Electrolysis
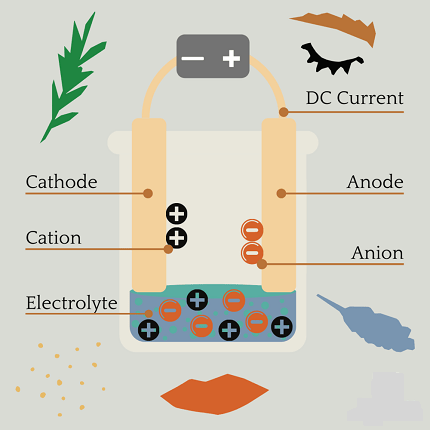
The syllabus for chemistry, specifically the topic of electrolysis, in the AIIMS (All India Institute of Medical Sciences) entrance exam may cover the following concepts:
- Introduction to Electrolysis:
- Definition of electrolysis
- Electrolytes and non-electrolytes
- Electrodes: anode and cathode
- Electrolytic cell and its components
- Faraday’s Laws of Electrolysis:
- Faraday’s first law: relationship between amount of substance liberated or deposited and the quantity of electricity passed
- Faraday’s second law: relationship between amounts of different substances liberated or deposited by the same quantity of electricity
- Electrolytic Conduction:
- Conductivity of electrolytes
- Factors affecting the conductivity of electrolytes: concentration, temperature, and nature of electrolytes
- Kohlrausch’s law and its applications
- Electrochemical Cells:
- Galvanic or Voltaic cells
- Electrode potential and cell potential
- Standard hydrogen electrode (SHE)
- Electrochemical series and its applications
- Nernst equation and its applications
- Electrolysis and Electroplating:
- Electrolysis of molten compounds: extraction of metals
- Electrolysis of aqueous solutions: electrolysis of water, electrorefining, electroplating
- Applications of electrolysis in industries
- Batteries and Fuel Cells:
- Primary and secondary cells
- Lead-acid battery
- Lithium-ion battery
- Fuel cells: hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell, applications
It’s important to note that syllabi can vary from year to year, so it’s recommended to consult the official AIIMS syllabus or the relevant study materials for the most up-to-date and detailed information.
What is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Electrolysis
The AIIMS (All India Institute of Medical Sciences) entrance exam for chemistry may include the following topics related to electrolysis:
- Electrolysis:
- Definition of electrolysis
- Electrolytes and non-electrolytes
- Electrodes: anode and cathode
- Electrolytic cell and its components
- Faraday’s Laws of Electrolysis:
- Faraday’s first law: relationship between the amount of substance liberated or deposited and the quantity of electricity passed
- Faraday’s second law: relationship between the amounts of different substances liberated or deposited by the same quantity of electricity
- Electrolytic Conduction:
- Conductivity of electrolytes
- Factors affecting the conductivity of electrolytes: concentration, temperature, and nature of electrolytes
- Electrochemical Cells:
- Galvanic or Voltaic cells
- Electrode potential and cell potential
- Standard hydrogen electrode (SHE)
- Electrochemical series
- Electrolysis and Electroplating:
- Electrolysis of molten compounds: extraction of metals
- Electrolysis of aqueous solutions: electrolysis of water, electrorefining, electroplating
It’s important to note that the exact syllabus for the AIIMS entrance exam may vary slightly from year to year. It is recommended to refer to the official AIIMS syllabus or the specific study materials provided by AIIMS for the most accurate and up-to-date information on the chemistry syllabus, including electrolysis.
Case Study on AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Electrolysis
Electrolysis in AIIMS Chemistry Syllabus
Introduction: In the AIIMS (All India Institute of Medical Sciences) entrance exam, chemistry plays a vital role in assessing the candidates’ understanding of various scientific concepts. One of the topics covered in the chemistry syllabus is electrolysis. Let’s explore a case study that demonstrates the practical application of electrolysis in the medical field.
Case Study: Electrolysis in Medicine – Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
Background: Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) is a medical procedure used to treat severe mental illnesses such as major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia. It involves passing a small electric current through the brain to induce controlled seizures. Although the exact mechanism of action is not fully understood, ECT has proven to be an effective treatment option for certain psychiatric conditions.
