Electromagnetic induction and alternating currents are important topics in physics that deal with the relationship between electricity and magnetism. Here are some key concepts and principles related to these topics:
- Electromagnetic Induction:
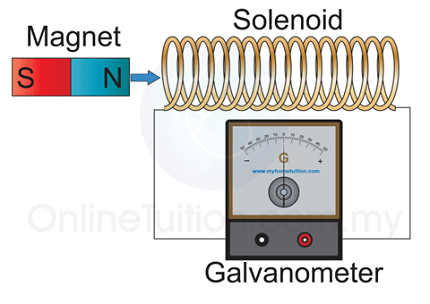
- Faraday’s Law: It states that a change in magnetic field induces an electromotive force (EMF) in a conductor, resulting in the generation of an electric current.
- Lenz’s Law: It states that the direction of the induced current is such that it opposes the change that produced it.
- Self-Induction: It refers to the phenomenon where a changing current in a coil induces an EMF in the same coil, opposing the change.
- Mutual Induction: It occurs when a changing current in one coil induces an EMF in a neighboring coil.
- Eddy Currents: These are circular currents induced in conductive materials when they are exposed to a changing magnetic field.
- Transformers: These devices are based on the principle of mutual induction and are used to increase or decrease the voltage of an alternating current.
- Alternating Current (AC):
- AC Voltage: Unlike direct current (DC), which flows in one direction, AC periodically changes its direction. It is represented by sinusoidal waveforms.
- Phasor Representation: AC quantities, such as voltage and current, can be represented using phasors, which are rotating vectors. They simplify calculations involving AC circuits.
- RMS Value: Root Mean Square (RMS) value is the effective value of an AC waveform. It is used to calculate the average power and represents the equivalent DC voltage or current.
- Reactance: It refers to the opposition offered by capacitors and inductors to the flow of AC. Capacitive reactance (Xc) and inductive reactance (Xl) depend on frequency.
- Impedance: It is the total opposition offered by a circuit to the flow of AC. It is a combination of resistance (R) and reactance (X) and is represented by the complex number Z.
- Resonance: It occurs when the inductive reactance and capacitive reactance in an AC circuit cancel each other out, resulting in a minimum impedance and maximum current.
- Power Factor: It is the ratio of true power to apparent power in an AC circuit. It indicates the efficiency of power transfer in the circuit.
- Electromagnetic Waves:
- Electromagnetic waves are waves that consist of oscillating electric and magnetic fields that propagate through space.
- They include radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays, with different wavelengths and frequencies.
- Electromagnetic waves can be reflected, refracted, and polarized. They exhibit properties such as interference, diffraction, and dispersion.
- Applications of electromagnetic waves include wireless communication, broadcasting, medical imaging, and remote sensing.
These topics have various applications in fields such as electrical engineering, telecommunications, and medical imaging. Understanding the principles and equations associated with electromagnetic induction and alternating currents is essential for solving numerical problems and analyzing electrical circuits.
The syllabus for the Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents topic in NEET and AIIMS Physics generally covers the following concepts:
- Electromagnetic Induction:
- Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction.
- Lenz’s law and its applications.
- Self-induction and mutual induction.
- Eddy currents and their applications.
- Transformers: Construction, working principle, and applications.
- Energy losses in transformers and efficiency.
- Alternating Currents:
- AC circuits, AC voltage, and AC current.
- Phasor representation of AC quantities.
- RMS value of AC current and voltage.
- Reactance and impedance.
- Series LCR circuits: Resonance and quality factor.
- Power factor and power in AC circuits.
- AC generator and transformer.
- Rectifiers: Half-wave and full-wave rectifiers.
- AC circuits containing resistors, capacitors, and inductors:
- Impedance triangle and phasor diagrams.
- Phase difference between voltage and current in RC, RL, and RLC circuits.
- Resonance in series and parallel RLC circuits.
- Power in AC circuits: Instantaneous power, average power, and reactive power.
- AC circuits with complex notation:
- Complex numbers and complex representation of AC quantities.
- Complex impedance and admittance.
