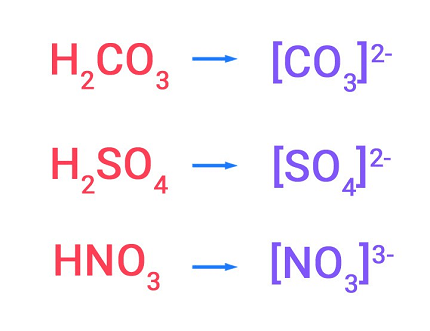
Salts of oxoacids are compounds formed by the reaction of an oxoacid with a base to produce a salt and water. Oxoacids are acids that contain oxygen, hydrogen, and at least one other element, and they typically have the general formula HmXOn, where X represents a nonmetallic element and m and n are integers.
When an oxoacid reacts with a base, the hydrogen ion (H+) from the acid is replaced by a metal or ammonium ion (NH4+), resulting in the formation of a salt. For example, the reaction between sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) produces sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) and water (H2O):
H2SO4 + 2 NaOH → Na2SO4 + 2 H2O
Similarly, the reaction between phosphoric acid (H3PO4) and calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) produces calcium phosphate (Ca3(PO4)2) and water:
2 H3PO4 + 3 Ca(OH)2 → Ca3(PO4)2 + 6 H2O
Salts of oxoacids have a wide range of applications, including as fertilizers, food additives, and water treatment agents.
What is Required Salts of oxoacids s-Block Elements
S-block elements, which include the alkali metals and alkaline earth metals, are highly reactive metals that readily react with oxoacids to form salts. The reaction typically involves the displacement of the hydrogen ion from the oxoacid by the metal ion.
For example, when sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is added to sulfuric acid (H2SO4), the hydrogen ions are replaced by sodium ions to form sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) and water (H2O):
H2SO4 + 2 NaOH → Na2SO4 + 2 H2O
Similarly, when calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) is added to nitric acid (HNO3), the hydrogen ions are replaced by calcium ions to form calcium nitrate (Ca(NO3)2) and water:
2 HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 → Ca(NO3)2 + 2 H2O
The resulting salts can have a wide range of applications, including as fertilizers, food additives, and in the production of other chemicals.
When is Required Salts of oxoacids s-Block Elements
As I mentioned earlier, s-block elements, including alkali metals and alkaline earth metals, are highly reactive metals that readily react with oxoacids to form salts. This reaction involves the displacement of the hydrogen ion from the oxoacid by the metal ion.
The resulting salts can have various uses, such as in the production of fertilizers, food additives, and water treatment agents. For instance, sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) is used as a filler in the manufacturing of detergents, while calcium nitrate (Ca(NO3)2) is used as a fertilizer.
Additionally, some salts of oxoacids are used in industrial processes, such as the production of titanium dioxide, which involves the use of sulfuric acid and titanium dioxide salts.
In summary, the formation of salts of oxoacids with s-block elements is an essential process with many applications in various industries.
Where is Required Salts of oxoacids s-Block Elements
Salts of oxoacids with s-block elements can be found in various industries and applications, including:
- Agriculture: Salts such as calcium nitrate (Ca(NO3)2) and potassium sulfate (K2SO4) are used as fertilizers to provide essential nutrients to plants.
- Food industry: Salts such as sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) and calcium sulfate (CaSO4) are used as additives in the food industry to improve texture, taste, and shelf life.
- Water treatment: Salts such as sodium chloride (NaCl) and calcium carbonate (CaCO3) are used in water treatment to remove impurities and adjust the pH level.
- Chemical production: Salts such as sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) and magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) are used in the production of various chemicals, such as detergents, paper, and pharmaceuticals.
- Metallurgy: Salts such as sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) and calcium oxide (CaO) are used in metallurgical processes to extract metals from ores and refine them.
In summary, the applications of salts of oxoacids with s-block elements are widespread and diverse, and they can be found in various industries and processes.
Nomenclature of Salts of oxoacids s-Block Elements
The nomenclature of salts of oxoacids with s-block elements follows a specific naming convention. The name of the salt is derived from the name of the oxoacid and the name of the metal involved in the reaction.
Here’s how to name salts of oxoacids with s-block elements:
- Start with the name of the oxoacid. If the oxoacid ends in “-ic,” the name of the corresponding salt will end in “-ate.” If the oxoacid ends in “-ous,” the name of the corresponding salt will end in “-ite.”
Examples:
- Nitric acid (HNO3) forms nitrates such as sodium nitrate (NaNO3) and calcium nitrate (Ca(NO3)2).
- Sulfurous acid (H2SO3) forms sulfites such as sodium sulfite (Na2SO3) and calcium sulfite (CaSO3).
- Next, add the name of the metal involved in the reaction. The name of the metal is typically included as a separate word in the name of the salt.
Examples:
- Calcium nitrate (Ca(NO3)2)
- Sodium sulfite (Na2SO3)
- Potassium perchlorate (KClO4)
- For some salts, a Roman numeral is included in the name to indicate the oxidation state of the metal ion.
Examples:
- Iron(III) sulfate (Fe2(SO4)3)
- Copper(II) nitrate (Cu(NO3)2)
In summary, the nomenclature of salts of oxoacids with s-block elements follows a specific naming convention that includes the name of the oxoacid, the name of the metal involved in the reaction, and sometimes a Roman numeral to indicate the oxidation state of the metal ion.
