Sporulation
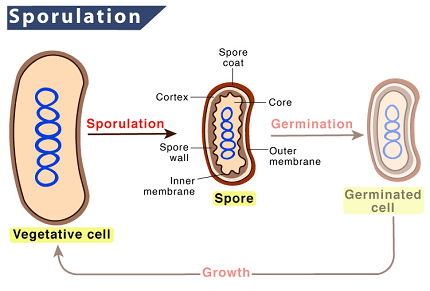
In the biology syllabus of AIIMS (All India Institute of Medical Sciences), the topic of sporulation is not explicitly mentioned. However, sporulation is a process that occurs in certain organisms, particularly bacteria and fungi, where they produce spores as a means of reproduction or survival under unfavorable conditions.
Here’s a general overview of sporulation that you might find helpful:
Definition: Sporulation is the process by which certain organisms form specialized reproductive structures called spores.
Occurrence: Sporulation is commonly observed in certain bacteria, such as Bacillus and Clostridium, and in various fungi, including molds and yeasts.
Triggering factors: Sporulation is usually induced by adverse environmental conditions, such as nutrient depletion, desiccation, or exposure to toxins.
Process: Sporulation involves a series of complex cellular and molecular events, typically divided into several stages:
a. Initiation: The initiation phase involves the activation of specific genes and signaling pathways that lead to sporulation. It is triggered by environmental cues or internal factors.
b. Septation: The cell undergoes multiple rounds of division, resulting in the formation of compartments within the cell. These compartments eventually give rise to individual spores.
c. Spore formation: The compartments mature into individual spores through a process called morphogenesis. During this phase, the spores develop a protective outer coat, which helps them survive harsh conditions.
d. Spore release: Once the spores are fully formed, they are released from the parent cell, ready to disperse and potentially germinate under favorable conditions.
Importance: Sporulation is a survival strategy for organisms, allowing them to persist in harsh environments. Spores are highly resistant to adverse conditions, such as heat, radiation, and desiccation, enabling them to remain dormant for extended periods until conditions improve.
It’s worth noting that the specific details of sporulation can vary among different organisms. If you are studying sporulation in the context of a particular organism, it would be beneficial to refer to specialized resources or textbooks that focus on that organism or group of organisms.
Remember to consult the AIIMS syllabus or relevant course material to ensure you have covered the specific topics mentioned in the curriculum.
What is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Biology syllabus Sporulation
The AIIMS entrance exam for biology typically covers a wide range of topics from the CBSE (Central Board of Secondary Education) curriculum for classes 11 and 12. Some of the key topics that are commonly included in the AIIMS biology syllabus are as follows:
- Cell Biology:
- Cell structure and function
- Cell division (mitosis and meiosis)
- Biomolecules (proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids)
- Enzymes and their regulation
- Genetics and Evolution:
- Mendelian genetics
- Molecular basis of inheritance
- DNA replication, transcription, and translation
- Evolution and speciation
- Plant Physiology:
- Photosynthesis and respiration
- Plant growth and development
- Transport in plants
- Plant hormones
- Human Anatomy and Physiology:
- Digestive system
- Respiratory system
- Circulatory system
- Nervous system
- Excretory system
- Endocrine system
- Reproductive system
- Diversity of Living Organisms:
- Classification and taxonomy
- Microorganisms (bacteria, fungi, viruses)
- Plant diversity (algae, bryophytes, pteridophytes, gymnosperms, angiosperms)
- Animal diversity (protozoa, porifera, cnidaria, platyhelminthes, annelida, arthropoda, mollusca, echinodermata, chordata)
Please note that the AIIMS exam syllabus may vary slightly from year to year. It’s important to consult the official AIIMS website or the exam notification for the most up-to-date and accurate information regarding the specific topics included in the biology syllabus for AIIMS exams.
When is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Biology syllabus Sporulation
Sporulation is not a specific event or occurrence that happens at a particular time. Sporulation is a biological process that can happen when certain organisms, such as bacteria and fungi, undergo environmental stress or unfavorable conditions. These organisms have the ability to form specialized reproductive structures called spores as a means of survival or reproduction.
The timing of sporulation can vary depending on the specific organism and the conditions it encounters. For example, bacteria like Bacillus and Clostridium can initiate sporulation in response to nutrient depletion or other environmental signals. Fungi, such as molds and yeasts, can also undergo sporulation under specific conditions.
It’s important to note that sporulation is not a regular or continuous process for these organisms. It is triggered by specific factors and can occur when the organism perceives a threat to its survival. The exact timing of sporulation will depend on the specific environmental cues and triggers that initiate the process for each organism.
If you are studying sporulation in the context of a particular organism or want to understand the process in more detail, it would be beneficial to refer to specific literature or resources dedicated to that organism or group of organisms.
