Ionic covalent
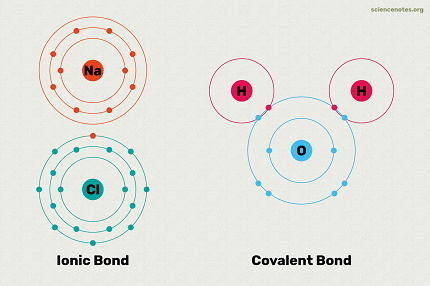
“Ionic” and “covalent” are terms used to describe the types of chemical bonds that can form between atoms.
Ionic Bond: An ionic bond is formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another. This results in the formation of positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions). The opposite charges attract each other, creating a strong electrostatic attraction between the ions. Ionic bonds are typically formed between metals and nonmetals.
Covalent Bond: A covalent bond is formed when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. In this type of bonding, atoms achieve a more stable electron configuration by sharing electrons with other atoms. Covalent bonds are typically formed between nonmetals, although they can also occur between nonmetals and metalloids.
Differences between Ionic and Covalent Bonds:
- Electron Sharing: In an ionic bond, electrons are transferred completely from one atom to another, leading to the formation of charged ions. In a covalent bond, electrons are shared between atoms.
- Bond Strength: Ionic bonds are generally stronger than covalent bonds due to the strong electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions. Covalent bonds are relatively weaker.
- Solubility: Ionic compounds tend to be soluble in polar solvents such as water, while covalent compounds are often soluble in nonpolar solvents.
- Physical Properties: Ionic compounds usually have high melting and boiling points, form crystalline structures, and are good conductors of electricity in a molten or aqueous state. Covalent compounds generally have lower melting and boiling points, exist in various physical states (solid, liquid, gas), and may be poor conductors of electricity.
- Examples: Sodium chloride (NaCl) is an example of an ionic compound, where sodium (Na) donates an electron to chlorine (Cl). Water (H2O) is an example of a covalent compound, where hydrogen (H) shares electrons with oxygen (O).
It’s important to note that in reality, bonds can have varying degrees of ionic and covalent character, forming a continuum known as polar covalent bonds. The classification as purely ionic or covalent is often used for simplicity, but many bonds exhibit characteristics of both types.
The integrated course AIIMS refers to the entrance exam conducted by the All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) for admission to various medical programs. While the specific syllabus for the AIIMS entrance exam may vary, I can provide you with a general overview of the chemistry syllabus that typically covers topics related to ionic and covalent bonding. Here are some key concepts you should be familiar with:
Ionic Bonding:
- Introduction to ions and ionic compounds
- Ionic bond formation and factors affecting bond strength
- Writing and balancing chemical equations for ionic compounds
- Properties of ionic compounds, such as crystal structure, melting and boiling points, solubility, and conductivity
- Lattice energy and Born-Haber cycle
- Common examples of ionic compounds, including their uses and applications
Covalent Bonding:
- Introduction to covalent bonds and electron sharing
- Lewis dot structures and octet rule
- Formal charge and resonance structures
- Electronegativity and polarity of covalent bonds
- VSEPR theory and molecular geometry
- Hybridization and molecular orbital theory
- Intermolecular forces and their effects on physical properties
- Common examples of covalent compounds, including organic molecules
In addition to the above topics, it’s essential to have a good understanding of general concepts in chemistry, including atomic structure, periodic table trends, chemical reactions, stoichiometry, acids and bases, thermodynamics, and equilibrium.
Remember, this is a general overview, and the actual syllabus may have specific topics or subtopics that vary from year to year. It’s always a good idea to refer to the official AIIMS syllabus or consult reliable study materials to get the most accurate and up-to-date information.
What is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Ionic covalent
The exact syllabus for the AIIMS entrance exam may vary from year to year. However, I can provide you with a general overview of the chemistry topics related to ionic and covalent bonding that are typically included in the AIIMS syllabus. Here are some key concepts you should be familiar with:
Ionic Bonding:
- Introduction to ions and ionic compounds
- Formation of cations and anions
- Ionic bond formation and factors affecting bond strength
- Writing and balancing chemical equations for ionic compounds
- Properties of ionic compounds, such as crystal structure, melting and boiling points, solubility, and conductivity
- Lattice energy and Born-Haber cycle
- Common examples of ionic compounds, including their uses and applications
Covalent Bonding:
- Introduction to covalent bonds and electron sharing
- Lewis dot structures and octet rule
- Formal charge and resonance structures
- Electronegativity and polarity of covalent bonds
- VSEPR theory and molecular geometry
- Hybridization and molecular orbital theory
- Intermolecular forces and their effects on physical properties
- Common examples of covalent compounds, including organic molecules
It’s important to note that the AIIMS syllabus may cover other topics in chemistry as well, including but not limited to atomic structure, periodic table trends, chemical reactions, stoichiometry, acids and bases, thermodynamics, and equilibrium.
