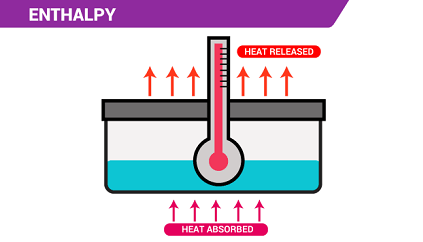
Enthalpy (H) is a thermodynamic property that describes the total heat content of a system at constant pressure. It is defined as the sum of the internal energy (U) of the system and the product of the pressure (P) and volume (V) of the system:
H = U + PV
Enthalpy is a state function, meaning that it only depends on the initial and final states of the system and not on the path taken to reach those states. Enthalpy is used in thermodynamics to describe the energy changes that occur during chemical reactions, physical changes of state (such as melting or boiling), and other processes. The change in enthalpy during a process is given by the formula:
ΔH = H final − H initial
Enthalpy is typically measured in units of joules or calories.
What is Required Enthalpy
Required enthalpy refers to the amount of heat or energy that must be added to or removed from a substance to achieve a desired change in its state. The term “required” implies that a specific amount of enthalpy is necessary to achieve the desired result.
For example, to melt a solid substance at its melting point, the required enthalpy is known as the heat of fusion, which is the amount of energy required to melt one mole of the substance at a constant temperature and pressure. Similarly, to vaporize a liquid substance at its boiling point, the required enthalpy is known as the heat of vaporization, which is the amount of energy required to vaporize one mole of the substance at a constant temperature and pressure.
Required enthalpy can also be used to calculate the amount of energy required to achieve a certain temperature change in a substance. This is known as the heat capacity or specific heat, which is the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one mole of a substance by one degree Celsius or Kelvin.
Overall, required enthalpy is an important concept in thermodynamics that helps to quantify the energy changes that occur during physical and chemical processes.
When is Required Enthalpy
“Required Enthalpy” is a term used in the context of thermodynamics and is applicable in various situations. It refers to the amount of energy or heat required to achieve a desired change in the state of a substance.
For example, when a solid is heated to its melting point, the required enthalpy is the heat of fusion, which is the amount of energy required to melt the solid and convert it into a liquid at a constant temperature and pressure. Similarly, when a liquid is heated to its boiling point, the required enthalpy is the heat of vaporization, which is the amount of energy required to vaporize the liquid and convert it into a gas at a constant temperature and pressure.
Required enthalpy can also be used to calculate the amount of energy required to achieve a certain temperature change in a substance. This is known as the heat capacity or specific heat, which is the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of a substance by one degree Celsius or Kelvin.
Overall, the concept of required enthalpy is applicable in a variety of thermodynamic situations where energy changes are involved.
Where is Required Enthalpy
“Required Enthalpy” is a concept used in thermodynamics and can be applicable in various fields and contexts.
In the field of chemical engineering, for example, required enthalpy can be used in the design and optimization of industrial processes such as distillation, drying, and evaporation. The knowledge of the required enthalpy of the substances involved in these processes is necessary for the calculation of the heat transfer rates and the energy requirements of the equipment involved.
In the field of materials science, required enthalpy can be used to study phase transformations and solid-state reactions. For instance, the heat of fusion or heat of crystallization of a material is a measure of the required enthalpy for melting or solidification, respectively. This information is important in the processing of materials such as metals, ceramics, and polymers.
Overall, the concept of required enthalpy can be applied in various fields where energy changes are involved, such as chemistry, physics, and engineering.
Nomenclature of Enthalpy
The nomenclature of enthalpy involves various terms and symbols that are used to describe and calculate the energy changes that occur during physical and chemical processes. The most commonly used terms and symbols include:
- Enthalpy (H): The total heat content of a system at constant pressure.
- Internal energy (U): The energy associated with the random motion of particles within a system.
- Pressure (P): The force exerted per unit area on a system.
- Volume (V): The amount of space occupied by a system.
- Heat of fusion (ΔHfus): The amount of energy required to melt one mole of a substance at its melting point.
- Heat of vaporization (ΔHvap): The amount of energy required to vaporize one mole of a substance at its boiling point.
- Heat of reaction (ΔHrxn): The amount of energy absorbed or released during a chemical reaction at constant pressure.
- Standard enthalpy change (ΔH°): The enthalpy change that occurs during a reaction under standard conditions (defined as 25°C and 1 atm pressure).
