Standard electrode potential
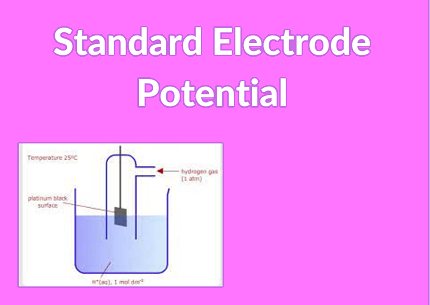
The Standard electrode potential is a measure of the potential difference between a half-cell electrode and a standard reference electrode, under standard conditions. It is denoted by E° and is expressed in volts.
In the context of the AIIMS (All India Institute of Medical Sciences) syllabus for chemistry, the topic of standard electrode potential is not explicitly mentioned. However, understanding this concept is important in the study of electrochemistry, which is a part of the syllabus.
In electrochemistry, the standard electrode potential is often used to determine the tendency of a chemical species to undergo oxidation or reduction. It provides information about the relative strengths of different redox reactions.
Some key points related to the standard electrode potential are:
- Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE): It is commonly used as the reference electrode for measuring standard electrode potentials. The standard electrode potential of the SHE is defined as 0 volts.
- Sign Convention: The sign of the standard electrode potential indicates the tendency of a half-cell to undergo reduction. A positive standard electrode potential implies that the species in the half-cell has a higher tendency to be reduced, while a negative value indicates a higher tendency for oxidation.
- Comparison of Standard Electrode Potentials: By comparing the standard electrode potentials of different half-cells, it is possible to predict the direction of electron flow in a cell and determine the spontaneity of a redox reaction.
- Cell Potential Calculation: The cell potential (Ecell) of a galvanic cell can be calculated by taking the difference between the standard electrode potentials of the two half-cells involved. Ecell = E°(cathode) – E°(anode).
- Nernst Equation: The Nernst equation allows for the calculation of electrode potentials under non-standard conditions. It takes into account the concentrations of species involved and the temperature of the system.
While the standard electrode potential is not explicitly mentioned in the AIIMS chemistry syllabus, it forms an essential part of understanding the principles of electrochemistry, which is relevant for medical and biological sciences.
What is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Standard electrode potential
The concept of standard electrode potential is an important topic in the field of electrochemistry. It refers to the potential difference between a half-cell electrode and a standard reference electrode under standard conditions. The standard electrode potential is denoted by E° and is expressed in volts.
While the AIIMS syllabus may not explicitly mention the standard electrode potential, understanding this concept is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of electrochemistry, which has applications in various fields including medicine and biology.
To calculate the standard electrode potential of a half-cell, it is typically compared to a standard reference electrode, most commonly the Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE). The standard electrode potential of the SHE is defined as 0 volts, serving as the reference point for other half-cell potentials.
The sign of the standard electrode potential indicates the tendency of a half-cell to undergo reduction. A positive value suggests a greater tendency for reduction, while a negative value indicates a greater tendency for oxidation.
The standard electrode potential can be used to predict the direction of electron flow in a cell and determine the spontaneity of redox reactions. By comparing the standard electrode potentials of different half-cells, it is possible to assess the relative strengths of different redox reactions.
It is important to note that the actual AIIMS syllabus may not specifically require you to memorize or calculate standard electrode potentials. However, understanding the principles and significance of standard electrode potential can provide you with a deeper understanding of electrochemical processes, which may be useful in the context of medical and biological sciences.
When is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Standard electrode potential
The concept of standard electrode potential is applicable in the field of electrochemistry and is not limited to a specific time or period. It is a fundamental concept that is used to describe the thermodynamic tendencies of redox reactions and the relative strengths of different half-cell reactions.
The standard electrode potential (E°) is a measure of the potential difference between a half-cell electrode and a standard reference electrode under standard conditions. It is a characteristic property of a specific redox couple and can be determined experimentally.
The standard electrode potential values for various redox couples are typically compiled in reference tables, such as the Standard Reduction Potentials table. These values are constant under standard conditions (25°C, 1 atm pressure, 1 M concentration), and they provide a basis for comparing the relative strengths of different redox reactions.
It’s important to note that the standard electrode potential values are determined experimentally and can be influenced by factors such as temperature and concentration. Under non-standard conditions, the Nernst equation is used to calculate the electrode potential.
So, to summarize, the concept of standard electrode potential is a fundamental principle of electrochemistry and is applicable at all times, providing a measure of the relative strengths of redox reactions.
