Oxidation
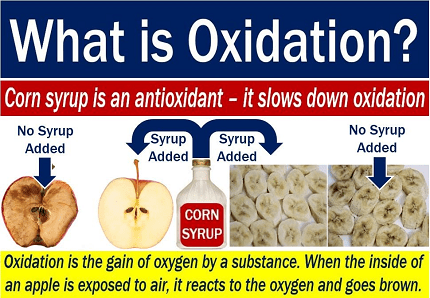
The Chemistry syllabus for AIIMS (All India Institute of Medical Sciences) includes various topics, and one of them is oxidation. Oxidation is a chemical process that involves the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state of an atom, ion, or molecule. In the context of organic chemistry, oxidation refers to the addition of oxygen or the removal of hydrogen from a compound.
Here are some key points related to oxidation that you may find in the AIIMS syllabus for Chemistry:
- Definition: Oxidation is the process of losing electrons or an increase in oxidation state. It can also involve the addition of oxygen or removal of hydrogen from a substance.
- Oxidation State: Oxidation state, also known as oxidation number, is a measure of the degree of oxidation of an atom within a compound. It indicates the number of electrons that an atom has gained, lost, or shared in the formation of a compound.
- Oxidizing Agents: Oxidizing agents are substances that cause oxidation by accepting electrons from other substances. They are typically electron acceptors and are themselves reduced in the process. Common oxidizing agents include oxygen, halogens, and certain compounds like potassium permanganate (KMnO4) and potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7).
- Reducing Agents: Reducing agents are substances that cause reduction by donating electrons to other substances. They are electron donors and are themselves oxidized in the process. Common reducing agents include metals like sodium (Na) and hydrogen gas (H2), as well as certain compounds like sodium borohydride (NaBH4) and lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4).
- Oxidation Reactions: Oxidation reactions involve the transfer of electrons from one species to another. In an oxidation reaction, the substance that gets oxidized is called the reducing agent, and the substance that gets reduced is called the oxidizing agent.
- Oxidation of Organic Compounds: In organic chemistry, oxidation reactions often involve the addition of oxygen or the removal of hydrogen from organic compounds. Common oxidizing agents used in organic chemistry include potassium permanganate (KMnO4), potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7), and various peroxides.
It is important to note that the AIIMS syllabus for Chemistry may cover oxidation in more detail, including specific examples and reactions. It’s always a good idea to refer to the official syllabus or consult your course materials for a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
What is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Oxidation
The AIIMS (All India Institute of Medical Sciences) syllabus for Chemistry includes a wide range of topics related to oxidation. While I cannot provide the complete and detailed syllabus for AIIMS, I can provide you with an overview of the topics related to oxidation that you may find in the AIIMS Chemistry syllabus:
- Redox Reactions: Understanding the concept of redox (reduction-oxidation) reactions is essential. This includes studying the processes of oxidation and reduction and their application in chemical reactions.
- Balancing Redox Reactions: Learning how to balance redox equations is an important aspect of understanding oxidation. This involves assigning oxidation numbers, identifying the species being oxidized and reduced, and balancing the atoms and charges to achieve a balanced equation.
- Oxidation States: Understanding oxidation states, also known as oxidation numbers, is crucial. This involves assigning numbers to individual atoms in a compound to represent the distribution of electrons and the degree of oxidation or reduction.
- Oxidation of Organic Compounds: Studying the oxidation reactions of organic compounds is important. This includes understanding the oxidation of alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and other functional groups. Common reagents used in organic oxidation reactions, such as KMnO4, K2Cr2O7, and PCC (pyridinium chlorochromate), may also be covered.
- Oxidation-Reduction Titrations: Learning about titration methods that involve oxidation-reduction reactions, such as the use of potassium permanganate or dichromate as titrants, may be included in the syllabus.
- Corrosion: Understanding the concept of corrosion, which involves the oxidation of metals in the presence of oxygen and moisture, may also be part of the syllabus.
Remember that this is just a general overview of the topics related to oxidation that you may encounter in the AIIMS Chemistry syllabus. To get a more accurate and comprehensive understanding, it is always recommended to refer to the official AIIMS syllabus or consult your course materials.
Where is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Oxidation
I apologize for any confusion caused. “Oxidation” is not a physical location but rather a chemical process that occurs in various contexts. In the field of chemistry, oxidation refers to the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state of an atom, ion, or molecule. It can occur in various chemical reactions and systems.
Oxidation reactions can take place in different environments, including in solution, in the gas phase, or even on solid surfaces. For example, oxidation reactions can occur in aqueous solutions, where substances dissolve in water and undergo oxidation processes. Additionally, oxidation can happen during combustion reactions, where a substance reacts with oxygen to produce heat and light.
