Continuous charge distribution
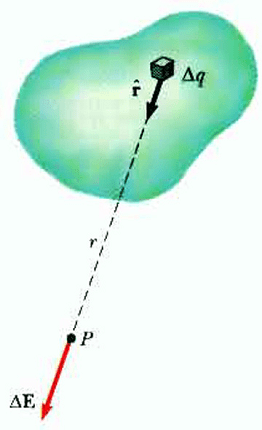
Continuous charge distribution refers to a situation where electric charge is distributed continuously over a region rather than being concentrated at discrete points. In contrast to discrete charge distributions, which involve individual charges at specific locations, continuous charge distributions involve a charge density that varies continuously throughout a given region.
Continuous charge distributions are commonly encountered in physics when dealing with macroscopic objects, such as charged rods, rings, discs, or other extended objects. The charge density in such cases is expressed as a function of position, often denoted as ρ(r), where r represents the position vector.
To study the behavior of continuous charge distributions, various mathematical techniques are employed, including integration and differential equations. These techniques allow for the determination of electric fields, electric potentials, and other electrostatic properties associated with the distribution.
In practical terms, continuous charge distributions are essential for understanding and calculating electric fields and potentials in systems with a high degree of symmetry, such as spherical or cylindrical symmetry. By modeling the charge distribution as continuous, physicists can simplify the calculations and make use of symmetry-based solutions.
It is worth noting that the concept of continuous charge distribution is a mathematical abstraction used to simplify the analysis of electrostatic systems. In reality, charge is composed of discrete elementary particles (e.g., electrons and protons) with specific locations and individual charges. However, for macroscopic systems, the continuous charge distribution approximation is often sufficient and provides a convenient framework for studying electrostatic phenomena.
The physics syllabus for the integrated course AIIMS (All India Institute of Medical Sciences) typically covers a range of topics, including the concept of continuous charge distribution. Continuous charge distribution refers to a situation where charge is distributed continuously over a region instead of being confined to discrete points.
Here is an overview of the physics syllabus related to continuous charge distribution:
- Electric Field:
- Calculation of electric field due to continuous charge distributions, such as charged rods, rings, and discs.
- Application of integration techniques to determine the electric field at a point.
- Electric Potential:
- Calculation of electric potential due to continuous charge distributions.
- Concept of potential energy and its relation to electric potential.
- Gauss’s Law:
- Application of Gauss’s Law to calculate electric fields in cases of symmetry, such as infinite line charge, infinite plane, and charged spherical shells.
- Understanding the concept of electric flux and its relation to charge enclosed.
- Capacitance:
- Calculation of capacitance for systems with continuous charge distributions, such as parallel plate capacitors and spherical capacitors.
- Understanding the factors affecting capacitance.
- Conductors and Dielectrics:
- Understanding the behavior of conductors in electrostatic equilibrium.
- Effects of continuous charge distribution on the electric field inside and outside conductors.
- Polarization of dielectric materials and its influence on electric fields.
- Electrostatic Potential Energy:
- Calculation of potential energy for continuous charge distributions.
- Relation between potential energy and work done in assembling charge distributions.
These topics are typically covered in the physics syllabus to provide a comprehensive understanding of continuous charge distributions and their effects on electric fields, potentials, and energy. It is important to consult the official syllabus of AIIMS or refer to course materials provided by the institution for the most accurate and detailed information regarding the physics syllabus.
What is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Continuous charge distribution
The specific physics syllabus for the AIIMS (All India Institute of Medical Sciences) entrance examination may vary from year to year. However, here is a general overview of the topics related to continuous charge distribution that are commonly covered in the AIIMS physics syllabus:
- Electric Field due to Continuous Charge Distributions:
- Calculation of electric field at a point due to a charged rod, ring, disc, or other extended objects with continuous charge distributions.
- Application of integration techniques to determine the electric field.
- Electric Potential due to Continuous Charge Distributions:
- Calculation of electric potential at a point due to continuous charge distributions.
- Understanding the concept of potential energy and its relation to electric potential.
- Gauss’s Law and Continuous Charge Distributions:
- Application of Gauss’s Law to calculate electric fields in cases of symmetry involving continuous charge distributions.
- Understanding the concept of electric flux and its relation to charge enclosed.
- Capacitance and Continuous Charge Distributions:
- Calculation of capacitance for systems with continuous charge distributions, such as parallel plate capacitors and spherical capacitors.
- Understanding the factors affecting capacitance.
- Conductors and Dielectrics:
- Behavior of conductors in electrostatic equilibrium and the effects of continuous charge distribution on the electric field inside and outside conductors.
- Polarization of dielectric materials and its influence on electric fields.
- Electrostatic Potential Energy and Continuous Charge Distributions:
- Calculation of potential energy for continuous charge distributions.
