Potential difference
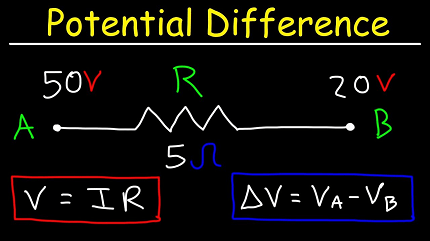
Potential difference, also known as voltage, is a fundamental concept in physics and electrical engineering. It refers to the difference in electric potential between two points in an electric field or an electrical circuit. Potential difference is denoted by the symbol “V” and is measured in volts (V).
Here are some key points about potential difference:
- Definition: Potential difference is defined as the work done per unit charge in moving a positive test charge from one point to another in an electric field. Mathematically, it can be expressed as V = W/Q, where V is the potential difference, W is the work done, and Q is the charge.
- Electric Potential: Electric potential at a point in an electric field is the amount of electric potential energy per unit charge at that point. Potential difference is a measure of the difference in electric potential between two points.
- Voltage Sources: Potential difference is commonly associated with voltage sources such as batteries and power supplies. These devices create an electric field that generates a potential difference between their terminals.
- Units: Potential difference is measured in volts (V). One volt is defined as the potential difference across a conductor when a current of one ampere (A) is flowing through it, and the power dissipated is one watt (W).
- Polarity: Potential difference has a polarity, indicating the direction of flow of positive charge. The point at a higher potential is considered positive, while the point at a lower potential is considered negative. Electric current flows from higher potential to lower potential.
- Circuit Analysis: Potential difference plays a crucial role in analyzing electrical circuits. It determines the flow of electric current and is used in calculations involving resistors, capacitors, and other circuit components.
- Measurement: Potential difference can be measured using a voltmeter, a device specifically designed to measure voltage. Voltmeters are connected in parallel across the points where the potential difference needs to be measured.
Understanding potential difference is essential for various applications, including circuit analysis, power distribution, and electrical device operation. It provides insights into the behavior of electric fields and enables the calculation of current, power, and energy in electrical systems.
The physics syllabus for the integrated course at AIIMS (All India Institute of Medical Sciences) typically covers a wide range of topics. One of the fundamental topics in physics is potential difference, which is related to the study of electricity and circuits. Here is an overview of the potential difference topic:
- Electric Potential Energy:
- Introduction to electric potential energy.
- Definition of electric potential.
- Calculation of electric potential due to a point charge.
- Electric Potential Difference:
- Definition of electric potential difference (voltage).
- Calculation of electric potential difference using the formula V = W/Q.
- Relationship between electric potential difference and electric field strength.
- Capacitors and Capacitance:
- Introduction to capacitors and their basic principles.
- Calculation of the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor.
- Relationship between potential difference, charge, and capacitance.
- Electric Circuits:
- Series and parallel connections of resistors and capacitors.
- Calculation of total resistance and total capacitance in different circuit configurations.
- Kirchhoff’s laws and their applications in solving circuit problems.
- Calculation of potential difference across various circuit elements.
- Ohm’s Law:
- Introduction to Ohm’s law and its relationship between current, potential difference, and resistance.
- Calculation of potential difference and current using Ohm’s law.
- Application of Ohm’s law in simple circuit analysis.
- Work, Energy, and Power:
- Calculation of work done and power in electrical circuits.
- Application of the work-energy theorem in electrical systems.
It is important to note that this is just an overview of the potential difference topic, and the actual syllabus at AIIMS may provide more specific details and include additional subtopics. It is recommended to refer to the official syllabus or course materials provided by AIIMS for a comprehensive understanding of the subject.
What is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Potential difference
As an AI language model, I don’t have access to the specific details of the AIIMS syllabus for physics. However, I can provide a general outline of the topics related to potential difference that are typically covered in physics syllabi. It’s important to consult the official AIIMS syllabus or course materials for the most accurate and detailed information. Here’s a broad overview:
- Electric Potential Energy:
- Introduction to electric potential energy.
- Calculation of electric potential energy using the formula U = qV, where U is the potential energy, q is the charge, and V is the potential difference.
- Electric Potential Difference:
- Definition of potential difference (voltage) as the change in electric potential between two points in an electric field.
- Calculation of potential difference using the formula V = W/q, where V is the potential difference, W is the work done, and q is the charge.
