule, use the prefix “diketo-” followed by the appropriate alkane name.
Examples:
- Propanone (acetone)
- Butanone (methyl ethyl ketone)
- Hexa-2,4-dione (diacetyl)
It is important to note that the nomenclature of aldehydes and ketones follows the rules of the IUPAC system of nomenclature, which is the standard system used in organic chemistry.
Career Opportunities of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Aldehydes and Ketones
The JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course in aldehydes and ketones provides a strong foundation in organic chemistry, which can lead to various career opportunities in both the private and public sectors. Here are some career options for students who have studied aldehydes and ketones:
- Chemical research: A career in chemical research involves conducting experiments and analyzing data related to the synthesis and properties of organic compounds, including aldehydes and ketones. This can lead to opportunities in industries such as pharmaceuticals, materials science, and biotechnology.
- Chemical engineering: Chemical engineers design, develop and optimize chemical processes and equipment for the production of a wide range of chemical products, including aldehydes and ketones. They can work in industries such as oil and gas, food and beverage, and cosmetics.
- Quality control and assurance: Quality control and assurance professionals ensure that products and processes meet the required standards of quality and safety. In industries that use aldehydes and ketones, such as pharmaceuticals and flavors and fragrances, quality control and assurance are essential.
- Academia: Students who study aldehydes and ketones can pursue careers in academia, including teaching and research positions in universities and research institutions.
- Regulatory agencies: Regulatory agencies, such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), employ chemists to ensure that chemicals and chemical products meet safety standards and regulations.
Overall, the JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course in aldehydes and ketones provides students with a strong foundation in organic chemistry, which can lead to a wide range of career opportunities in various industries and sectors.