To get the most accurate and up-to-date information about the AIIMS syllabus, it is recommended to refer to the official AIIMS website or the information provided by the exam conducting authority. Additionally, consulting reliable study materials specifically designed for AIIMS preparation can help you ensure that you cover all the necessary topics in chemistry.
When is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Ionic covalent
The exact schedule or timing of the AIIMS entrance exam and its syllabus may vary from year to year. As an AI language model, I don’t have access to real-time information or the specific details of the AIIMS syllabus for a particular year. Therefore, it’s important to consult the official AIIMS website or the information provided by the exam conducting authority to get the most accurate and up-to-date information about the AIIMS syllabus, including the specific topics related to ionic and covalent bonding.
The AIIMS entrance exam typically assesses a wide range of topics in chemistry, including ionic and covalent bonding. It is important to thoroughly study and understand the concepts related to ionic and covalent bonding as part of your preparation for the AIIMS exam.
I recommend regularly checking the official AIIMS website or contacting the exam conducting authority for the most recent information on the syllabus, exam dates, and any updates or changes related to the AIIMS entrance exam.
Where is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Ionic covalent
The detailed syllabus for the AIIMS entrance exam, including the topics related to ionic and covalent bonding in chemistry, is typically provided by the exam conducting authority or AIIMS itself. To access the AIIMS syllabus for chemistry, you can visit the official AIIMS website or refer to the information provided by the exam conducting authority.
On the official AIIMS website, you can look for the section related to the entrance exam or admission process. There, you may find a dedicated section or a downloadable document that outlines the syllabus for each subject, including chemistry. The syllabus document will provide you with a comprehensive list of topics that are included in the AIIMS chemistry syllabus, covering various areas of chemistry, including ionic and covalent bonding.
If the syllabus is not readily available on the website, you can also contact the AIIMS authorities directly through their official contact information to inquire about the detailed syllabus for chemistry.
Remember, the AIIMS syllabus may be subject to periodic updates or changes. Therefore, it is always recommended to refer to the most recent and official sources for the most accurate and up-to-date information regarding the AIIMS chemistry syllabus.
How is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Ionic covalent
The AIIMS syllabus for chemistry covers a wide range of topics, including those related to ionic and covalent bonding. While the exact structure and organization of the syllabus may vary from year to year, here is a general outline of how the AIIMS syllabus may cover ionic and covalent bonding:
- Introduction to Chemical Bonding:
- Overview of different types of chemical bonds
- Importance of chemical bonding in understanding molecular properties and reactions
- Ionic Bonding:
- Definition of ions and their formation
- Ionic compounds and their properties
- Factors influencing ionic bond strength
- Lattice energy and its calculation
- Formation of ionic compounds and their chemical equations
- Crystal structure and properties of ionic compounds
- Applications and uses of ionic compounds
- Covalent Bonding:
- Definition of covalent bonds and electron sharing
- Lewis dot structures and octet rule
- Covalent compounds and their properties
- Electronegativity and polarity in covalent bonds
- Molecular geometry and VSEPR theory
- Hybridization and molecular orbital theory
- Intermolecular forces and their effects on physical properties
- Organic compounds and their classification
The syllabus may also include specific examples and case studies to illustrate concepts related to ionic and covalent bonding. Additionally, it is common for the syllabus to cover foundational topics in chemistry such as atomic structure, periodic table trends, chemical reactions, stoichiometry, acids and bases, thermodynamics, and equilibrium, which provide the necessary background for understanding ionic and covalent bonding.
It’s important to note that the specific topics and depth of coverage may vary between different editions of the AIIMS syllabus. Therefore, it is recommended to refer to the official AIIMS website or the syllabus provided by the exam conducting authority for the most accurate and up-to-date information regarding the AIIMS chemistry syllabus.
Nomenclature of AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Ionic covalent
The AIIMS syllabus for chemistry typically includes a section on nomenclature, which covers the naming and identification of compounds. This is relevant for both ionic and covalent compounds. Here is a general overview of the nomenclature topics that may be included in the AIIMS chemistry syllabus:
- Ionic Compound Nomenclature:
- Naming binary ionic compounds: These compounds consist of a metal cation and a nonmetal anion. The names typically involve the metal’s name followed by the nonmetal’s name with the suffix “-ide.”
- Naming ionic compounds with polyatomic ions: Some ionic compounds contain polyatomic ions, which are groups of atoms that carry a charge. The names of these compounds involve the names of the individual ions.
- Covalent Compound Nomenclature:
- Naming binary covalent compounds: These compounds consist of two nonmetals. The names typically involve using prefixes to indicate the number of atoms of each element present in the compound, followed by the element names with the suffix “-ide.”
