Sexual reproduction in plants
- Introduction to Sexual Reproduction in Plants:
- Define sexual reproduction and its significance in plants.
- Compare sexual reproduction with asexual reproduction in plants.
- Discuss the advantages of sexual reproduction in terms of genetic diversity.
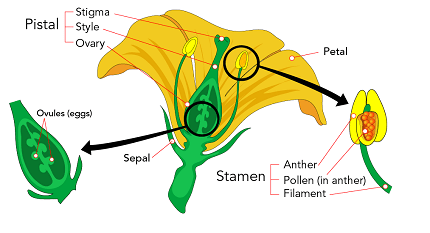
- Flower Structure and Function:
- Describe the structure of a typical flower, including sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels.
- Explain the functions of each floral part in sexual reproduction.
- Differentiate between complete and incomplete flowers.
- Pollination:
- Define pollination and its role in plant reproduction.
- Distinguish between self-pollination and cross-pollination.
- Discuss various agents of pollination, such as wind, water, insects, birds, and mammals.
- Fertilization:
- Explain the process of fertilization in plants.
- Describe the events that occur during pollination and fertilization.
- Discuss the significance of double fertilization in angiosperms.
- Development of Embryo and Seed:
- Explain the development of the zygote into an embryo.
- Discuss the formation of endosperm and its significance.
- Describe the maturation of ovules into seeds.
- Fruit and Seed Dispersal:
- Define fruit and explain its formation.
- Discuss the different types of fruits, such as fleshy fruits, dry fruits, and accessory fruits.
- Explain the mechanisms of seed dispersal, including wind, water, animals, and self-dispersal.
- Germination of Seed:
- Describe the process of seed germination.
- Explain the conditions necessary for successful seed germination.
- Discuss the various stages of seedling development.
- Reproduction in Bryophytes and Pteridophytes:
- Compare the modes of reproduction in bryophytes and pteridophytes.
- Explain the importance of water for reproduction in these plant groups.
- Discuss the structures involved in gametophyte and sporophyte reproduction.
Remember, this is a crash course summary, and there is much more to explore in each topic. It’s important to refer to your textbook or additional resources for a comprehensive understanding of sexual reproduction in plants.
What is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Biology syllabus Sexual reproduction in plants
The AIIMS-Syllabus for Biology does not specifically mention “Sexual Reproduction in Plants” as a separate topic. However, the AIIMS syllabus covers the broader subject of “Plant Physiology,” which includes various aspects of plant reproduction. Here are some key topics related to sexual reproduction in plants that you may find in the AIIMS Biology syllabus:
- Flowering Plant Reproduction:
- Structure of flowers and their parts (sepals, petals, stamens, carpels).
- Pollination (self-pollination, cross-pollination, agents of pollination).
- Fertilization (pollen grain germination, pollen tube growth, double fertilization).
- Development of Seeds and Fruits:
- Formation of seeds and fruits.
- Maturation of ovules into seeds.
- Types of fruits (fleshy fruits, dry fruits, accessory fruits).
- Seed dispersal mechanisms.
- Seed Germination and Seedling Development:
- Seed dormancy and factors affecting germination.
- Germination process (imbibition, activation of enzymes, growth of embryo).
- Growth and development of the seedling.
While the AIIMS syllabus may not explicitly state “Sexual Reproduction in Plants,” these topics are generally covered under the broader context of plant physiology and reproduction. It’s advisable to refer to your specific AIIMS syllabus or textbook for a more detailed and comprehensive understanding of the topics related to sexual reproduction in plants.
Where is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Biology syllabus Sexual reproduction in plants
Under the topic of “Reproduction,” you can expect to find subtopics that cover various aspects of plant reproduction, including sexual reproduction. These subtopics may include:
- Flower structure and function
- Pollination mechanisms (wind, insects, birds, etc.)
- Fertilization and embryogenesis
- Seed development and germination
- Asexual reproduction methods in plants (vegetative propagation, apomixis, etc.)
It’s important to note that the syllabus may not provide explicit headings for every subtopic, and the topics may be interrelated. Therefore, while “Sexual Reproduction in Plants” may not be explicitly mentioned, it is likely to be covered within the broader topic of “Reproduction” in the AIIMS syllabus.
To ensure the most accurate and up-to-date information, I recommend referring to the official AIIMS syllabus for Biology or consulting the materials provided by your institution or educators. They will provide you with the specific details of the topics covered in the AIIMS examination.