How is Required Salts of oxoacids s-Block Elements
Salts of oxoacids with s-block elements are typically prepared by the reaction of the oxoacid with a base or metal carbonate that contains the s-block metal. The reaction involves the displacement of the hydrogen ions from the oxoacid by the metal ions to form the corresponding salt and water.
For example, the reaction between sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) produces sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) and water (H2O):
H2SO4 + 2 NaOH → Na2SO4 + 2 H2O
Similarly, the reaction between phosphoric acid (H3PO4) and calcium carbonate (CaCO3) produces calcium phosphate (Ca3(PO4)2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) gas:
2 H3PO4 + 3 CaCO3 → Ca3(PO4)2 + 3 CO2 + 3 H2O
The reaction conditions, such as temperature, pressure, and concentration of the reactants, can affect the yield and purity of the resulting salt. In some cases, additional purification steps, such as filtration or crystallization, may be required to obtain a high-quality product.
In summary, salts of oxoacids with s-block elements are prepared by the reaction of the oxoacid with a base or metal carbonate that contains the s-block metal, and the conditions of the reaction can affect the yield and purity of the product.
Case Study on Salts of oxoacids s-Block Elements
Here’s a case study on the use of salts of oxoacids with s-block elements in the production of fertilizers.
Case Study: Production of Fertilizers
Fertilizers are substances added to soil to provide essential nutrients for plant growth. One type of fertilizer, known as phosphate fertilizer, is produced using salts of oxoacids with s-block elements, specifically phosphoric acid (H3PO4) and either calcium or potassium salts.
The production of phosphate fertilizers typically involves three main steps:
- Phosphate rock is treated with sulfuric acid to produce phosphoric acid.
- The phosphoric acid is then reacted with a s-block element salt to produce the corresponding phosphate salt.
- The resulting phosphate salt is then processed and formulated into the final fertilizer product.
For example, the production of calcium phosphate fertilizer involves the reaction between phosphoric acid and calcium carbonate, which is a s-block element salt:
2 H3PO4 + 3 CaCO3 → Ca3(PO4)2 + 3 CO2 + 3 H2O
The resulting calcium phosphate salt, Ca3(PO4)2, is then processed and formulated into various types of fertilizers, such as single superphosphate, triple superphosphate, and diammonium phosphate.
Similarly, the production of potassium phosphate fertilizer involves the reaction between phosphoric acid and potassium carbonate, which is another s-block element salt:
2 H3PO4 + 3 K2CO3 → 2 K3PO4 + 3 CO2 + 3 H2O
The resulting potassium phosphate salt, K3PO4, is then processed and formulated into various types of fertilizers, such as monoammonium phosphate and potassium dihydrogen phosphate.
Salts of oxoacids with s-block elements, particularly phosphoric acid and calcium or potassium salts, play a critical role in the production of phosphate fertilizers, which are essential for agricultural productivity and food security.
In summary, the use of salts of oxoacids with s-block elements in the production of fertilizers is a crucial application that demonstrates the versatility and importance of these compounds in various industries.
White paper on Salts of oxoacids s-Block Elements
Here’s a white paper on the topic of salts of oxoacids with s-block elements.
Title: Salts of Oxoacids with s-Block Elements: Properties, Applications, and Future Prospects
Introduction:
Salts of oxoacids with s-block elements are a class of compounds that have numerous applications in various industries, including agriculture, food, water treatment, chemical production, metallurgy, and pharmaceuticals. These compounds are formed by the reaction of oxoacids with a base or metal carbonate that contains the s-block metal. This white paper aims to provide an overview of the properties, applications, and future prospects of salts of oxoacids with s-block elements.
Properties:
Salts of oxoacids with s-block elements have unique properties that make them useful in various applications. They are typically soluble in water and have high melting and boiling points. These salts can also exhibit hygroscopic properties, meaning they can absorb moisture from the air. The properties of these salts can vary depending on the specific oxoacid and s-block element involved in their formation.
Applications:
Salts of oxoacids with s-block elements have numerous applications in various industries. Some of the major applications are:
- Agriculture: Salts such as calcium nitrate (Ca(NO3)2) and potassium sulfate (K2SO4) are used as fertilizers to provide essential nutrients to plants.
- Food industry: Salts such as sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) and calcium sulfate (CaSO4) are used as additives in the food industry to improve texture, taste, and shelf life.
- Water treatment: Salts such as sodium chloride (NaCl) and calcium carbonate (CaCO3) are used in water treatment to remove impurities and adjust the pH level.
- Chemical production: Salts such as sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) and magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) are used in the production of various chemicals, such as detergents, paper, and pharmaceuticals.
- Metallurgy: Salts such as sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) and calcium oxide (CaO) are used in metallurgical processes to extract metals from ores and refine them.
Future Prospects:
The use of salts of oxoacids with s-block elements is expected to grow in the future due to their increasing demand in various industries. The development of new and innovative applications for these compounds is also expected to increase, driven by the need for sustainable and environmentally friendly technologies. Additionally, advancements in technology and chemical synthesis techniques may lead to the production of new and more efficient salts of oxoacids with s-block elements.
Conclusion:
Salts of oxoacids with s-block elements are a diverse class of compounds that have numerous applications in various industries. These compounds exhibit unique properties that make them useful in a wide range of applications. The increasing demand for sustainable and environmentally friendly technologies is expected to drive the development of new and innovative applications for salts of oxoacids with s-block elements in the future.
