Human physiology
Human physiology is the scientific study of the functions and mechanisms of the human body. It involves understanding how different systems and organs work together to maintain homeostasis and support the overall functioning of the body.
Here are some key aspects and systems studied in human physiology:
- Cardiovascular System: This system includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood. It is responsible for the transportation of oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products throughout the body.
- Respiratory System: Comprised of the lungs and respiratory passages, this system facilitates the exchange of gases, allowing the body to take in oxygen and eliminate carbon dioxide.
- Digestive System: The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of food into smaller molecules that can be absorbed and utilized by the body. It includes organs such as the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and associated glands.
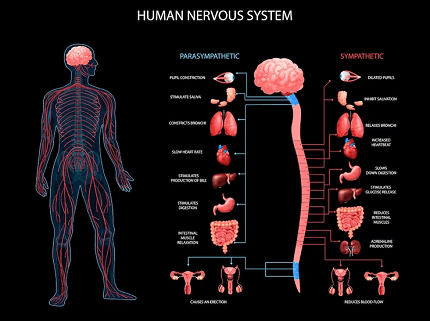
- Nervous System: This complex system includes the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. It coordinates and regulates body activities through electrical signals and chemical messengers, allowing for communication and control of bodily functions.
- Endocrine System: Comprising various glands such as the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, and others, the endocrine system produces and releases hormones that regulate processes such as growth, metabolism, reproduction, and mood.
- Musculoskeletal System: This system includes the muscles, bones, joints, and connective tissues. It provides support, protection, and movement to the body, allowing for posture, locomotion, and other physical activities.
- Urinary System: The urinary system, consisting of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, plays a vital role in filtering waste products from the blood, maintaining fluid balance, and regulating electrolyte concentrations.
- Reproductive System: The reproductive system is involved in the production of offspring. In males, it includes the testes, prostate gland, and associated structures, while in females, it involves the ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes, and mammary glands.
- Integumentary System: The integumentary system refers to the skin, hair, nails, and associated structures. It provides protection against external factors, regulates body temperature, and participates in sensory perception.
These systems and their various components work together harmoniously to ensure the proper functioning of the human body. The study of human physiology involves exploring the mechanisms and processes within these systems, as well as understanding their integration and regulation.
The NEET Biology syllabus for human physiology covers various aspects of the functioning of the human body. Here’s an overview of the topics included in the syllabus:
- Digestion and Absorption:
- Alimentary canal: Structure and functions of different parts
- Digestive enzymes and their action
- Absorption of digested and undigested food
- Disorders related to the digestive system
- Breathing and Respiration:
- Respiratory organs and their functions
- Mechanism of breathing
- Transport of gases and their exchange in tissues
- Disorders related to the respiratory system
- Body Fluids and Circulation:
- Composition and functions of blood
- Blood groups and their compatibility
- Structure and working of the heart
- Blood vessels and their types
- Disorders related to the circulatory system
- Excretory Products and Their Elimination:
- Structure and function of the kidney
- Urine formation and its composition
- Disorders related to the excretory system
- Locomotion and Movement:
- Structure and functions of the skeletal system
- Joints and types of movements
- Structure and functioning of muscles
- Disorders related to the musculoskeletal system
- Neural Control and Coordination:
- Structure and functions of the nervous system
- Reflex action and sensory reception
- Structure and functions of the brain and spinal cord
- Disorders related to the nervous system
- Chemical Coordination and Regulation:
- Endocrine glands and their hormones
- Mechanism of hormone action
- Role of hormones in growth, reproduction, and metabolism
- Disorders related to the endocrine system
It’s important to note that the NEET syllabus may vary slightly from year to year, so it’s always a good idea to refer to the official syllabus provided by the conducting body or the exam authorities.