Case Study on AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Standard electrode potential
Electroplating Process
Electroplating is a widely used industrial process that involves depositing a layer of metal onto a substrate using an electrochemical cell. Let’s consider the case of silver electroplating, where a silver layer is deposited onto a surface.
The electroplating cell consists of two electrodes: an anode and a cathode. The anode is typically made of silver, while the cathode is the object to be plated. The electrolyte used is a solution of silver nitrate (AgNO3).
- Half-Reactions: The oxidation half-reaction occurs at the anode: Ag(s) → Ag⁺(aq) + e⁻
The reduction half-reaction occurs at the cathode: Ag⁺(aq) + e⁻ → Ag(s)
- Standard Electrode Potential: To determine the feasibility of the electroplating process, we can look at the standard electrode potentials of the half-reactions involved. The standard electrode potential of the Ag⁺/Ag half-cell is +0.80 volts. This means that silver ions have a higher tendency to be reduced to form solid silver (Ag) compared to the reduction of other ions with lower standard electrode potentials.
- Cell Potential Calculation: The cell potential (Ecell) can be calculated using the difference between the standard electrode potentials of the half-reactions. In this case, Ecell = E°(cathode) – E°(anode). Since the standard electrode potential of the Ag⁺/Ag half-cell is +0.80 volts and the anode reaction is the oxidation of silver (Ag) with a potential of 0 volts, the overall cell potential for the electroplating process is +0.80 volts.
- Electroplating Process: When an external power source is connected to the electroplating cell, the anode becomes the positive electrode and the cathode becomes the negative electrode. Silver ions (Ag⁺) are attracted to the negatively charged cathode and are reduced to solid silver (Ag), forming a layer of silver on the object to be plated.
By controlling factors such as the current, time, and concentration of the electrolyte, the thickness and quality of the electroplated layer can be controlled.
This case study illustrates the application of the standard electrode potential in understanding and designing electrochemical processes like electroplating. It demonstrates how the standard electrode potential plays a crucial role in determining the feasibility and direction of redox reactions in electrochemical cells.
White paper on AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Standard electrode potential
Title: Understanding Standard Electrode Potential in the AIIMS Chemistry Syllabus
Abstract:
This white paper aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the concept of standard electrode potential within the AIIMS (All India Institute of Medical Sciences) Chemistry syllabus. Standard electrode potential is a fundamental concept in electrochemistry and plays a crucial role in understanding redox reactions, cell potentials, and electrochemical processes. This paper explores the significance of standard electrode potential in the context of the AIIMS Chemistry syllabus and its applications in medical and biological sciences.
Introduction
1.1 Overview of AIIMS Chemistry Syllabus
1.2 Importance of Standard Electrode Potential in Electrochemistry
Definition and Significance of Standard Electrode Potential
2.1 Standard Electrode Potential and Redox Reactions
2.2 Role of Standard Electrode Potential in Determining Spontaneity
2.3 Applications in Electrochemical Cells and Batteries
Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE) as a Reference
3.1 Role of SHE in Determining Standard Electrode Potentials
3.2 Measurement and Construction of SHE
Calculation and Interpretation of Standard Electrode Potentials
4.1 Comparison of Standard Electrode Potentials
4.2 Cell Potentials and Nernst Equation
Electrochemical Processes and Medical Applications
5.1 Electroplating and Biomaterials
5.2 Electrophysiology and Biochemical Analysis
5.3 Importance in Pharmaceutical and Medicinal Chemistry
Experimental Techniques and Measurements
6.1 Determining Standard Electrode Potentials Experimentally
6.2 Factors Affecting Standard Electrode Potentials
AIIMS Chemistry Syllabus Relevance
7.1 Electrochemistry and Redox Reactions
7.2 Applications in Biochemical Processes and Medical Sciences
7.3 Clinical Significance and Diagnostic Tools
Conclusion
8.1 Summary of Standard Electrode Potential Concepts
8.2 Importance of Standard Electrode Potential in AIIMS Syllabus
8.3 Implications for Medical and Biological Sciences
References:
[Provide a comprehensive list of references used in the white paper]
This white paper provides an in-depth analysis of the concept of standard electrode potential within the AIIMS Chemistry syllabus. It explores its significance, applications, and relevance in medical and biological sciences. The understanding of standard electrode potential enhances knowledge in electrochemistry, enabling students to comprehend various electrochemical processes and their implications in medical practice and research.