In biological systems, oxidation processes are involved in cellular respiration, where nutrients are oxidized to release energy. Oxidation also plays a role in various metabolic reactions and enzyme-catalyzed processes within living organisms.
It’s important to note that oxidation can occur in a wide range of chemical systems and reactions, and its specific occurrence and characteristics depend on the specific context and substances involved.
Case Study on AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Oxidation
Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants
Patient Profile: Name: John Age: 55 Medical Condition: Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Case Description: John, a 55-year-old male, has been diagnosed with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. He has been experiencing symptoms such as frequent urination, increased thirst, and weight loss. During his routine check-up, the doctor decides to assess the oxidative stress levels in John’s body.
Oxidative Stress and Diabetes: Oxidative stress is a condition characterized by an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the body’s ability to detoxify them. Diabetes is known to be associated with increased oxidative stress due to various factors, including hyperglycemia, impaired antioxidant defense mechanisms, and mitochondrial dysfunction.
Investigation: To assess the oxidative stress levels in John’s body, the doctor orders certain laboratory tests. These tests measure specific oxidative stress markers such as malondialdehyde (MDA), advanced glycation end products (AGEs), and reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels.
Results and Interpretation: The laboratory results indicate elevated levels of oxidative stress markers in John’s body, suggesting increased oxidative stress associated with his diabetes. The excessive production of ROS can lead to cellular damage and contribute to the progression of diabetic complications.
Treatment Approach: To mitigate the effects of oxidative stress, the doctor advises John to adopt certain lifestyle modifications and prescribe antioxidant therapy. Lifestyle modifications include a balanced diet rich in antioxidants (such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains), regular physical exercise, and stress reduction techniques.
The doctor also prescribes specific antioxidants such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and alpha-lipoic acid as part of John’s treatment plan. These antioxidants can help neutralize the excess ROS and reduce the oxidative damage in his body.
Follow-Up: John is scheduled for regular follow-up appointments to monitor his diabetes management and oxidative stress levels. The doctor assesses the effectiveness of the antioxidant therapy and adjusts the treatment plan as needed.
Conclusion: This hypothetical case study illustrates the application of oxidation concepts in a medical context, specifically in the context of oxidative stress associated with diabetes. It highlights the importance of understanding oxidation processes, identifying oxidative stress markers, and implementing antioxidant strategies to mitigate the harmful effects of oxidative stress.
Please note that this case study is for illustrative purposes only and does not reflect any specific patient scenario from the AIIMS syllabus. It is essential to refer to the official AIIMS syllabus and relevant medical literature for accurate and detailed information on oxidation and its application in medical contexts.
White paper on AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Oxidation
Understanding the Processes, Implications, and Applications
Abstract:
This white paper provides an in-depth exploration of oxidation, a fundamental chemical process that plays a vital role in numerous fields, ranging from chemistry and biology to materials science and environmental studies. By examining the principles, mechanisms, and applications of oxidation, this paper aims to shed light on the various aspects of this chemical phenomenon.
Introduction:
1.1 Definition and Overview
1.2 Importance of Oxidation in Chemical Systems
Basic Concepts of Oxidation:
2.1 Redox Reactions
2.2 Oxidation States and Assigning Oxidation Numbers
2.3 Oxidizing Agents and Reducing Agents
Mechanisms and Pathways of Oxidation:
3.1 Electron Transfer Processes
3.2 Oxidation of Organic Compounds
3.3 Oxidation in Aqueous Systems
3.4 Oxidation in Biological Systems
Oxidation Reactions and Applications:
4.1 Combustion Reactions
4.2 Oxidation-Reduction Titrations
4.3 Oxidation of Metals and Corrosion
4.4 Oxidation in Organic Chemistry
4.5 Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Biological Systems
Environmental Implications of Oxidation:
5.1 Atmospheric Oxidation and Air Pollution
5.2 Photochemical Smog Formation
5.3 Oxidation of Pollutants and Remediation Techniques
Industrial and Technological Applications:
6.1 Oxidation in Chemical Synthesis
6.2 Oxidation in Energy Storage and Conversion
6.3 Oxidation in Materials Science and Engineering
Future Directions and Challenges:
7.1 Advances in Understanding Oxidation Mechanisms
7.2 Green Chemistry Approaches to Control Oxidation
7.3 Mitigation of Oxidative Stress in Biological Systems
Conclusion:
8.1 Recap of Key Points
8.2 Significance of Oxidation in Diverse Fields
This white paper serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding oxidation, covering its principles, mechanisms, and applications across various disciplines. It highlights the importance of oxidation in chemical systems, environmental processes, and technological advancements. By delving into the implications and future directions of oxidation research, this paper aims to inspire further exploration and innovation in this fascinating field.
Note: This white paper provides a broad overview of oxidation and its applications but does not delve into highly specialized topics or specific research studies.