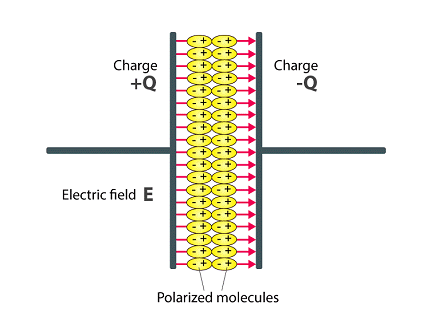
Dielectrics are materials that do not conduct electricity, but can store electric charges. They are used in various applications, such as capacitors, insulation, and in electronic devices to prevent short-circuits. Dielectrics are also known as insulators and have high resistivity to the flow of electric current.
Without dielectrics, electrical systems would not be able to function as intended. Capacitors, for example, rely on dielectric materials to store electric charges, and without them, capacitors would not work. Insulators are also essential in preventing electrical conductors from coming into contact with each other, which could cause short-circuits and damage to electrical equipment.
Overall, dielectrics are crucial components in electrical systems and play a vital role in ensuring the safe and reliable operation of electronic devices.
What is Required Without dielectrics
If dielectrics were not available, it would be challenging to build many of the electrical and electronic devices that we rely on today. Some alternatives to dielectric materials could be used, but they may not provide the same level of performance and safety as dielectrics.
For example, instead of using a capacitor with a dielectric material, you could use an air capacitor where the plates are separated by a vacuum or air gap. However, air capacitors are not as efficient as capacitors with dielectric materials and have lower capacitance values.
Similarly, instead of using an insulating material as a dielectric, you could use a conducting material with a high resistivity, like a metal oxide. However, using conducting materials in place of dielectrics would increase the risk of short circuits and electrical arcing.
In summary, without dielectric materials, it would be challenging to design and build many of the electronic devices that we rely on today. While alternative solutions could be used, they may not provide the same level of performance and safety as dielectrics.
When is Required Without dielectrics
It is difficult to determine specific situations where dielectrics would not be required since they are used in a wide range of applications in electrical and electronic systems. However, there may be situations where dielectric materials are not as necessary or can be replaced with other materials.
For example, in some high-temperature applications, dielectrics may break down and degrade over time. In these situations, alternative materials with high-temperature stability, such as ceramics, may be used instead of traditional dielectrics.
Additionally, in certain low voltage applications, such as in some simple electrical circuits or hobbyist projects, dielectrics may not be necessary. However, for most modern electronic devices and electrical systems, dielectric materials are still essential components for safe and reliable operation.
In summary, while there may be some situations where dielectrics are not strictly required, they are still a crucial component in most electrical and electronic systems, and alternative solutions may not always provide the same level of performance or safety.
Where is Required Without dielectrics
As dielectric materials are used in a wide range of applications in electrical and electronic systems, it is difficult to determine specific situations where they are not required. However, there may be certain circumstances where alternative materials can be used in place of dielectrics.
For example, in some high-temperature applications, traditional dielectrics may not be suitable due to their thermal limitations. In these situations, alternative materials such as ceramics or refractory metals may be used instead.
Additionally, in some cases where high voltages are involved, such as in high-voltage power transmission lines, air or gas can be used as an insulating material instead of a dielectric.
However, it is important to note that while alternative solutions may be available, dielectric materials are still essential components in most electrical and electronic systems. They provide important functions such as capacitive energy storage, electrical insulation, and preventing electrical arcing and short circuits.
In summary, while there may be some situations where dielectrics are not strictly required, they are still a crucial component in most electrical and electronic systems, and alternative solutions may not always provide the same level of performance or safety.
How is Required Without dielectrics
Without dielectric materials, it would be challenging to design and build many of the electrical and electronic devices that we rely on today. Dielectric materials are essential components in many electrical and electronic systems, and they serve a variety of important functions, including:
- Capacitance: Dielectrics are used to create capacitors, which store electrical energy. Without dielectrics, capacitors would not be able to store energy efficiently, and their performance would be severely limited.
- Insulation: Dielectrics are used as insulation materials to prevent electrical conductors from coming into contact with each other, which can cause short circuits and damage to electrical equipment. Without dielectrics, electrical systems would be much more vulnerable to damage.
- Electric Field Control: Dielectrics can be used to control the electric field in electrical systems. This is important for a wide range of applications, such as in transformers and in electronic devices.
