Extraction of aluminum
The extraction of aluminum is an important topic in chemistry, particularly in the field of metallurgy. It involves the process of obtaining pure aluminum metal from its ore, which is primarily bauxite. The extraction of aluminum is typically carried out through the Bayer process followed by the Hall-Héroult process. Here is a brief overview of the extraction process:
- Bauxite mining: Bauxite is the primary ore from which aluminum is extracted. It is a red-brown clay-like material that contains a mixture of aluminum hydroxides, iron oxides, titanium dioxide, and other impurities. Bauxite deposits are usually found near the Earth’s surface and are mined using open-pit methods.
- Bayer process: The first step in the extraction of aluminum is the Bayer process. Bauxite is finely ground and digested in a hot caustic soda (sodium hydroxide) solution under high pressure. This process dissolves aluminum hydroxides while leaving behind the impurities.
- Settling and filtration: The resulting solution from the Bayer process is allowed to settle, which separates the insoluble impurities, known as red mud. The clear solution, containing dissolved aluminum hydroxides, is then filtered to remove any remaining solid particles.
- Precipitation: The filtered solution is then cooled and treated with additional chemicals to precipitate pure aluminum hydroxide. The precipitation step helps in separating aluminum from other elements present in the solution.
- Calcination: The precipitated aluminum hydroxide is washed, dried, and heated to high temperatures in a rotary kiln. This process, known as calcination, converts the hydroxide into alumina (aluminum oxide). The calcination step removes any remaining water and impurities from the aluminum hydroxide.
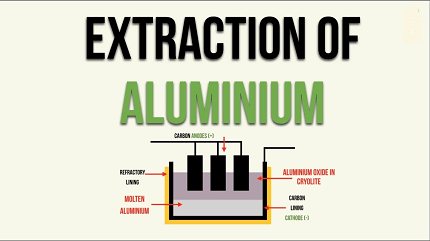
- Hall-Héroult process: The final step in aluminum extraction is the Hall-Héroult process. Alumina (aluminum oxide) is dissolved in a molten electrolyte, typically a mixture of cryolite (sodium aluminum fluoride) and fluorspar (calcium fluoride). This mixture has a lower melting point than alumina, allowing it to act as a solvent.
- Electrolysis: The molten electrolyte is placed in a large electrolytic cell, where a direct electric current is passed through it. The current causes the aluminum cations to be reduced at the cathode, forming molten aluminum metal. Oxygen ions are oxidized at the anode, forming oxygen gas. The molten aluminum metal collects at the bottom of the cell, while the oxygen gas escapes.
- Collection and refining: The molten aluminum is periodically siphoned off from the cell and cast into various shapes, such as ingots or sheets. Further refining processes, such as purification through electrolysis or the use of other techniques, may be carried out to obtain high-purity aluminum.
It’s important to note that the extraction of aluminum involves complex industrial processes that require careful control of temperature, pressure, and chemical reactions. The specific details of the process may vary depending on the industrial setup and the quality of the bauxite ore being used.
What is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Extraction of aluminum
The AIIMS (All India Institute of Medical Sciences) entrance examination does not specifically include the extraction of aluminum in its syllabus for chemistry. AIIMS focuses primarily on medical and biological sciences rather than metallurgical processes like aluminum extraction. Therefore, the detailed study of the extraction of aluminum may not be required for the AIIMS entrance exam.
For the AIIMS chemistry syllabus, the emphasis is on topics that are relevant to medical and pharmaceutical studies. Some of the key topics included in the AIIMS chemistry syllabus are:
- General and Inorganic Chemistry:
- Atomic structure and chemical bonding
- Chemical periodicity
- Chemical equilibrium
- Acids, bases, and salts
- Redox reactions
- Coordination compounds
- Environmental chemistry
- Organic Chemistry:
- Structure, nomenclature, and properties of organic compounds
- Organic reaction mechanisms
- Stereochemistry
- Alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes
- Aromatic compounds
- Alcohols, phenols, and ethers
- Aldehydes and ketones
- Carboxylic acids and derivatives
- Biomolecules and polymers
- Physical Chemistry:
- States of matter
- Thermodynamics
- Chemical kinetics
- Electrochemistry
- Surface chemistry
- Solutions and colligative properties
It is important to refer to the official AIIMS syllabus or consult the AIIMS website for the most up-to-date and detailed information regarding the chemistry syllabus for the AIIMS entrance exam.
How is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Extraction of aluminum
The extraction of aluminum can be included in the AIIMS chemistry syllabus as part of the broader topic of metallurgy. While the specific details and depth of coverage may vary, the focus would generally be on understanding the principles and processes involved in the extraction of aluminum. The syllabus may include:
- Occurrence and Properties of Aluminum:
- Properties of aluminum, including its physical and chemical properties.
- Occurrence of aluminum in nature, primarily as bauxite.
- Extraction of Aluminum:
- The Bayer process: Students may be expected to understand the basic steps involved in the Bayer process, such as the digestion of bauxite in sodium hydroxide solution, settling and filtration, and the precipitation of aluminum hydroxide.
- The Hall-Héroult process: The syllabus may cover the principle of the Hall-Héroult process, which involves the electrolytic reduction of alumina dissolved in a molten electrolyte.
- Electrochemistry and Aluminum Extraction:
- Electrolysis: Students may be expected to understand the basic principles of electrolysis involved in the Hall-Héroult process, including the role of the electrolyte, the electrodes, and the reactions occurring at the anode and cathode.