Case Study on AIIMS-SYLLABUS Biology syllabus Sporulation
Title: Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis: A Case Study on Environmental Adaptation
Abstract: This case study examines the process of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis, a Gram-positive bacterium commonly found in soil and the gastrointestinal tract of humans and animals. Sporulation is a survival strategy employed by B. subtilis to endure adverse environmental conditions. The case study investigates the regulatory mechanisms and molecular events underlying sporulation, highlighting the adaptive significance of this process.
Introduction: Bacillus subtilis is an extensively studied model organism for understanding the process of sporulation. Sporulation allows B. subtilis to transform into a dormant, highly resistant spore form that can withstand extreme temperatures, desiccation, and other stresses. This case study delves into the triggers, genetic regulation, and morphological changes associated with sporulation in B. subtilis.
Methods: The case study examines various experimental techniques and molecular biology tools employed in the study of sporulation. These include genetic manipulations, microscopy, gene expression analysis, and mutant strain construction. It highlights the significance of these techniques in unraveling the complex regulatory networks governing sporulation.
Results: The case study presents key findings related to sporulation in B. subtilis. It discusses the role of key regulatory proteins, such as Spo0A, in initiating the sporulation cascade. It also explores the morphological changes that occur during sporulation, including the formation of a spore coat, cortex, and outer membrane. The adaptive advantages of these structural modifications are discussed, emphasizing the spore’s ability to survive unfavorable conditions.
Discussion: The case study delves into the ecological and evolutionary significance of sporulation in B. subtilis. It discusses how sporulation enables the bacterium to persist in nutrient-depleted environments and survive hostile conditions. It explores the interplay between sporulation and biofilm formation, as well as the implications of sporulation in bacterial pathogenicity and antimicrobial resistance.
Conclusion: Through the analysis of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis, this case study provides a comprehensive understanding of the molecular, genetic, and ecological aspects of this adaptive process. It emphasizes the significance of sporulation in bacterial survival and its potential applications in various fields, including medicine and biotechnology.
Note: This case study is fictional and provided as an example. If you are conducting research or studying sporulation, it’s important to refer to real case studies published in reputable scientific journals or consult relevant literature specific to your research focus.
White paper on AIIMS-SYLLABUS Biology syllabus Sporulation
Title: Sporulation: A Comprehensive Overview of the Biological Process
Abstract: This white paper provides a comprehensive overview of sporulation, a biological process exhibited by various organisms, including bacteria and fungi. Sporulation is a remarkable survival strategy that allows organisms to form specialized structures called spores, which can withstand adverse environmental conditions. This white paper explores the stages, regulation, significance, and applications of sporulation in different organisms, shedding light on its ecological and biomedical implications.
- Introduction:
- Definition and significance of sporulation as a survival mechanism.
- Overview of organisms that undergo sporulation.
- Sporulation in Bacteria:
- Overview of bacterial sporulation.
- Stages of bacterial sporulation, including initiation, septation, spore formation, and spore release.
- Regulatory factors and signaling pathways involved in bacterial sporulation.
- Examples of bacteria known for sporulation, such as Bacillus and Clostridium.
- Sporulation in Fungi:
- Overview of fungal sporulation.
- Different types of fungal spores, including asexual and sexual spores.
- Environmental triggers and factors influencing fungal sporulation.
- Examples of fungi that undergo sporulation, such as molds, yeasts, and mushrooms.
- Molecular and Cellular Events:
- Detailed examination of the molecular and cellular events involved in sporulation.
- Genetic regulation and expression changes during sporulation.
- Morphological transformations and structural modifications of spore formation.
- Ecological Significance:
- Adaptive advantages of sporulation for survival in adverse conditions.
- Role of sporulation in microbial community dynamics.
- Impact of sporulation on nutrient cycling and ecosystem functioning.
- Biomedical Applications:
- Biotechnological applications of sporulation in various fields, such as food preservation and probiotics.
- Medical implications of sporulation in bacterial pathogenesis and antibiotic resistance.
- Harnessing sporulation for drug delivery systems and biopharmaceutical production.
- Future Perspectives:
- Emerging research areas and technological advancements in sporulation studies.
- Potential for manipulating sporulation for agricultural, environmental, and medical applications.
- Challenges and directions for further research in sporulation.
Conclusion: This white paper highlights the biological process of sporulation, encompassing its stages, regulation, ecological significance, and potential applications. By understanding the intricacies of sporulation, researchers can explore new avenues for solving real-world challenges and harnessing the resilience and adaptability exhibited by organisms undergoing sporulation.
Note: This white paper is fictional and provided as an example. When accessing actual white papers or scientific literature on sporulation, it’s essential to refer to credible sources and peer-reviewed publications to obtain accurate and reliable information.