What is Required NEET-BIOLOGY-SYLLABUS Human physiology
The NEET Biology syllabus for human physiology requires a comprehensive understanding of the following topics:
- Digestion and Absorption:
- Structure and functions of the digestive system
- Digestive enzymes and their action
- Absorption of digested and undigested food
- Disorders related to the digestive system
- Breathing and Respiration:
- Structure and functions of the respiratory system
- Mechanism of breathing
- Transport of gases and their exchange in tissues
- Disorders related to the respiratory system
- Body Fluids and Circulation:
- Composition and functions of blood
- Blood groups and their compatibility
- Structure and working of the heart
- Blood vessels and their types
- Disorders related to the circulatory system
- Excretory Products and Their Elimination:
- Structure and function of the kidney
- Urine formation and its composition
- Disorders related to the excretory system
- Locomotion and Movement:
- Structure and functions of the skeletal system
- Joints and types of movements
- Structure and functioning of muscles
- Disorders related to the musculoskeletal system
- Neural Control and Coordination:
- Structure and functions of the nervous system
- Reflex action and sensory reception
- Structure and functions of the brain and spinal cord
- Disorders related to the nervous system
- Chemical Coordination and Regulation:
- Endocrine glands and their hormones
- Mechanism of hormone action
- Role of hormones in growth, reproduction, and metabolism
- Disorders related to the endocrine system
These topics cover the essential aspects of human physiology as per the NEET Biology syllabus. It’s crucial to study these topics in detail, understanding the structures, functions, and interrelationships between different systems and organs. Additionally, it’s advisable to refer to the official syllabus provided by the conducting body or the exam authorities to ensure you are fully prepared for the examination.
When is Required NEET-BIOLOGY-SYLLABUS Human physiology
The NEET Biology syllabus, including the topic of human physiology, is part of the curriculum for the National Eligibility cum Entrance Test (NEET). NEET is a national-level entrance examination conducted in India for students seeking admission to undergraduate medical and dental courses (MBBS/BDS) in various medical colleges across the country.
The human physiology topics within the NEET Biology syllabus are required to be studied and understood by aspiring medical and dental students preparing for the NEET exam. These topics are essential for answering questions related to human physiology that may appear in the NEET Biology section.
It’s important to note that the NEET exam is typically held once a year, usually in the months of May or June. However, specific dates for the exam may vary from year to year, and it is advisable to check the official notifications and announcements from the National Testing Agency (NTA), which is the conducting body for NEET, to get accurate and up-to-date information regarding the exam schedule.
Where is Required NEET-BIOLOGY-SYLLABUS Human physiology
The NEET-Biology syllabus, which includes the topic of human physiology, is a part of the curriculum that needs to be studied by candidates appearing for the NEET (National Eligibility cum Entrance Test) examination in India. The NEET exam is conducted by the National Testing Agency (NTA) and serves as the entrance examination for admission to undergraduate medical (MBBS) and dental (BDS) courses in various medical colleges across India.
The NEET-Biology syllabus, including human physiology, can be found in the official information brochure and syllabus provided by the NTA. The official website of the NTA (https://ntaneet.nic.in/) is the primary source of information for NEET-related updates, including the detailed syllabus for each subject.
Candidates preparing for the NEET exam are advised to refer to the official NEET-Biology syllabus provided by the NTA and use it as a guideline for their preparation. It outlines the specific topics and subtopics that need to be covered in human physiology and other areas of biology to perform well in the NEET examination.
How is Required NEET-BIOLOGY-SYLLABUS Human physiology
The NEET-Biology syllabus for human physiology is typically studied by aspiring medical and dental students to prepare for the NEET exam. Here’s a general approach to studying the required NEET-Biology syllabus for human physiology:
- Understand the syllabus: Familiarize yourself with the specific topics and subtopics mentioned in the NEET-Biology syllabus for human physiology. This will give you a clear idea of what you need to study.
- Gather study materials: Collect textbooks, reference books, study guides, and other relevant resources that cover human physiology in line with the NEET syllabus. You can consult books like “Human Physiology” by Stuart Ira Fox, “Textbook of Medical Physiology” by Guyton and Hall, or other trusted sources.
- Break it down: Divide the human physiology section into smaller topics and create a study plan accordingly. This will help you manage your time effectively and ensure comprehensive coverage of the syllabus.
- Study the concepts: Begin by understanding the fundamental concepts of human physiology, such as the structure and function of organs and systems, physiological processes, and regulatory mechanisms. Pay attention to key terms, definitions, and interrelationships between different systems.
- Make use of visual aids: Human physiology often involves complex processes and structures. Utilize diagrams, flowcharts, and illustrations to visualize and understand concepts better. This can aid in remembering and explaining physiological processes accurately.
