Electrolytic solutions
The syllabus for AIIMS (All India Institute of Medical Sciences) chemistry does not specifically mention electrolytic solutions. However, electrolytic solutions are a part of the broader topic of solutions and electrochemistry, which is an important area of study in chemistry. Here’s an overview of the electrolytic solutions topic that you may find useful:
- Electrolytes: Understand the concept of electrolytes and non-electrolytes. Electrolytes are substances that, when dissolved in water or melted, produce ions that can conduct electricity. Non-electrolytes do not produce ions and do not conduct electricity.
- Ionic compounds: Study the properties of ionic compounds. Ionic compounds dissociate into ions when dissolved in water, making them good electrolytes. Learn about common examples of ionic compounds and their dissociation behavior.
- Electrolysis: Explore the process of electrolysis, which involves the decomposition of a compound by passing an electric current through an electrolyte. Learn about the setup of an electrolytic cell, the role of electrodes (anode and cathode), and the movement of ions during electrolysis.
- Faraday’s Laws of Electrolysis: Familiarize yourself with Faraday’s laws, which describe the quantitative relationships between the amount of substance transformed during electrolysis and the quantity of electricity passed through the electrolyte. Understand how these laws are applied to calculate the amount of substance deposited or liberated during electrolysis.
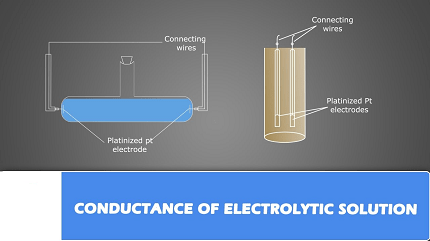
- Conductivity of electrolytic solutions: Study the factors that affect the conductivity of electrolytic solutions, such as concentration, temperature, and nature of electrolyte. Learn about the terms like specific conductance, molar conductance, and their calculations.
- Kohlrausch’s Law: Understand Kohlrausch’s law, which relates the molar conductivity of an electrolyte at infinite dilution to its limiting molar conductivity. Learn how to calculate the degree of dissociation of weak electrolytes using this law.
- Applications of electrolysis: Explore various applications of electrolysis, such as electroplating, electrorefining, and electrolytic cells used in industries. Understand the principles behind these processes and their significance.
Remember to refer to your specific AIIMS syllabus for chemistry to ensure that you cover all the topics specified. Additionally, consult your textbooks, lecture notes, and other relevant study materials to gain a comprehensive understanding of electrolytic solutions and related concepts.
What is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Electrolytic solutions
- Solutions and concentration units: Understand the concept of solutions, solvents, and solutes. Study different concentration units such as molarity, molality, normality, and percentage composition.
- Conductivity of solutions: Learn about the conductivity of solutions and the factors that affect it, including the presence of electrolytes and the concentration of ions. Understand the terms like specific conductance, molar conductance, and equivalent conductance.
- Electrolytes and non-electrolytes: Differentiate between electrolytes and non-electrolytes. Understand the behavior of ionic compounds and their dissociation in water to form ions.
- Faraday’s Laws of Electrolysis: Familiarize yourself with Faraday’s laws, which describe the relationship between the amount of substance deposited or liberated during electrolysis and the quantity of electricity passed through the electrolyte.
- Redox reactions: Study redox reactions and their significance in electrolytic solutions. Learn about the oxidation and reduction half-reactions, balancing redox equations, and the role of electrons in redox processes.
- Electrochemical cells: Understand the basic principles of electrochemical cells, including galvanic cells and electrolytic cells. Learn about the construction, working, and applications of these cells.
- Electroplating: Study the process of electroplating, which involves depositing a layer of metal on the surface of an object using electrolysis. Understand the principles behind electroplating and its applications.
It is important to note that the syllabus may vary slightly from year to year, so it’s recommended to refer to the official AIIMS website or the information provided by the conducting body for the most up-to-date and specific syllabus for chemistry. Additionally, consulting textbooks and reference materials recommended for medical entrance exams can further enhance your preparation for electrolytic solutions and related topics.
When is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Electrolytic solutions
As of my knowledge cutoff in September 2021, AIIMS (All India Institute of Medical Sciences) does not release a specific syllabus for chemistry, including electrolytic solutions. AIIMS and other medical entrance exams typically follow a broader syllabus based on the core concepts of chemistry, physics, biology, and general knowledge.
The chemistry syllabus for AIIMS generally covers topics from the NCERT (National Council of Educational Research and Training) textbooks of Class 11 and Class 12. It includes subjects such as organic chemistry, inorganic chemistry, physical chemistry, and some topics of biochemistry.
While electrolytic solutions may not be specifically mentioned in the AIIMS syllabus, the broader topic of electrochemistry and solutions is relevant. It is advisable to thoroughly study the concepts related to solutions, concentration units, electrolytes, conductance of solutions, redox reactions, and basic principles of electrochemical cells.