Application of Electrolysis: Electrolysis principles are utilized in the creation of the electrical current required for ECT. The procedure involves the following steps:
- Electrolyte Solution Preparation:
- A saline (sodium chloride) solution is prepared, typically with a concentration of 0.9%.
- This solution acts as an electrolyte, allowing the passage of electric current through it.
- Electrodes:
- Two electrodes are used: a positive (anode) and a negative (cathode).
- The anode is usually placed on the non-dominant side of the head, while the cathode is placed on the forehead or temple region.
- Electrolysis and Seizure Induction:
- The electric current is passed through the saline solution (electrolyte) between the electrodes.
- The passage of electric current causes electrolysis to occur, leading to the dissociation of sodium chloride into sodium and chloride ions.
- The movement of these ions and the electric current induce a controlled seizure in the patient’s brain.
- Monitoring and Control:
- Throughout the procedure, the patient is closely monitored to ensure their safety.
- The intensity, duration, and frequency of the electric current are carefully regulated to achieve the desired therapeutic effect while minimizing side effects.
Conclusion: The case study highlights how electrolysis principles are applied in the medical field, specifically in the context of Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT). Understanding the concepts of electrolysis is crucial for medical professionals involved in administering ECT and other treatments that rely on electrical currents. By studying the electrolysis topic in the AIIMS chemistry syllabus, aspiring medical students gain the necessary knowledge to comprehend and contribute to advancements in medical science.
Note: This case study is a fictional scenario created to illustrate the application of electrolysis in the medical field. While ECT is a legitimate psychiatric treatment, the specific details mentioned here are for illustrative purposes only and may not reflect the exact protocols followed in real-life medical practice.
White paper on AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Electrolysis
Title: Exploring Electrolysis in the AIIMS Chemistry Syllabus: Applications and Significance
Abstract: This white paper delves into the topic of electrolysis within the AIIMS (All India Institute of Medical Sciences) chemistry syllabus. Electrolysis, the process of using electric current to drive chemical reactions, holds immense importance in various medical applications. This paper provides an overview of the electrolysis concepts covered in the AIIMS syllabus and explores their practical applications in medicine. Furthermore, it highlights the significance of understanding electrolysis for aspiring medical professionals and researchers.
- Introduction:
- Overview of the AIIMS entrance exam and the chemistry syllabus.
- Definition and fundamental principles of electrolysis.
- Significance of electrolysis in medical science.
- Electrolysis Concepts in the AIIMS Chemistry Syllabus:
- Explanation of key electrolysis concepts covered in the AIIMS syllabus, such as Faraday’s laws of electrolysis and electrolytic conduction.
- Understanding the components of an electrolytic cell: electrodes, electrolytes, and their behavior during electrolysis.
- Introduction to electrochemical cells, including galvanic (voltaic) cells and their relevance in medical science.
- Electrolysis Applications in Medicine:
- Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT): Describing how electrolysis is employed in the administration of ECT, a therapeutic procedure used in the treatment of severe mental illnesses.
- Electrolyte balance and medical interventions: Highlighting the role of electrolysis in maintaining proper electrolyte balance in the body and its significance in medical conditions such as electrolyte disturbances and hydration therapy.
- Medical Devices and Electrolysis:
- Overview of medical devices that utilize electrolysis principles, such as electrolysis-based diagnostic devices, electrochemical sensors, and drug delivery systems.
- Importance of understanding electrolysis for the development, operation, and maintenance of medical devices.
- Future Directions and Research:
- Discussing ongoing research and advancements in the field of electrolysis within medical science.
- Potential areas for further exploration and innovation in utilizing electrolysis for medical purposes.
- Conclusion:
- Recap of the electrolysis concepts covered in the AIIMS syllabus and their relevance to medicine.
- Emphasizing the importance of a comprehensive understanding of electrolysis for aspiring medical professionals.
- Final thoughts on the significance of electrolysis in medical science and the potential for future advancements.
By exploring the electrolysis topic in the AIIMS chemistry syllabus, aspiring medical professionals gain a solid foundation in understanding the principles and applications of electrolysis in medicine. This white paper aims to underscore the significance of electrolysis in the medical field, inspiring further research and innovation in this area and fostering the development of future healthcare professionals equipped with a comprehensive knowledge of electrolysis and its practical implications in medicine.