- Practice with diagrams and labeling: Practice drawing and labeling diagrams of organs, systems, and their components. This will help you become familiar with the anatomical structures and reinforce your understanding of human physiology.
- Take notes and create summaries: While studying, take concise notes summarizing important points and concepts. These notes can serve as quick references during revision.
- Practice with past papers and mock tests: Solve NEET-Biology question papers from previous years and take mock tests to assess your understanding of human physiology. This will familiarize you with the exam format, time management, and help identify areas that need further improvement.
- Seek clarification and guidance: If you encounter difficulties or have doubts, consult your teachers, mentors, or subject experts. They can provide additional explanations and guidance to ensure a thorough understanding of human physiology.
- Regular revision: Plan regular revision sessions to consolidate your knowledge and reinforce important concepts. Reviewing the syllabus frequently will help you retain information and enhance your overall preparation.
Remember, studying human physiology for the NEET exam requires a combination of conceptual understanding, factual knowledge, and the ability to apply that knowledge to problem-solving. Therefore, practice solving questions and analyzing case studies related to human physiology to enhance your problem-solving skills.
Additionally, staying updated with the latest developments and research in the field of human physiology can further deepen your understanding and provide a broader perspective on the subject.
Production of NEET-BIOLOGY-SYLLABUS Human physiology
The NEET-Biology syllabus for human physiology is not produced by any single entity. The syllabus is determined and defined by the National Testing Agency (NTA), which is the conducting body responsible for organizing the NEET (National Eligibility cum Entrance Test) examination in India.
The NTA, in consultation with various medical experts, educators, and relevant authorities, designs the NEET syllabus for Biology, including the topic of human physiology. The aim is to create a comprehensive and representative syllabus that covers the essential concepts and knowledge required for medical and dental undergraduate courses.
The process of developing the NEET-Biology syllabus involves a careful analysis of the core concepts, principles, and topics that are considered important in the field of human physiology. The syllabus is designed to ensure that aspiring medical and dental students have a solid understanding of human physiology and its relevance in the medical profession.
It’s important to note that the NEET-Biology syllabus is periodically reviewed and updated by the NTA to align with the advancements and changes in the field of biology and medical education. Therefore, candidates are advised to refer to the official NEET-Biology syllabus provided by the NTA to obtain accurate and up-to-date information on the specific topics and subtopics included in human physiology for the NEET exam.
Case Study on NEET-BIOLOGY-SYLLABUS Human physiology
Certainly! Here’s a case study on human physiology:
Case Study: Cardiovascular Health and Hypertension
Patient Profile: Name: John Age: 55 Gender: Male Medical History: Family history of hypertension and heart disease, sedentary lifestyle, unhealthy diet
Presenting Complaint: John visits his primary care physician with complaints of occasional dizziness, shortness of breath during physical exertion, and increasing fatigue. He also mentions that he has been experiencing frequent headaches and occasional chest discomfort.
Medical Examination and Diagnosis: Upon examination, John’s blood pressure is found to be consistently elevated, with readings averaging around 160/100 mmHg. His physician suspects hypertension (high blood pressure) as the underlying cause of his symptoms. To confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of organ damage, additional tests are ordered.
Further Investigations and Findings:
- Blood Tests:
- Lipid profile: Elevated LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels, low HDL cholesterol levels.
- Renal function tests: Normal kidney function.
- Electrolyte levels: Within the normal range.
- Echocardiogram:
- Left ventricular hypertrophy (thickening of the heart muscle).
- Impaired diastolic function.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG):
- Left ventricular strain pattern indicative of cardiac stress.
Diagnosis and Discussion: Based on the findings, John is diagnosed with hypertension. Hypertension is a chronic medical condition characterized by persistently high blood pressure, which puts increased strain on the arteries and the heart. Over time, this can lead to cardiovascular complications.
In John’s case, the elevated blood pressure has caused the heart to work harder, resulting in left ventricular hypertrophy and impaired diastolic function. The strain pattern observed on the ECG further supports the presence of cardiac stress.
Management and Treatment: The primary goals of managing hypertension in John’s case are to lower his blood pressure, reduce the strain on his cardiovascular system, and minimize the risk of complications. The treatment plan may include the following:
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Dietary changes: Encouraging a low-sodium, heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Regular exercise: Encouraging moderate aerobic exercises such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming.
