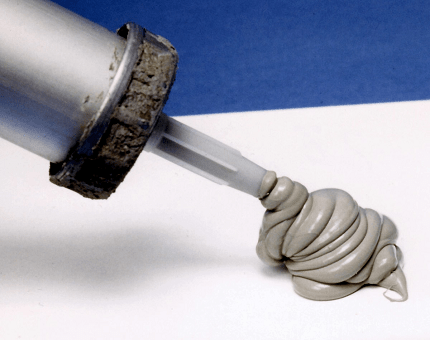
Group 14 silicones, also known as organosilicones or organosilanes, are a group of chemical compounds that contain silicon atoms bonded to organic groups. They are commonly used in a wide range of industrial and commercial applications due to their unique properties, including high thermal stability, low surface energy, and resistance to chemicals and UV radiation.
One common type of Group 14 silicone is polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), which is used in various products such as silicone oils, sealants, and lubricants. PDMS has a high degree of flexibility and is often used as a base material for medical implants, contact lenses, and other applications where biocompatibility is important.
Another type of Group 14 silicone is methylphenylsiloxane (MPS), which is commonly used as a coating material for electronic components and as a surfactant in the production of foam products.
Other Group 14 silicones include vinylsiloxanes, phenylsilanes, and alkylsilanes, each with their own unique properties and applications. Overall, Group 14 silicones have become an integral part of many industries due to their versatility and superior performance characteristics.
Silicon

Silicon is a compound component with the image Si and nuclear number 14. It is a hard, fragile translucent strong with a blue-dim metallic gloss, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is an individual from bunch 14 in the occasional table: carbon is above it; and germanium, tin, lead, and flerovium are underneath it. It is moderately lifeless.
As a result of its high compound fondness for oxygen, it was only after 1823 that Jöns Jakob Berzelius was first ready to plan it and describe it in unadulterated structure. Its oxides structure a group of anions known as silicates. Its softening and edges of boiling over of 1414 °C and 3265 °C, individually, are the second most noteworthy among all the metalloids and nonmetals, being outperformed simply by boron.
Silicon is the eighth most normal component known to man by mass, however seldom happens as the unadulterated component in the World’s outside layer. It is broadly circulated in space in enormous tidies, planetoids, and planets as different types of silicon dioxide (silica) or silicates. Over 90% of the World’s outside is made out of silicate minerals, making silicon the second most plentiful component in the World’s hull (around 28% by mass), after oxygen.
Most silicon is utilized monetarily without being isolated, frequently with very little handling of the normal minerals. Such use incorporates modern development with muds, silica sand, and stone. Silicates are utilized in Portland concrete for mortar and plaster, and blended in with silica sand and rock to make concrete for walkways, establishments, and streets. They are likewise utilized in whiteware pottery like porcelain, and in customary silicate-based soft drink lime glass and numerous other specialty glasses. Silicon mixtures, for example, silicon carbide are utilized as abrasives and parts of high-strength ceramics. Silicon is the premise of the broadly utilized manufactured polymers called silicones.
The late twentieth 100 years to mid 21st century has been depicted as the Silicon Age (otherwise called the Advanced Age or Data Age) due to the huge effect that essential silicon has on the cutting edge world economy. The little piece of profoundly decontaminated natural silicon utilized in semiconductor gadgets (<10%[citation needed]) is fundamental for the semiconductors and coordinated circuit chips utilized in most present day innovation, for example, cell phones and different PCs. In 2019, 32.4% of the semiconductor market section was for organizations and specialized gadgets, and the semiconductors business is projected to reach $726.73 billion by 2027.
Silicon is a fundamental component in science. Just follows are expected by most creatures, yet some ocean wipes and microorganisms, like diatoms and radiolaria, discharge skeletal designs made of silica. Silica is kept in many plant tissues.
Silicone rubber
Silicone rubber is an elastomer (rubber-like material) composed of silicone—itself a polymer—containing silicon together with carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Silicone rubbers are widely used in industry, and there are multiple formulations. Silicone rubbers are often one- or two-part polymers, and may contain fillers to improve properties or reduce cost.
Silicone rubber is generally non-reactive, stable, and resistant to extreme environments and temperatures from −55 to 300 °C (−70 to 570 °F) while still maintaining its useful properties. Due to these properties and its ease of manufacturing and shaping, silicone rubber can be found in a wide variety of products, including voltage line insulators; automotive applications; cooking, baking, and food storage products; apparel such as undergarments, sportswear, and footwear; electronics; medical devices and implants; and in home repair and hardware, in products such as silicone sealants.
RTV silicone
RTV silicone (room-temperature-vulcanizing silicone) is a sort of silicone elastic that fixes at room temperature. It is accessible as a one-part item, or blended from two-parts (a base and healing). Producers give it in a scope of hardnesses from exceptionally delicate to medium — as a rule from 15 to 40 Shore A. RTV silicones can be relieved with an impetus comprising of one or the other platinum or a tin compound, for example, dibutyltin dilaurate. Applications incorporate low-temperature over-embellishment, making molds for recreating, and focal point applications for a few optically clear grades. It is likewise utilized broadly in the auto business as a cement/sealant, for instance to make gaskets set up.