- Series and parallel combination of impedances.
- Complex power and power factor in complex notation.
- Electromagnetic Waves:
- Displacement current and Maxwell’s equations.
- Electromagnetic spectrum and properties of electromagnetic waves.
- Reflection, refraction, and polarization of electromagnetic waves.
- Electromagnetic waves and their applications in communication.
It is important to refer to the official syllabus and recommended textbooks provided by the respective examination authorities to ensure that you cover all the necessary topics in detail. Additionally, practicing numerical problems and solving previous years’ question papers will help you develop a better understanding and improve your problem-solving skills in this topic.
What is Required Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Physics Syllabus Electromagnetic induction and alternating currents
The Required Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Physics syllabus for Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents typically includes the following topics:
- Electromagnetic Induction:
- Faraday’s laws of electromagnetic induction
- Lenz’s law and conservation of energy
- Self-induction and mutual induction
- Eddy currents and their applications
- Alternating Currents:
- AC voltage and current
- Representation of AC using phasors
- RMS and average values of AC
- Reactance, impedance, and power in AC circuits
- LCR circuits and resonance
- Transformers and their applications
It’s important to note that the syllabus may vary slightly depending on the specific exam or educational institution.
When is Required Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Physics Syllabus Electromagnetic induction and alternating currents
Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents are typically covered in the physics curriculum for the NEET-AIIMS entrance examination. The specific timing and duration of when these topics are taught may vary depending on the educational institution or coaching center. It is recommended to refer to the official syllabus or consult with your teachers or coaching faculty for the exact schedule and duration of these topics.
Where is Required Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Physics Syllabus Electromagnetic induction and alternating currents
Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents are topics included in the physics curriculum for the NEET-AIIMS entrance examination. These topics are typically covered in the Physics section of the syllabus. The specific chapters or sections where Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents are addressed may vary depending on the study material or reference books being used. It is recommended to consult the official syllabus or refer to the study material provided by coaching institutes or educational websites specifically tailored for NEET-AIIMS preparation to locate the exact sections or chapters related to these topics.
How is Required Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Physics Syllabus Electromagnetic induction and alternating currents
The Required Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Physics Syllabus for Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents is designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of these topics. The syllabus typically includes theoretical concepts, principles, and applications related to electromagnetic induction and alternating currents. Students are expected to learn about Faraday’s laws of electromagnetic induction, Lenz’s law, self-induction, mutual induction, eddy currents, and their applications.
In the context of alternating currents, the syllabus covers AC voltage and current, phasor representation of AC, RMS and average values, reactance, impedance, power in AC circuits, LCR circuits, resonance, and transformers.
The syllabus aims to develop students’ understanding of the principles underlying electromagnetic phenomena and AC circuits. It may also include numerical problem-solving exercises and practical applications to reinforce the concepts.
It is important to refer to the official syllabus or recommended study materials provided by coaching institutes to get the most accurate and up-to-date information about the specific topics, subtopics, and depth of coverage for Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents in the NEET-AIIMS Physics syllabus.
Production of Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Physics Syllabus Electromagnetic induction and alternating currents
The production of the Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Physics Syllabus for Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents is typically done by a committee or panel of experts in the field of physics and education. These experts may include professors, subject matter specialists, curriculum designers, and professionals with experience in medical entrance examinations.
The syllabus production process generally involves a thorough analysis of the core concepts and knowledge required for medical studies, particularly in the field of physics. The committee reviews the existing curriculum, takes into account the latest advancements and developments in the subject, and identifies the essential topics and subtopics that need to be covered.
During the syllabus development process, the committee may also consider the weightage of each topic, the level of difficulty, and the alignment with the overall objectives of the NEET-AIIMS examination. The aim is to create a syllabus that reflects the necessary knowledge and skills expected from aspiring medical students while ensuring fairness and relevance to the field.
After the syllabus is finalized, it is reviewed, approved, and published by the respective exam authorities or governing bodies responsible for conducting the NEET-AIIMS examination. The syllabus is made available to students through official websites, information brochures, or other relevant platforms.