- Weight management: Aiming for a healthy body weight through a combination of dietary control and regular physical activity.
- Smoking cessation: Encouraging John to quit smoking to reduce further cardiovascular risk.
- Medications:
- Antihypertensive medications: Prescribing appropriate medications to lower blood pressure. This may include angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, or diuretics, depending on the individual’s specific needs.
- Regular Monitoring:
- Regular blood pressure checks to assess the effectiveness of the treatment plan and adjust medications if necessary.
- Periodic follow-up visits to monitor cardiovascular health, assess organ function, and evaluate overall progress.
- Patient Education:
- Educating John about the importance of adherence to medication, lifestyle modifications, and regular monitoring of blood pressure.
- Providing information on the potential complications of hypertension and the benefits of controlling blood pressure.
Conclusion: This case study highlights the impact of hypertension on cardiovascular health. John’s diagnosis emphasizes the need for early detection, appropriate management, and lifestyle modifications to reduce blood pressure and minimize the risk of complications. By implementing lifestyle changes, taking prescribed medications, and adhering to regular follow-up visits, John can improve his cardiovascular health and overall well-being.
White paper on NEET-BIOLOGY-SYLLABUS Human physiology
Title: Understanding Human Physiology: A Comprehensive White Paper
Abstract: This white paper aims to provide a comprehensive overview of human physiology, exploring the intricacies of the body’s systems, their interrelationships, and their role in maintaining homeostasis. By delving into the fundamental principles of human physiology, this paper aims to enhance our understanding of the complex mechanisms that govern our bodily functions.
- Introduction:
- Definition of human physiology
- Significance of studying human physiology
- Brief overview of the major systems in the human body
- Cellular Physiology:
- Structure and function of cells
- Membrane transport mechanisms
- Cellular metabolism and energy production
- Cellular communication and signaling
- Nervous System:
- Organization and components of the nervous system
- Neurons and their functions
- Sensory reception and processing
- Motor control and coordination
- Endocrine System:
- Overview of endocrine glands and their hormones
- Regulation of hormone synthesis, release, and action
- Major endocrine pathways and feedback mechanisms
- Role of hormones in growth, metabolism, and reproduction
- Cardiovascular System:
- Anatomy and function of the heart
- Circulatory system and blood vessels
- Cardiac cycle and blood pressure regulation
- Transport of gases, nutrients, and waste products
- Respiratory System:
- Structure and function of the respiratory system
- Pulmonary ventilation and gas exchange
- Oxygen and carbon dioxide transport
- Regulation of respiration
- Digestive System:
- Anatomy and functions of the digestive system
- Mechanical and chemical digestion processes
- Nutrient absorption and assimilation
- Regulation of gastrointestinal activities
- Urinary System:
- Structure and function of the urinary system
- Renal filtration, reabsorption, and secretion
- Fluid and electrolyte balance
- Acid-base balance and waste elimination
- Musculoskeletal System:
- Structure and function of muscles
- Skeletal system and bone physiology
- Muscular contraction and movement
- Integration of the musculoskeletal system with other systems
- Reproductive System:
- Male and female reproductive anatomy
- Hormonal regulation of reproductive processes
- Gametogenesis and fertilization
- Pregnancy, childbirth, and lactation
- Homeostasis and Integration:
- Concept of homeostasis and its significance
- Feedback mechanisms and control systems
- Integration of systems to maintain balance
- Role of the hypothalamus in regulating body functions
- Aging and Physiological Changes:
- Effects of aging on organ systems
- Physiological changes associated with aging
- Impact of lifestyle factors on aging and health
- Clinical Applications:
- Common physiological disorders and their mechanisms
- Diagnostic techniques and monitoring of physiological parameters
- Therapeutic interventions based on physiological principles
- Conclusion:
- Summary of key points discussed
- Importance of understanding human physiology in healthcare
- Future directions and advancements in the field of human physiology
By comprehensively exploring the intricate workings of the human body, this white paper aims to provide a solid foundation of knowledge in human physiology. It serves as a valuable resource for students, researchers, healthcare professionals, and anyone interested in gaining a deeper understanding of the fascinating mechanisms that drive our physiological processes.