- Naming covalent compounds with polyatomic ions: Similar to ionic compounds, covalent compounds can also contain polyatomic ions. The names of these compounds involve the names of the individual ions.
- Organic Compound Nomenclature:
- Naming organic compounds: Organic compounds, which are based on carbon structures, follow a specific nomenclature system known as the IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) system. This involves using prefixes, suffixes, and numerical locants to indicate the structure and functional groups present in the compound.
The AIIMS chemistry syllabus may cover additional nomenclature topics related to other compound types, such as acids, bases, and coordination compounds. It’s important to study and practice the rules and conventions of nomenclature to be able to correctly identify and name compounds in different contexts.
To get the most accurate and up-to-date information about the nomenclature topics included in the AIIMS syllabus, it is recommended to refer to the official AIIMS website or the syllabus provided by the exam conducting authority.
Case Study on AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Ionic covalent
Case Study: Ionic and Covalent Bonding in Water Molecules
Water (H2O) is a common example that illustrates both ionic and covalent bonding. The water molecule consists of two hydrogen atoms bonded covalently to one oxygen atom.
Covalent Bonding in Water: The covalent bond in water is formed by the sharing of electrons between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms. Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron, and the oxygen atom contributes two electrons, resulting in a total of eight valence electrons around the oxygen atom. This satisfies the octet rule, which states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration with eight valence electrons.
Ionic Character in Water: Although the water molecule is primarily covalently bonded, it also exhibits some ionic character. The oxygen atom is more electronegative than the hydrogen atoms, meaning it has a greater ability to attract electrons towards itself. As a result, the oxygen atom has a partial negative charge (δ-) while the hydrogen atoms have partial positive charges (δ+). This uneven distribution of charge creates a polarity within the water molecule, making it a polar covalent compound.
Hydrogen Bonding: The presence of polar covalent bonds in water allows for hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonding occurs when the partially positive hydrogen atom in one water molecule is attracted to the partially negative oxygen atom in another water molecule. This interaction is responsible for many unique properties of water, such as its high boiling point, surface tension, and ability to dissolve various substances.
Overall, the water molecule demonstrates both covalent bonding, as seen in the sharing of electrons between the hydrogen and oxygen atoms, and ionic character, due to the partial charges present within the molecule. The combination of these bonding types, along with hydrogen bonding, contributes to the properties and behavior of water that are essential for numerous biological and chemical processes.
It’s important to note that this case study focuses on water as an example to illustrate the concepts of ionic and covalent bonding. There are many other compounds and molecules that exhibit different degrees of ionic and covalent character, and studying them can provide a broader understanding of bonding principles.
White paper on AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Ionic covalent
Title: Ionic and Covalent Bonds: A Comprehensive Overview
Abstract: This white paper provides a comprehensive exploration of ionic and covalent bonds, two fundamental types of chemical bonding. Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons between atoms, leading to the formation of charged ions, while covalent bonds result from the sharing of electrons. By understanding the principles and characteristics of these bonding types, we can gain insights into the behavior and properties of various compounds. This paper delves into the mechanisms, properties, and examples of both ionic and covalent bonds, highlighting their significance in chemical interactions and biological processes.
- Introduction
- Importance of chemical bonding
- Overview of ionic and covalent bonds
- Ionic Bonding
- Definition and characteristics
- Formation of cations and anions
- Electrostatic interactions and lattice structures
- Factors influencing ionic bond strength
- Applications and examples of ionic compounds
- Covalent Bonding
- Definition and characteristics
- Electron sharing and stability
- Lewis dot structures and octet rule
- Polarity and electronegativity
- Molecular geometry and hybridization
- Examples of covalent compounds, including organic molecules
- Ionic vs. Covalent Bonds
- Differences in electron sharing or transfer
- Bond strength and energy considerations
- Physical properties of compounds with ionic or covalent bonds
- Examples of compounds with mixed or intermediate bonding
- Importance in Biological Systems
- Role of ionic bonds in maintaining cell structure and function
- Covalent bonds in biological macromolecules (proteins, DNA, etc.)
- Impact of bonding on enzyme-substrate interactions
- Conclusion
- Recap of key points on ionic and covalent bonding
- Significance in various fields of science and everyday life
This white paper aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of ionic and covalent bonds, highlighting their fundamental principles, properties, and applications. By delving into the intricacies of these bonding types, researchers, students, and professionals can gain a deeper comprehension of chemical interactions and their impact on diverse disciplines, including chemistry, biology, materials science, and more.
Note: This white paper serves as a general overview and introduction to the topic of ionic and covalent bonding. Further research and exploration into specific areas of interest are encouraged to develop a more nuanced understanding of this subject matter.