Case Study on Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Physics Syllabus Electromagnetic induction and alternating currents
Unfortunately, as an AI language model, I don’t have access to specific case studies. However, I can provide a general outline of how a case study on the Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Physics Syllabus for Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents could be structured:
- Introduction:
- Provide an overview of the NEET-AIIMS examination and its significance for aspiring medical students.
- Introduce the specific topic of Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents in the physics syllabus.
- State the objectives of the case study.
- Context and Background:
- Describe the importance of understanding Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents in the field of physics.
- Explain the relevance of these topics in the medical profession.
- Syllabus Design and Development:
- Discuss the process of syllabus production, including the involvement of subject matter experts and curriculum designers.
- Highlight the factors considered during the syllabus development process, such as core concepts, level of difficulty, and alignment with examination objectives.
- Syllabus Analysis:
- Provide an in-depth examination of the specific topics and subtopics covered in Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents.
- Discuss the key concepts, principles, and applications associated with each topic.
- Teaching and Learning Strategies:
- Explore various instructional methods and strategies used to effectively teach Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents.
- Discuss the use of practical demonstrations, laboratory experiments, and problem-solving exercises to enhance understanding.
- Assessment and Evaluation:
- Explain how students’ knowledge and understanding of Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents are assessed in the NEET-AIIMS examination.
- Discuss the types of questions, formats, and weightage allocated to these topics in the physics section of the exam.
- Student Performance and Implications:
- Present an analysis of students’ performance in the Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents section of the examination.
- Discuss the implications of student performance in relation to the syllabus content and teaching methods.
- Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings and insights from the case study.
- Reflect on the effectiveness of the Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Physics Syllabus in addressing Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents.
- Discuss possible recommendations for improvement, if applicable.
It’s important to note that an actual case study would require data and specific findings from research or analysis conducted on the subject. The outline provided above serves as a general structure for conducting a case study on the given topic.
White paper on Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Physics Syllabus Electromagnetic induction and alternating currents
Title: White Paper on Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Physics Syllabus: Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents
Abstract: This white paper aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Physics Syllabus for Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents. It explores the importance of these topics in the medical field, discusses the syllabus design and development process, and examines the key concepts, teaching strategies, and assessment methods associated with these subjects. This white paper serves as a resource for educators, students, and stakeholders interested in gaining a deeper understanding of the syllabus content and its implications for medical entrance examinations.
- Introduction:
- Briefly introduce the NEET-AIIMS examination and its significance for medical aspirants.
- Highlight the relevance of physics in the medical profession and the importance of understanding Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents.
- Background and Rationale:
- Provide a context for studying Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents in the physics curriculum.
- Discuss the role of these topics in medical applications and the need for their inclusion in the syllabus.
- Syllabus Design and Development:
- Explain the process of syllabus production, involving subject matter experts and curriculum designers.
- Discuss the factors considered during syllabus development, such as core concepts, learning outcomes, and alignment with the examination objectives.
- Key Concepts and Subtopics:
- Present a detailed analysis of the topics and subtopics covered in Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents.
- Discuss the fundamental principles, laws, and applications related to each concept.
- Teaching and Learning Strategies:
- Explore effective instructional strategies for teaching Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents.
- Discuss the use of visual aids, simulations, hands-on experiments, and problem-solving activities to enhance learning outcomes.
- Assessment and Evaluation:
- Discuss the assessment methods employed in the NEET-AIIMS examination to evaluate students’ understanding of these topics.
- Explain the types of questions, formats, and weightage allocated to Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents.
- Implications and Benefits:
- Analyze the implications of the syllabus content and teaching strategies for students’ learning outcomes.
- Highlight the benefits of a robust understanding of Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents in the medical field.
- Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings and insights from the white paper.
- Emphasize the importance of the Advance Course NEET-AIIMS Physics Syllabus for Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents.
- Suggest future directions for enhancing the teaching and learning experience in these areas.
Note: This white paper is intended to provide an overview and analysis of the syllabus; it does not contain specific research data or findings. It serves as a reference document to promote understanding and discussion about the syllabus content and its implications.