- Capacitors and Capacitance:
- Introduction to capacitors and their behavior in circuits.
- Calculation of the capacitance of a capacitor using the formula C = Q/V, where C is the capacitance, Q is the charge stored, and V is the potential difference.
- Electric Circuits:
- Analysis of simple electric circuits involving resistors, capacitors, and voltage sources.
- Calculation of potential difference across circuit elements using Ohm’s law, Kirchhoff’s laws, and appropriate circuit equations.
- Power and Energy:
- Calculation of power dissipated in electrical circuits using the formula P = IV, where P is power, I is current, and V is potential difference.
- Calculation of energy consumed or transferred in electrical circuits using the formula E = Pt, where E is energy, P is power, and t is time.
Again, please refer to the official AIIMS syllabus or course materials for the specific topics, subtopics, and depth of coverage related to potential difference in the physics syllabus.
When is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Potential difference
The specific timing or duration allocated to the topic of potential difference in the AIIMS syllabus for physics may vary depending on the curriculum and the depth of study. Typically, potential difference is introduced and covered as part of the broader topic of electricity and circuits. It is a fundamental concept in physics and is essential for understanding various aspects of electrical phenomena.
In most physics courses, potential difference is introduced early on and serves as a foundational concept for subsequent topics. The exact timing may depend on the structure and organization of the curriculum. Potential difference is often covered alongside other related concepts such as electric fields, electric current, resistance, and Ohm’s law.
To determine the specific timing of potential difference in the AIIMS physics syllabus, it is best to consult the official syllabus or course outline provided by AIIMS or refer to the course materials and schedule given to you by your instructors. These resources will provide the most accurate and up-to-date information regarding when potential difference is taught and the extent of its coverage within the AIIMS syllabus for physics.
Where is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Potential difference
The exact location or placement of the topic of potential difference within the AIIMS syllabus for physics may depend on the specific curriculum and the structure of the course. It is typically included as part of the broader topic of electricity and circuits. To find the specific location of potential difference in the AIIMS physics syllabus, you should refer to the official syllabus or course outline provided by AIIMS.
The AIIMS syllabus for physics may be available on the official AIIMS website or in the course materials provided to students. The syllabus will provide a detailed breakdown of the topics covered in the physics curriculum, including potential difference. It will specify the order in which topics are taught and may provide information on the depth of coverage and any prerequisite knowledge required.
Consulting the official AIIMS syllabus or reaching out to your instructors or academic advisors at AIIMS will provide you with the accurate and up-to-date information about the specific location of potential difference within the physics syllabus. They will be able to guide you on where to find the detailed syllabus and how potential difference is incorporated into the overall curriculum.
How is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Potential difference
To obtain the detailed AIIMS syllabus for physics, including the topic of potential difference, you should refer to the official AIIMS website or reach out to AIIMS directly for the most accurate and up-to-date information. The AIIMS syllabus for physics is designed to cover a wide range of topics, and potential difference is a fundamental concept within that framework. Here are some general guidelines on how potential difference might be covered in the AIIMS syllabus:
- Introduction to Electricity: The syllabus may start with an introduction to electricity, including the concept of electric charge, electric fields, and electric potential.
- Potential Difference and Electric Circuits: The syllabus is likely to cover potential difference as it relates to electric circuits. This may include understanding the flow of current, resistance, and the role of potential difference in circuit analysis.
- Circuit Components: The syllabus might discuss various circuit components, such as resistors, capacitors, and voltage sources, and how potential difference is associated with these elements.
- Calculation and Applications: The syllabus may involve calculations involving potential difference, such as determining potential difference across resistors or capacitors in different circuit configurations. It may also include practical applications of potential difference in areas such as medical instrumentation or diagnostic techniques.
Remember that the above information is a general outline and the actual AIIMS syllabus may provide more specific details and additional subtopics related to potential difference in physics. It is essential to consult the official AIIMS syllabus or course materials for the most accurate and comprehensive information regarding the potential difference topic within the AIIMS physics syllabus.
Case Study on AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Potential difference
Case Study: Potential Difference in Household Electrical Safety
Introduction:
Potential difference plays a crucial role in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of electrical systems, particularly in households. This case study focuses on the application of potential difference in maintaining electrical safety within a residential setting.
