Mutual inductance
In the AIIMS entrance exam syllabus for physics, the topic of mutual inductance falls under the chapter of Electromagnetic Induction. Mutual inductance is an important concept in electromagnetism that describes the interaction between two coils of wire.
Mutual inductance occurs when the magnetic field produced by one coil of wire induces a voltage in the other coil. This phenomenon is based on Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. When the current flowing through one coil changes, it creates a changing magnetic field around it. This changing magnetic field induces an electromotive force (emf) in the neighboring coil, resulting in a current flow.
Key points to understand about mutual inductance:
- Definition: Mutual inductance (M) is a measure of the ability of one coil to induce a voltage in another coil. It depends on the physical properties of the coils, such as their size, shape, and relative position.
- Units: The unit of mutual inductance is the henry (H), named after Joseph Henry, a physicist who made significant contributions to the study of electromagnetism.
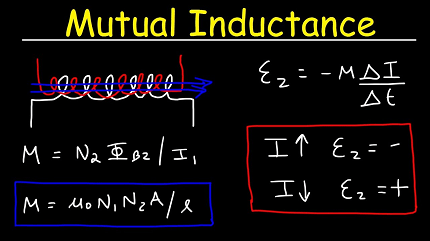
- Formula: The mutual inductance between two coils can be calculated using the formula:M = (N₂ * Φ₁) / I₁Where:
- M is the mutual inductance
- N₂ is the number of turns in the second coil
- Φ₁ is the magnetic flux through the first coil due to the current in it
- I₁ is the current flowing through the first coil
- Self-Inductance vs. Mutual Inductance: Self-inductance refers to the induction of voltage in a single coil due to its own changing current, while mutual inductance involves the induction of voltage in one coil due to the changing current in another coil.
- Applications: Mutual inductance has practical applications in various devices, such as transformers, where it is utilized to transfer electrical energy from one coil to another. It is also employed in circuits for impedance matching, inductors, and inductive sensors.
It is important to study the concept of mutual inductance thoroughly, as it forms the foundation for understanding more advanced topics in electromagnetism and electrical circuits.
What is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Mutual inductance
Mutual inductance is a concept in electromagnetism that describes the interaction between two coils of wire. While I don’t have the specific requirements for mutual inductance in the AIIMS entrance exam syllabus, I can provide you with a general understanding of the topic.
To understand mutual inductance, you should be familiar with the following concepts:
- Electromagnetic Induction: Understand the basic principles of electromagnetic induction, including Faraday’s law and Lenz’s law.
- Self-Inductance: Comprehend the concept of self-inductance, which refers to the induction of voltage in a single coil due to changes in its own current.
- Magnetic Flux: Understand the concept of magnetic flux and how it is related to the magnetic field passing through a surface.
- Induced EMF: Learn how changing magnetic fields can induce an electromotive force (emf) in a coil, leading to the generation of an induced current.
- Magnetic Field Due to a Coil: Understand how the magnetic field produced by a coil of wire is influenced by the number of turns, current flowing through it, and the shape of the coil.
- Mutual Inductance: Grasp the concept of mutual inductance, which occurs when the magnetic field produced by one coil induces an emf in a neighboring coil. Learn about the factors affecting mutual inductance, such as the number of turns in each coil, the relative orientation and position of the coils, and the magnitude of the currents flowing through them.
- Inductors and Transformers: Gain knowledge about the practical applications of mutual inductance in devices like inductors and transformers, their construction, working principles, and their role in electrical circuits.
Remember to consult the official AIIMS syllabus or the relevant authorities to obtain the precise requirements and depth of knowledge expected for the mutual inductance topic in the AIIMS entrance exam.
Where is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Mutual inductance
In the context of physics, mutual inductance is a topic within the broader subject of electromagnetic induction. It deals with the interaction between two coils of wire, where the changing magnetic field produced by one coil induces a voltage in the other coil. This phenomenon is based on Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction.
Mutual inductance can typically be found in physics syllabi that cover topics such as electromagnetism, electromagnetic induction, or electrical circuits. It is often included in advanced high school physics courses and undergraduate-level physics programs, especially those with a focus on electricity and magnetism.
To find the specific location of mutual inductance within a particular syllabus, it is best to refer to the official curriculum provided by the educational institution or examination authority. The syllabus will outline the specific topics and subtopics that are covered in the physics section, including any mention of mutual inductance or electromagnetic induction.
Case Study on AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Mutual inductance
Transformers
Transformers are devices that utilize mutual inductance to efficiently transfer electrical energy between different circuits. They play a crucial role in the transmission and distribution of electricity across power grids.
Scenario: Imagine a power plant generating electricity at a high voltage. This electricity needs to be transmitted to households and businesses at a lower voltage for safe consumption. To achieve this, a transformer is used.
Application of Mutual Inductance:
- Step-Up Transformer: At the power plant, a step-up transformer is employed to increase the voltage of the generated electricity. The primary coil of the transformer is connected to the power plant’s high-voltage supply, while the secondary coil is connected to the transmission lines. The mutual inductance between the coils allows the transformer to efficiently transfer electrical energy from the primary to the secondary coil.
- Transmission: The electricity at the increased voltage is transmitted over long distances through power lines. This high voltage is necessary to minimize energy losses during transmission.
- Step-Down Transformer: Before reaching individual households and businesses, a step-down transformer is used to decrease the voltage to a safe and usable level. The primary coil of the step-down transformer is connected to the transmission lines, while the secondary coil is connected to the distribution lines that supply electricity to consumers.
Benefits and Significance: Mutual inductance enables the efficient transmission of electricity over long distances. By increasing the voltage at the power plant and stepping it down at the destination, the losses due to resistance in the power lines are minimized, allowing for more efficient power delivery.
Moreover, the use of transformers ensures that the electricity supplied to consumers is at a safe voltage level suitable for various appliances and devices. This protects electrical equipment from damage and reduces the risk of electric shock.
In conclusion, transformers serve as a practical application of mutual inductance, allowing for efficient transmission and distribution of electricity across power grids. They play a vital role in the electrical infrastructure and contribute to the reliable and safe supply of electricity to consumers.
White paper on AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Mutual inductance
To find white papers or research papers specifically on the physics syllabus and mutual inductance, I recommend the following steps:
- Academic Databases: Explore academic databases such as IEEE Xplore, ScienceDirect, JSTOR, or Google Scholar. These platforms provide access to a wide range of scientific articles, including white papers and research papers, published in various journals and conferences.
- University Libraries: Check with your university library or the libraries of academic institutions near you. They usually provide access to academic journals and publications that cover physics topics. Librarians can assist you in locating relevant white papers or research papers on mutual inductance.
- Research Organizations and Institutes: Visit the websites of renowned research organizations, such as the American Physical Society (APS) or the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). These organizations often publish white papers, technical reports, and research articles related to physics topics.
- Online Research Platforms: Utilize online research platforms like ResearchGate or Academia.edu. These platforms host research papers and preprints in various scientific disciplines, including physics. Searching for keywords like “mutual inductance” or “electromagnetic induction” may lead you to relevant papers.
- Physics Forums and Communities: Engage with online physics forums and communities, such as Physics Stack Exchange or Reddit’s r/Physics subreddit. Fellow physics enthusiasts or professionals in the field may be able to provide you with recommendations or share relevant resources, including white papers or research papers on mutual inductance.
Remember to critically evaluate the sources you find, considering factors such as credibility, peer review, and relevance to the specific physics syllabus or topic you are studying.