- Energy Storage: Dielectric materials can store energy when an electric field is applied. This is known as dielectric energy storage, and it has many potential applications in areas such as energy storage and high-power electronics.
In summary, without dielectric materials, it would be challenging to build many of the electrical and electronic devices that we rely on today. Dielectric materials are essential components in many electrical and electronic systems, and they serve a variety of important functions, including capacitance, insulation, electric field control, and energy storage.
Nomenclature of Without dielectrics
Without dielectrics, the nomenclature and naming conventions used in electrical and electronic systems would be different. Dielectric materials are an important part of the vocabulary used to describe electrical and electronic components and systems.
For example, the capacitance of a capacitor is directly related to the dielectric material used in its construction. Capacitors are often named according to the dielectric material they use, such as ceramic capacitors or electrolytic capacitors.
Similarly, the insulation resistance of a cable or wire is often related to the dielectric material used in its insulation. Without dielectric materials, different materials would need to be used for insulation, and different naming conventions would need to be developed to describe their properties.
Overall, the absence of dielectric materials would require a rethinking of the way electrical and electronic components and systems are named and described. New materials and naming conventions would need to be developed to account for the absence of dielectric materials.
Case Study on Without dielectrics
One potential case study for a situation where dielectrics are not used is in high-voltage power transmission lines. While dielectrics are commonly used as insulators in electrical systems, high-voltage transmission lines often use air or gas as the insulating material instead.
In high-voltage transmission lines, the electrical potential between the conductors is very high, which can cause electrical breakdown in most dielectric materials. However, air or gas, at the high voltages used in transmission lines, can act as an effective insulator to prevent electrical arcing and short circuits.
Instead of using a solid dielectric material, high-voltage transmission lines use tall towers and insulator strings to keep the electrical conductors separated from each other. These insulator strings are made up of individual insulators, often made from glass or ceramic materials, that are strung together in a series.
The use of air or gas as an insulator in high-voltage transmission lines has several advantages over solid dielectric materials. First, it is less expensive and easier to maintain than solid dielectric materials. Second, it is less likely to degrade over time, as it is not subject to the same thermal or chemical stresses as many solid dielectrics.
However, there are also some disadvantages to using air or gas as an insulator in high-voltage transmission lines. For example, the insulator strings required to maintain the separation between the conductors can be very large and heavy, making the towers used in transmission lines very tall and imposing. Additionally, in some environmental conditions, such as in areas with high levels of pollution or dust, the insulators can become dirty or contaminated, reducing their effectiveness as an insulator.
In summary, while dielectric materials are commonly used as insulators in electrical systems, high-voltage power transmission lines represent a case where air or gas is used as the insulating material instead. While this approach has some advantages over solid dielectric materials, it also has some disadvantages that must be carefully managed.
White paper on Without dielectrics
Here is a brief white paper on the topic of “Without Dielectrics” that explains the importance of dielectric materials in electrical and electronic systems and explores the potential consequences of their absence.
Introduction:
Dielectrics are essential components in many electrical and electronic systems, serving a variety of important functions, including capacitance, insulation, electric field control, and energy storage. Without dielectric materials, it would be challenging to design and build many of the electrical and electronic devices that we rely on today.
Capacitance:
Dielectrics are used to create capacitors, which store electrical energy. Without dielectrics, capacitors would not be able to store energy efficiently, and their performance would be severely limited.
Insulation:
Dielectrics are used as insulation materials to prevent electrical conductors from coming into contact with each other, which can cause short circuits and damage to electrical equipment. Without dielectrics, electrical systems would be much more vulnerable to damage.
Electric Field Control:
Dielectrics can be used to control the electric field in electrical systems. This is important for a wide range of applications, such as in transformers and in electronic devices.
Energy Storage:
Dielectric materials can store energy when an electric field is applied. This is known as dielectric energy storage, and it has many potential applications in areas such as energy storage and high-power electronics.
Potential Consequences:
Without dielectric materials, it would be challenging to build many of the electrical and electronic devices that we rely on today. Capacitors, transformers, and many other devices would not function properly, and electrical systems would be much more vulnerable to damage from short circuits and other electrical faults.
Conclusion:
Dielectric materials are essential components in many electrical and electronic systems, serving a variety of important functions. Without dielectric materials, many of the electrical and electronic devices that we rely on today would not function properly, and electrical systems would be much more vulnerable to damage. As such, it is crucial to continue to research and develop new dielectric materials and technologies to ensure that we can continue to build and improve the electrical and electronic systems that drive our modern world.