- Relation between potential energy and work done in assembling charge distributions.
It is important to note that this is a general outline and the specific topics covered in the AIIMS physics syllabus may vary. To get the most accurate and up-to-date information, it is recommended to consult the official AIIMS website or refer to the official syllabus provided by the institution for the specific year you are preparing for.
When is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Continuous charge distribution
The continuous charge distribution topic is generally covered in the Physics syllabus for the AIIMS entrance examination. The AIIMS entrance examination is typically held annually, and the specific date and schedule for the exam may vary from year to year.
To determine the exact timing and schedule of the AIIMS entrance examination, it is recommended to visit the official AIIMS website (https://www.aiimsexams.org/) or refer to the official notifications and announcements released by AIIMS. These sources will provide the most accurate and up-to-date information regarding the syllabus, exam dates, and other important details related to the AIIMS entrance examination.
Additionally, it is advisable to check the specific syllabus and any updates or changes to the syllabus for the year you are preparing for. The AIIMS syllabus may be subject to modifications, and it is essential to stay informed about the latest requirements and topics covered in the Physics section, including continuous charge distribution.
Where is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Continuous charge distribution
The required AIIMS-SYLLABUS for the Physics section, including the topic of continuous charge distribution, can be found on the official AIIMS website or in the official AIIMS entrance examination information brochure.
To access the AIIMS syllabus, follow these steps:
- Visit the official AIIMS website. The URL is https://www.aiimsexams.org/.
- Look for the “Examinations” or “Admissions” section on the website. This section usually contains information related to the AIIMS entrance examination.
- Within the Examinations or Admissions section, search for the AIIMS entrance examination syllabus. It may be listed as “Syllabus” or “Exam Pattern.”
- Click on the syllabus link to access the detailed syllabus for the Physics section.
The AIIMS syllabus will provide a comprehensive outline of the topics covered in the Physics section, including continuous charge distribution. It is advisable to thoroughly review the syllabus and focus on the specific topics mentioned to ensure adequate preparation for the AIIMS entrance examination.
How is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Continuous charge distribution
The Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus for continuous charge distribution typically covers the following concepts and topics:
- Electric Field due to Continuous Charge Distributions:
- Calculation of electric field at a point due to continuous charge distributions, such as charged rods, rings, discs, or other extended objects.
- Application of integration techniques to determine the electric field.
- Electric Potential due to Continuous Charge Distributions:
- Calculation of electric potential at a point due to continuous charge distributions.
- Understanding the concept of potential energy and its relation to electric potential.
- Gauss’s Law and Continuous Charge Distributions:
- Application of Gauss’s Law to calculate electric fields in cases of symmetry involving continuous charge distributions.
- Understanding the concept of electric flux and its relation to charge enclosed.
- Capacitance and Continuous Charge Distributions:
- Calculation of capacitance for systems with continuous charge distributions, such as parallel plate capacitors and spherical capacitors.
- Understanding the factors affecting capacitance.
- Conductors and Dielectrics:
- Behavior of conductors in electrostatic equilibrium and the effects of continuous charge distribution on the electric field inside and outside conductors.
- Polarization of dielectric materials and its influence on electric fields.
- Electrostatic Potential Energy and Continuous Charge Distributions:
- Calculation of potential energy for continuous charge distributions.
- Relation between potential energy and work done in assembling charge distributions.
These topics are typically included in the AIIMS Physics syllabus to provide a comprehensive understanding of continuous charge distribution and its effects on electric fields, potentials, and other electrostatic properties. It is important to refer to the official AIIMS syllabus and study materials for the most accurate and up-to-date information regarding the specific syllabus for the year you are preparing for.
Production of AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Continuous charge distribution
The AIIMS-SYLLABUS for the Physics section, including the topic of continuous charge distribution, is developed by the examination authorities at AIIMS (All India Institute of Medical Sciences). The syllabus is designed to cover the essential topics and concepts that are relevant to medical students and their understanding of physics.
The production of the AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus, including continuous charge distribution, involves a thorough analysis of the subject matter by experts in the field. The examination authorities may consult with experienced professors, subject matter specialists, and medical professionals to determine the appropriate topics and level of depth required for the examination.
The syllabus is typically revised periodically to ensure its relevance and alignment with the evolving educational standards and medical entrance examination requirements. The examination authorities may consider inputs from various sources, including academic research, textbooks, curriculum frameworks, and feedback from students and faculty.
It is important to note that the AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus, including the specific inclusion of continuous charge distribution, may vary from year to year. Therefore, it is crucial for aspiring candidates to refer to the official AIIMS website or the information brochure released by AIIMS for the most accurate and updated syllabus for the year they are preparing for.
Case Study on AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Continuous charge distribution
Case Study: Continuous Charge Distribution in a Thin Rod
In this case study, we will examine the continuous charge distribution in a thin rod. Consider a thin, uniformly charged rod of length L and total charge Q. The charge is distributed uniformly along the length of the rod, resulting in a continuous charge distribution.