Medical grade silicone
Clinical grade silicones will be silicones tried for biocompatibility and are suitable to be utilized for clinical applications. In the US, the Food and Medication Organization (FDA) Community for Gadgets and Radiological Wellbeing (CDRH) manages gadgets embedded into the body. It doesn’t manage materials other than specific dental materials. The FDA control silicones utilized in food contact under the protection of the Middle for Sanitation and Sustenance (CFSAN) and for use in drugs under the sponsorship of the Middle for Medication Assessment and Exploration (CDER).
Clinical grade silicones are by and large gathered into three classifications: non implantable, present moment implantable, and long haul implantable. Materials endorsed as Class V and VI can be viewed as clinical grade. Most clinical grade silicones are essentially Class VI affirmed. Silicone providers and some silicone prototyping organizations give rules to material use.
Silicone oil
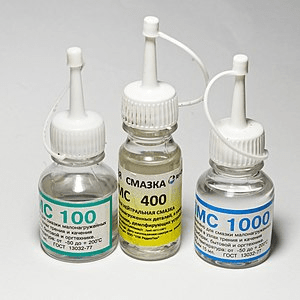
A silicone oil is any fluid polymerized siloxane with natural side chains. The main part is polydimethylsiloxane. These polymers are of business interest on account of their somewhat high warm strength, greasing up, and dielectric properties.
Case Study on p-Block Elements Group 14 Silicones
Here is a case study on the use of p-Block Elements Group 14 Silicones in the production of silicone sealants:
Silicone sealants are commonly used in the construction industry to seal gaps and joints in various building materials, such as concrete, glass, and metal. These sealants need to withstand a wide range of environmental conditions, including temperature changes, UV radiation, and exposure to chemicals and moisture.
One type of silicone sealant is made using p-Block Elements Group 14 Silicones, specifically polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) as the primary component. PDMS is a highly flexible material that can withstand temperature extremes and has excellent chemical resistance. It is commonly used in the production of silicone sealants due to its superior performance characteristics and its ability to adhere well to a variety of substrates.
The manufacturing process for silicone sealants involves mixing PDMS with other additives, such as fillers, cross-linking agents, and curing agents, to create a paste-like substance that can be easily applied to gaps and joints. Once applied, the sealant cures and forms a durable, flexible seal that can withstand the stresses of the surrounding environment.
One of the main advantages of using PDMS in silicone sealants is its ability to maintain its properties over a wide range of temperatures. This makes it an ideal choice for applications in which the sealant will be exposed to extreme temperature changes, such as in the automotive or aerospace industries.
Another advantage of using PDMS in silicone sealants is its resistance to moisture and chemicals. This makes it an excellent choice for applications in which the sealant will be exposed to water or chemicals, such as in industrial or marine environments.
In conclusion, the use of p-Block Elements Group 14 Silicones, specifically PDMS, in the production of silicone sealants has revolutionized the construction industry by providing a durable, flexible, and long-lasting solution for sealing gaps and joints. With its superior performance characteristics, PDMS has become an integral part of many construction projects and has contributed to the development of safer, more durable, and more environmentally-friendly buildings.
White paper on p-Block Elements Group 14 Silicones
Here is a white paper on p-Block Elements Group 14 Silicones:
Introduction
The p-Block Elements Group 14 of the periodic table includes carbon, silicon, germanium, tin, and lead. Of these elements, silicon is the second most abundant element in the Earth’s crust, and it has unique properties that make it an important material in many industries. In particular, Group 14 silicones are widely used in a variety of applications due to their thermal stability, low surface energy, and resistance to chemicals and UV radiation.
Properties of Group 14 Silicones
Group 14 silicones are a group of chemical compounds that contain silicon atoms bonded to organic groups. One common type of Group 14 silicone is polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), which has a high degree of flexibility and is often used as a base material for medical implants, contact lenses, and other applications where biocompatibility is important.
Other Group 14 silicones include methylphenylsiloxane (MPS), which is commonly used as a coating material for electronic components and as a surfactant in the production of foam products. Vinylsiloxanes, phenylsilanes, and alkylsilanes are other examples of Group 14 silicones, each with their own unique properties and applications.
One of the key properties of Group 14 silicones is their thermal stability. These materials can withstand high temperatures without breaking down or losing their properties, making them ideal for use in high-temperature applications such as automotive and aerospace industries.
Another important property of Group 14 silicones is their low surface energy, which makes them highly resistant to adhesion. This property is useful in applications where a non-stick surface is required, such as in the production of non-stick coatings and release agents.
Group 14 silicones are also highly resistant to chemicals and UV radiation, which makes them ideal for use in harsh environments such as industrial and marine applications.
Applications of Group 14 Silicones
Group 14 silicones are used in a wide range of industrial and commercial applications. One of the most common applications is in the production of silicone sealants, which are used in the construction industry to seal gaps and joints in various building materials.
Group 14 silicones are also used in the production of medical devices and implants, such as contact lenses and pacemakers. Their biocompatibility and flexibility make them an ideal choice for these applications.
In addition, Group 14 silicones are used in the production of electronic components, such as coatings for circuit boards and encapsulants for semiconductor chips. Their thermal stability and chemical resistance make them ideal for use in these applications.
Conclusion
Group 14 silicones are a versatile group of materials that have a wide range of properties and applications. Their thermal stability, low surface energy, and resistance to chemicals and UV radiation make them an ideal choice for many industrial and commercial applications. As new applications are developed, it is likely that Group 14 silicones will continue to play an important role in many industries.