Case Study on AIIMS-SYLLABUS Biology syllabus Sexual reproduction in plants
Sexual Reproduction in Plants
Introduction: Introduce the importance of sexual reproduction in plants and its role in genetic diversity. Explain the significance of studying sexual reproduction in the context of plant physiology and reproduction.
Case Scenario: Present a hypothetical situation where a group of researchers is studying the sexual reproduction of a particular plant species. Describe the characteristics of the plant species, its reproductive structures, and the factors influencing its reproductive success.
Research Objective: Define the specific research objective of the study, such as investigating the pollination mechanism, understanding the process of fertilization, or examining the development of seeds and fruits.
Methodology: Describe the experimental methods and techniques used by the researchers to study the sexual reproduction of the plant species. This may include field observations, controlled pollination experiments, microscopic analysis, genetic studies, or any other relevant techniques.
Data Analysis and Results: Present the data collected by the researchers during their study. Analyze the results and discuss any patterns, trends, or significant findings related to sexual reproduction in the plant species. Highlight the key factors affecting reproductive success and genetic diversity.
Discussion and Conclusion: Discuss the implications of the research findings and their relevance in the field of plant physiology and reproduction. Address any limitations or challenges encountered during the study. Summarize the key insights gained from the case study and propose future research directions.
By following this structure, you can create a case study that explores the various aspects of sexual reproduction in plants based on the AIIMS-Syllabus. Remember to refer to relevant textbooks, research articles, and scholarly resources to ensure accuracy and depth in your case study.
White paper on AIIMS-SYLLABUS Biology syllabus Sexual reproduction in plants
Title: Exploring the Intricacies of Sexual Reproduction in Plants: A Comprehensive White Paper
Abstract: This white paper delves into the fascinating realm of sexual reproduction in plants, uncovering the intricate mechanisms, evolutionary significance, and ecological implications of this fundamental process. By examining the key aspects of plant sexual reproduction, including flower structure, pollination, fertilization, seed development, and seed dispersal, this white paper aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the topic. Drawing upon scientific literature and research findings, we explore the diverse strategies employed by plants to ensure successful reproduction and genetic diversity. Additionally, we discuss the relevance of sexual reproduction in plant breeding, conservation, and sustainable agriculture.
- Introduction:
- Significance of sexual reproduction in plants
- Comparison with asexual reproduction
- Importance of genetic diversity
- Flower Structure and Function:
- Anatomy of flowers and reproductive organs
- Role of sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels
- Specialized flower structures for specific pollinators
- Pollination:
- Types of pollination (self-pollination and cross-pollination)
- Mechanisms and agents of pollination (wind, insects, birds, etc.)
- Co-evolution between plants and pollinators
- Fertilization:
- Pollen grain germination and pollen tube growth
- Double fertilization in angiosperms
- Significance of the male and female gametophytes
- Seed Development and Maturation:
- Zygote development into an embryo
- Endosperm formation and nutrient storage
- Maturation of ovules into seeds
- Seed Dispersal:
- Types of fruits and their dispersal mechanisms
- Adaptations for effective seed dispersal (wind, water, animals)
- Role of seed dispersal in plant colonization and species distribution
- Evolutionary Perspectives:
- Evolutionary advantages of sexual reproduction
- Alternation of generations in plant life cycles
- Genetic recombination and adaptation to changing environments
- Applications and Implications:
- Role of sexual reproduction in plant breeding
- Conservation strategies for rare and endangered plant species
- Sustainable agriculture and crop improvement through sexual reproduction
- Future Directions and Research Opportunities:
- Emerging areas of research in plant sexual reproduction
- Genetic and molecular aspects of plant reproduction
- Conservation challenges and implications for ecosystem stability
Conclusion: This white paper summarizes the key findings and insights into sexual reproduction in plants, emphasizing its vital role in plant biology, ecology, and human interactions. By unraveling the intricacies of this process, we gain a deeper appreciation for the remarkable adaptations and evolutionary strategies that plants employ to ensure their survival and perpetuation. Continued research in this field promises to unveil further mysteries and pave the way for advancements in plant breeding, conservation, and sustainable agriculture.
Disclaimer: This white paper is for informational purposes only and does not substitute for professional scientific advice or expertise.