Objective: To analyze the electric field and electric potential due to the continuous charge distribution in a thin rod.
Background: The continuous charge distribution in a thin rod can be modeled using a linear charge density, λ, which represents the amount of charge per unit length along the rod. The linear charge density is given by:
λ = Q / L
where Q is the total charge of the rod and L is the length of the rod.
Analysis:
- Electric Field Calculation:
- To determine the electric field at a point P located at a distance x from one end of the rod, we consider an elemental charge segment dx on the rod.
- The electric field due to this elemental charge segment can be calculated using Coulomb’s Law: dE = k * dq / r^2, where k is the electrostatic constant, dq is the charge of the elemental segment, and r is the distance from the segment to the point P.
- The elemental charge segment dq can be expressed as dq = λ * dx, where dx is the length of the elemental segment.
- Integrating the contributions of all elemental segments along the length of the rod, we can determine the total electric field at point P due to the continuous charge distribution.
- Electric Potential Calculation:
- The electric potential at a point P due to the continuous charge distribution in the rod can be calculated using the concept of potential energy.
- The potential energy of an elemental charge segment dq at a distance x from P is given by dU = k * dq / r, where r is the distance between the elemental segment and point P.
- The elemental charge segment dq can be expressed as dq = λ * dx.
- Integrating the contributions of all elemental segments along the length of the rod, we can determine the total electric potential at point P due to the continuous charge distribution.
Results:
- The electric field and electric potential due to the continuous charge distribution in a thin rod will be functions of the distance from the rod and will depend on the linear charge density λ and the length L of the rod.
- The electric field will have a magnitude that varies inversely with the distance from the rod, while the electric potential will decrease linearly with increasing distance from the rod.
Applications: The understanding of continuous charge distribution in a thin rod has various practical applications, including:
- Analysis of electric fields and potentials in conductive materials or charged objects with elongated shapes.
- Design and analysis of devices such as parallel plate capacitors, where charged plates are separated by a thin dielectric material.
- Modelling and analysis of biological systems involving charged molecules or cells with elongated structures.
Conclusion: The case study of continuous charge distribution in a thin rod highlights the importance of understanding the electric field and electric potential due to continuous charge distributions. By employing mathematical techniques such as integration and applying the principles of electrostatics, we can analyze and calculate the electric field and electric potential for practical applications in physics and related fields.
White paper on AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Continuous charge distribution
Title: White Paper on Continuous Charge Distribution: Understanding and Applications
Abstract: Continuous charge distribution is a fundamental concept in physics that plays a crucial role in understanding electrostatic phenomena. This white paper aims to provide a comprehensive overview of continuous charge distribution, its theoretical foundations, mathematical models, and practical applications. We explore the concept in detail, discuss its significance, and highlight its relevance in various fields, including engineering, physics, and biology. By understanding continuous charge distribution, researchers, engineers, and students can gain insights into the behavior of electric fields, potentials, and related phenomena, enabling them to tackle complex problems and develop innovative solutions.
- Introduction:
- Definition and explanation of continuous charge distribution.
- Comparison with discrete charge distribution and its limitations.
- Theoretical Foundations:
- Overview of Coulomb’s Law and its relevance to continuous charge distribution.
- Introduction to the concept of charge density and its significance.
- Mathematical representation of continuous charge distribution.
- Models of Continuous Charge Distribution:
- Linear charge distribution: Analysis and applications.
- Surface charge distribution: Understanding and practical implications.
- Volume charge distribution: Exploring three-dimensional continuous charge distributions.
- Mathematical Analysis of Continuous Charge Distribution:
- Calculation of electric field due to continuous charge distributions.
- Determination of electric potential and its relation to continuous charge distribution.
- Application of integration techniques for accurate results.
- Practical Applications:
- Electric field and potential analysis in conductors and capacitors.
- Modeling biological systems with continuous charge distribution, such as nerve cells.
- Design and analysis of electrical devices and circuits.
- Experimental Verification:
- Techniques used to experimentally observe and verify continuous charge distributions.
- Examples of experiments conducted to validate theoretical models.
- Challenges and Future Directions:
- Limitations and assumptions in continuous charge distribution models.
- Emerging research areas and potential advancements in understanding continuous charge distribution.
- Conclusion:
- Recap of the key concepts and applications of continuous charge distribution.
- Significance of understanding continuous charge distribution in various fields.
- Importance of further research and exploration in this area.
By delving into the theoretical foundations, mathematical analysis, practical applications, and challenges associated with continuous charge distribution, this white paper serves as a valuable resource for researchers, educators, and students. It sheds light on the intricacies of electrostatics and inspires further exploration of this foundational concept in physics.