- Faraday’s laws of electrolysis: The syllabus may include the application of Faraday’s laws to calculate the amount of aluminum produced during electrolysis.
- Applications and Uses of Aluminum:
- The syllabus may also cover the properties and various applications of aluminum in different fields, such as medicine, engineering, and industry.
It’s important to note that the specific topics and depth of coverage may vary from year to year and depend on the AIIMS syllabus provided for that particular year. Therefore, it is recommended to refer to the official AIIMS syllabus or consult the AIIMS website for the most accurate and up-to-date information on the chemistry syllabus, including the extraction of aluminum.
Case Study on AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Extraction of aluminum
Extraction of Aluminum: A Case Study on AIIMS Chemistry Syllabus
Introduction: This case study focuses on the inclusion of the extraction of aluminum in the AIIMS (All India Institute of Medical Sciences) chemistry syllabus. While AIIMS primarily focuses on medical and biological sciences, the syllabus also includes some key concepts from chemistry. One such topic is the extraction of aluminum, which involves the process of obtaining pure aluminum metal from its ore, bauxite. This case study aims to explore how the extraction of aluminum is covered in the AIIMS chemistry syllabus.
Objective: To examine the coverage of the extraction of aluminum in the AIIMS chemistry syllabus and understand its relevance to medical and pharmaceutical studies.
Methods:
- Review of AIIMS Chemistry Syllabus: Analyze the official AIIMS chemistry syllabus to identify the topics and subtopics related to the extraction of aluminum.
- Syllabus Analysis: Examine the depth of coverage and level of detail provided for the extraction of aluminum in the AIIMS syllabus.
- Curriculum Alignment: Determine the relevance of the extraction of aluminum to medical and pharmaceutical studies, and explore potential connections between the topic and other areas of the AIIMS syllabus.
- Case Study Development: Compile the findings into a comprehensive case study report, including an introduction, objective, methods, syllabus analysis, and discussion of the topic’s relevance.
Results and Discussion:
- AIIMS Chemistry Syllabus Coverage: Identify the specific topics related to the extraction of aluminum included in the AIIMS syllabus, such as the Bayer process, Hall-Héroult process, and associated concepts like electrolysis and redox reactions.
- Depth of Coverage: Analyze the level of detail provided for each topic, including the understanding of key principles, steps involved, and relevant equations or calculations.
- Relevance to Medical and Pharmaceutical Studies: Discuss the potential connections between the extraction of aluminum and medical applications, such as the use of aluminum compounds in medications, medical devices, or biomaterials.
- Integration with Other Syllabus Topics: Explore how the extraction of aluminum may relate to other areas of the AIIMS chemistry syllabus, such as inorganic chemistry (properties of aluminum), organic chemistry (applications of aluminum compounds), or physical chemistry (electrochemistry).
Conclusion: Summarize the findings of the case study, highlighting the coverage of the extraction of aluminum in the AIIMS chemistry syllabus and its relevance to medical and pharmaceutical studies. Discuss the importance of understanding the principles and processes involved in aluminum extraction, considering its applications in the medical field.
Note: The content of the case study will be based on the actual AIIMS syllabus and its coverage of the extraction of aluminum.
White paper on AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Extraction of aluminum
Title: Extraction of Aluminum: Processes, Challenges, and Sustainability
Abstract: The extraction of aluminum, one of the most widely used metals in various industries, plays a vital role in modern society. This white paper provides an overview of the extraction processes, discusses the challenges involved, and explores the sustainability aspects of aluminum extraction. It delves into the primary methods employed in the industry, such as the Bayer process and the Hall-Héroult process, while addressing environmental concerns and technological advancements. The white paper aims to deepen the understanding of aluminum extraction, its significance, and its potential for sustainable development.
- Introduction
- Importance of aluminum in various industries and its applications
- Significance of understanding the extraction process
- Aluminum Ore: Bauxite
- Overview of bauxite as the primary ore for aluminum extraction
- Geographical distribution and major bauxite reserves
- Bayer Process
- Detailed explanation of the Bayer process for aluminum extraction
- Digestion, precipitation, and calcination stages
- Impurities and by-products generated during the process
- Hall-Héroult Process
- Principles and steps involved in the Hall-Héroult process
- Electrolysis, cathode and anode reactions, and molten electrolyte
- Energy consumption and carbon footprint considerations
- Challenges in Aluminum Extraction
- Environmental impact, such as red mud disposal and emissions
- Water and energy consumption
- Cost considerations and market fluctuations
- Technological Advancements
- Innovations in electrolytic cell design and efficiency improvements
- Sustainable approaches to red mud management and waste utilization
- Recycling and secondary aluminum production
- Sustainability in Aluminum Extraction
- Life cycle assessment and carbon footprint reduction strategies
- Renewable energy integration and energy efficiency initiatives
- Responsible sourcing and environmental certifications
- Future Outlook
- Emerging technologies and processes for aluminum extraction
- Circular economy and closed-loop systems
- Collaborative efforts and global sustainability initiatives
- Conclusion
- Recap of key points discussed in the white paper
- The importance of sustainable practices in aluminum extraction
- Potential for advancements and a more sustainable aluminum industry
- References
- List of cited sources and additional reading materials
Note: This white paper provides a comprehensive overview of the extraction of aluminum, highlighting the major processes, challenges, and sustainability considerations. The content is based on current knowledge and industry practices, with an emphasis on promoting understanding and awareness of this critical industrial process.