Background:
Consider a typical household electrical system. It consists of a distribution panel (main electrical panel), circuit breakers, electrical outlets, and various electrical appliances. The potential difference, or voltage, provided by the utility company is typically 120 or 240 volts AC (alternating current) in many countries.
Case Scenario:
In this case, we will examine the potential difference-related safety aspects when using a faulty electrical appliance.
Scenario:
John, a resident in a suburban area, notices that one of his wall outlets is not working. He plugs in a faulty appliance, unaware that it has a damaged power cord. As soon as he turns on the appliance, he experiences an electrical shock.
Analysis:
Potential Difference: The wall outlet is connected to the electrical supply and has a potential difference of 120 volts AC. This potential difference is required for the proper functioning of electrical appliances.
Faulty Appliance: The faulty appliance has a damaged power cord, which can result in exposed wires or loose connections. As a result, when John turns on the appliance, there is a potential for an electrical short circuit or leakage of current.
Electric Shock: Due to the damaged power cord, a potential difference is created between the exposed wire and any conductive material in contact with it. When John touches the faulty appliance, he completes a circuit, and a current flows through his body. The potential difference between the wire and John’s body causes an electric shock.
Safety Measures:
a. Grounding: To mitigate such risks, electrical systems are designed with a grounding system. The grounding wire provides a low-resistance path for the current in case of faults, diverting it safely to the ground.
b. Residual Current Devices (RCDs): RCDs, commonly known as ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs), are installed in electrical circuits to detect any imbalances in the current flow. They quickly interrupt the circuit if an imbalance is detected, protecting individuals from electric shocks.
c. Regular Inspections: Regular inspections of electrical systems, including outlets, power cords, and appliances, are essential to identify any damage or potential hazards. Prompt repairs or replacements should be carried out to maintain electrical safety.
Conclusion:
Potential difference, a fundamental concept in electricity, has significant implications for household electrical safety. Understanding the importance of maintaining the integrity of electrical systems, using grounded outlets, and adhering to safety measures can help prevent electrical hazards and ensure the well-being of individuals within a residential setting. Regular inspections, prompt repairs, and the use of safety devices like RCDs contribute to maintaining a safe electrical environment.
White paper on AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Potential difference
Title: Understanding Potential Difference: Concepts, Applications, and Significance
Abstract:
This white paper provides a comprehensive overview of potential difference, also known as voltage, and its importance in various fields. It explores the fundamental principles of potential difference, its measurement, and its applications in different domains. The paper discusses the significance of potential difference in electrical systems, its role in circuit analysis, and its impact on safety and efficiency. It also examines the practical applications of potential difference in industries such as energy, electronics, and telecommunications. By presenting a detailed analysis of potential difference, this white paper aims to enhance understanding and promote further research in this critical area of study.
Table of Contents:
Introduction
1.1 Overview
1.2 Importance of Potential Difference
Fundamentals of Potential Difference
2.1 Definition and Concept
2.2 Electric Fields and Potential Energy
2.3 Calculation and Units
Measurement of Potential Difference
3.1 Voltmeters and Measurement Techniques
3.2 Analog vs. Digital Voltmeters
3.3 Practical Considerations
Potential Difference in Electrical Circuits
4.1 Ohm’s Law and Resistance
4.2 Kirchhoff’s Laws and Circuit Analysis
4.3 Series and Parallel Connections
4.4 Power Dissipation and Energy Transfer
Potential Difference and Safety
5.1 Electrical Safety Considerations
5.2 Grounding Systems and Protection Devices
5.3 Residual Current Devices (RCDs)
5.4 Impact on Human Safety
Potential Difference in Industrial Applications
6.1 Power Generation and Distribution
6.2 Electronics and Telecommunications
6.3 Renewable Energy Systems
Advanced Concepts and Emerging Trends
7.1 Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC)
7.2 Three-Phase Power Systems
7.3 High Voltage and Power Transmission
Conclusion
8.1 Key Takeaways
8.2 Future Directions
This white paper aims to provide readers with a comprehensive understanding of potential difference, its significance, and its wide-ranging applications. By delving into the core concepts, measurement techniques, and practical implications, readers will gain a solid foundation to further explore and apply potential difference in their respective fields. Whether in electrical engineering, physics, or related disciplines, this paper serves as a valuable resource for researchers, professionals, and enthusiasts seeking to deepen their knowledge of potential difference and its implications.