To ensure you are adequately prepared, it is recommended to consult the official AIIMS website or the information provided by the conducting body for the most up-to-date and specific syllabus for chemistry. Additionally, referring to the recommended textbooks and study materials for AIIMS preparation can help you cover all the essential topics in chemistry.
Case Study on AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Electrolytic solutions
Electrolyte Imbalance and Treatment
Patient Profile: A 60-year-old male presents to the emergency department with symptoms of weakness, fatigue, and muscle cramps. The patient has a history of chronic kidney disease and is on hemodialysis.
Background: Electrolytes play a crucial role in maintaining various physiological functions within the body. Imbalances in electrolyte levels can lead to significant health issues. In this case, the patient’s symptoms are indicative of an electrolyte imbalance.
Diagnosis and Treatment: Upon further investigation, it is determined that the patient has a low potassium (hypokalemia) and low calcium (hypocalcemia) level. These electrolyte imbalances could be a result of the patient’s chronic kidney disease and impaired renal function.
To address the electrolyte imbalances, the following treatment plan is implemented:
- Potassium Supplementation: The patient’s low potassium level is corrected through oral or intravenous potassium supplementation. The appropriate dosage is determined based on the severity of the imbalance and the patient’s renal function. Regular monitoring of potassium levels is essential to ensure it remains within the optimal range.
- Calcium Administration: To address the hypocalcemia, intravenous calcium gluconate or calcium chloride may be administered, depending on the severity of the imbalance. The patient’s response to calcium administration is closely monitored, and additional treatments may be required if necessary.
- Monitoring and Follow-up: The patient’s electrolyte levels are monitored regularly to ensure they remain within the appropriate range. Adjustments to the treatment plan are made as needed based on the patient’s response and ongoing lab results.
Importance of Electrolytic Solutions: Understanding electrolytic solutions is vital in managing patients with electrolyte imbalances, particularly in cases of chronic kidney disease and renal dysfunction. Knowledge of electrolyte concentrations, ion movements, and the principles of electrolysis assists healthcare professionals in diagnosing and treating electrolyte imbalances effectively.
Conclusion: The case study highlights the significance of electrolytic solutions in the context of patient care. The understanding of electrolyte imbalances and their appropriate treatment is essential for medical professionals, including those preparing for exams like AIIMS, as they encounter patients with diverse medical conditions.
White paper on AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Electrolytic solutions
Title: Electrolytic Solutions: Understanding Principles and Applications
Abstract: This white paper provides an in-depth analysis of electrolytic solutions, exploring their fundamental principles, properties, and applications. Electrolytic solutions play a crucial role in various scientific and industrial fields, including chemistry, electrochemistry, materials science, and biochemistry. Understanding the behavior of electrolytic solutions and their applications is essential for advancing our knowledge in these domains and developing innovative technologies. This white paper covers key concepts, experimental techniques, and real-world examples related to electrolytic solutions, aiming to provide a comprehensive overview of this fascinating area of study.
- Introduction
- Definition of electrolytic solutions
- Importance of electrolytes and their role in conducting electricity
- Ionic Dissociation in Electrolytic Solutions
- Ionic compounds and their behavior in water
- Ionization and dissociation processes
- Strong and weak electrolytes
- Conductivity of Electrolytic Solutions
- Electrical conductivity and factors affecting it
- Specific conductance, molar conductance, and equivalent conductance
- Conductivity measurements and techniques
- Electrolysis and Faraday’s Laws
- Principles of electrolysis
- Faraday’s first and second laws
- Applications of Faraday’s laws in quantitative analysis and electroplating
- Electrochemical Cells
- Galvanic cells and electrolytic cells
- Cell notation and electrochemical cell diagrams
- Half-cell reactions and electrode potentials
- Kohlrausch’s Law and Degree of Dissociation
- Kohlrausch’s law and its application in measuring conductivity
- Calculation of degree of dissociation for weak electrolytes
- Applications of Electrolytic Solutions
- Electroplating and metal deposition
- Electrowinning and electrorefining processes
- Electrolysis in water treatment and electrochemical sensors
- Medical and Biological Relevance
- Electrolyte balance in the human body
- Clinical significance of electrolyte imbalances
- Future Directions and Emerging Technologies
- Advancements in electrolyte research and applications
- Electrolytes in energy storage and conversion devices
- Conclusion
- Recap of key concepts and applications
- Importance of electrolytic solutions in scientific and technological advancements
This white paper serves as a comprehensive resource for researchers, students, and professionals seeking to deepen their understanding of electrolytic solutions. By exploring the principles, properties, and applications of electrolytic solutions, it contributes to the advancement of knowledge in various fields and inspires further research and innovation in this area.