- Heat capacity (Cp): The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one mole of a substance by one degree Celsius or Kelvin at constant pressure.
These terms and symbols are widely used in thermodynamics to describe and quantify the energy changes that occur during various physical and chemical processes.
How is Required Enthalpy
The concept of “Required Enthalpy” is used to describe the amount of energy or heat that is needed to achieve a specific change in a substance’s state or temperature. The calculation of required enthalpy depends on the specific process involved and the thermodynamic properties of the substance.
For example, to calculate the required enthalpy for melting a solid, we need to know the heat of fusion, which is the amount of energy required to melt one mole of the substance at its melting point. The required enthalpy for melting can then be calculated by multiplying the heat of fusion by the number of moles of the substance being melted.
Similarly, to calculate the required enthalpy for vaporizing a liquid, we need to know the heat of vaporization, which is the amount of energy required to vaporize one mole of the substance at its boiling point. The required enthalpy for vaporization can then be calculated by multiplying the heat of vaporization by the number of moles of the substance being vaporized.
The calculation of required enthalpy is also used in the design and optimization of industrial processes. For example, in distillation processes, the required enthalpy is used to calculate the amount of energy needed to vaporize a liquid and separate it from other components. In heat exchangers, the required enthalpy is used to calculate the heat transfer rate between two fluids at different temperatures.
Overall, the calculation of required enthalpy is an important concept in thermodynamics that allows scientists and engineers to understand and quantify the energy changes that occur during various physical and chemical processes.
Case Study on Enthalpy
One example of a case study on enthalpy is the design of a heating and cooling system for a residential building. The goal is to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature throughout the year while minimizing energy consumption and costs.
To design the heating and cooling system, the required enthalpy for each component must be calculated. For example, the required enthalpy for heating can be calculated by multiplying the heat capacity of the building by the temperature difference between the indoor and outdoor air. Similarly, the required enthalpy for cooling can be calculated by multiplying the heat capacity by the temperature difference between the indoor and desired temperature.
The calculation of required enthalpy is used to determine the energy requirements and the capacity of the heating and cooling system. The efficiency of the system can also be improved by incorporating energy-saving measures such as insulation and efficient equipment.
Additionally, the required enthalpy is used to determine the amount of energy that needs to be supplied or removed by the heating and cooling system. This information is used to select the appropriate equipment such as boilers, heat pumps, and air conditioners.
The design of a heating and cooling system is an example of how the concept of enthalpy is applied in real-world situations. By understanding the required enthalpy for each component, engineers and architects can design energy-efficient systems that meet the needs of the occupants while minimizing costs and environmental impact.
White paper on Enthalpy
Here is a white paper on the concept of enthalpy:
Introduction:
Enthalpy is a thermodynamic property that describes the total energy content of a system. It is an important concept in chemical thermodynamics that is used to describe and quantify energy changes that occur during various physical and chemical processes. This white paper will provide an overview of the concept of enthalpy, its applications, and how it is calculated.
Enthalpy Defined:
Enthalpy (H) is defined as the sum of the internal energy (U) of a system and the product of the system’s pressure (P) and volume (V). Mathematically, this can be expressed as H = U + PV. Enthalpy is a state function, which means that its value depends only on the current state of the system and not on how it got there.
Enthalpy Change:
The enthalpy change (ΔH) is the difference in enthalpy between the initial and final states of a system. It is a measure of the energy transferred during a process or reaction. If ΔH is positive, the process or reaction is endothermic, meaning that energy is absorbed by the system. If ΔH is negative, the process or reaction is exothermic, meaning that energy is released by the system.
Applications of Enthalpy:
Enthalpy is a useful concept in many areas of science and engineering. It is commonly used in the design and optimization of industrial processes such as distillation, heat exchangers, and combustion. In the chemical industry, enthalpy is used to predict the energy required or released during chemical reactions. In materials science, enthalpy is used to study the behavior of materials at high temperatures or under extreme conditions.
Calculation of Enthalpy:
The enthalpy change for a process or reaction can be calculated using various methods. One common method is to measure the heat transfer associated with the process or reaction using calorimetry. Another method is to use the enthalpies of formation of the reactants and products, which are the enthalpies required to form one mole of the substance from its elements in their standard states.
Conclusion:
Enthalpy is a fundamental concept in chemical thermodynamics that describes the total energy content of a system. Its applications are diverse, ranging from the design of industrial processes to the study of materials science. The calculation of enthalpy change is an important tool for predicting the energy requirements or released during physical and chemical processes.
