Ohms law
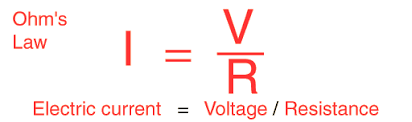
Ohm’s Law is a fundamental principle in electrical physics that relates the current flowing through a conductor to the voltage across it and the resistance of the conductor. It states that the current (I) flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage (V) across the conductor and inversely proportional to the resistance (R) of the conductor.
Mathematically, Ohm’s Law is expressed as:
V = I * R
where: V is the voltage across the conductor (measured in volts, V), I is the current flowing through the conductor (measured in amperes, A), R is the resistance of the conductor (measured in ohms, Ω).
According to Ohm’s Law, if the voltage across a conductor is kept constant, then the current flowing through the conductor will be directly proportional to the resistance. Similarly, if the resistance is kept constant, then the current will be directly proportional to the voltage. This relationship allows us to calculate one parameter (current, voltage, or resistance) if the other two are known.
Ohm’s Law is widely used in various applications, such as circuit analysis, electrical engineering, and electronics. It forms the basis for understanding and calculating the behavior of electric circuits and helps in designing and troubleshooting electrical systems.
The syllabus for the Integrated Course AIIMS (All India Institute of Medical Sciences) may vary from year to year. However, I can provide you with a general overview of the Physics syllabus that often includes topics like Ohm’s Law. Please note that this information is based on the knowledge available up until September 2021, and there may have been updates or changes to the syllabus since then.
Physics Syllabus for Integrated Course AIIMS (General Overview):
- Physical World and Measurement:
- Introduction to physics as a discipline
- Units and dimensions
- Fundamental and derived units
- Measurement techniques and tools
- Kinematics:
- Motion in one dimension
- Motion in two and three dimensions
- Laws of motion
- Projectile motion
- Circular motion
- Laws of Thermodynamics:
- Basic concepts and definitions
- Zeroth law, first law, and second law of thermodynamics
- Heat transfer and work
- Optics:
- Reflection and refraction of light
- Optical instruments (telescope, microscope, etc.)
- Wave nature of light
- Interference, diffraction, and polarization
- Electricity and Magnetism:
- Electrostatics
- Electric current and circuits
- Ohm’s Law and its applications
- Magnetic effects of electric current
- Electromagnetic induction
- AC and DC circuits
- Modern Physics:
- Dual nature of radiation and matter
- Atomic models and structure
- Nuclear physics
- Elementary particles
Please keep in mind that this is a general outline, and specific topics may vary. It is advisable to refer to the official AIIMS syllabus or contact the institution directly to obtain the most accurate and up-to-date information on the Physics syllabus for the Integrated Course.
What is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Ohms law
Ohm’s Law is a fundamental principle in electrical physics that relates the current flowing through a conductor to the voltage across it and the resistance of the conductor. It is named after the German physicist Georg Simon Ohm, who formulated this law.
Ohm’s Law states that the current (I) flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage (V) across the conductor and inversely proportional to the resistance (R) of the conductor. Mathematically, Ohm’s Law is represented as:
V = I * R
where: V is the voltage across the conductor (measured in volts, V), I is the current flowing through the conductor (measured in amperes, A), R is the resistance of the conductor (measured in ohms, Ω).
In simpler terms, Ohm’s Law tells us that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage applied across it and inversely proportional to the resistance of the conductor. It means that if the voltage remains constant, an increase in resistance will result in a decrease in current flow, and vice versa. Similarly, if the resistance remains constant, an increase in voltage will result in an increase in current flow.
Ohm’s Law is a fundamental concept in electrical engineering and is widely used in various applications, such as circuit analysis, designing electrical systems, and troubleshooting electrical problems. It provides a basic framework for understanding and calculating the behavior of electric circuits.
When is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Ohms law
Ohm’s Law is applicable to any situation involving the flow of electric current through a conductor, as long as the conductor obeys Ohm’s Law. It is a fundamental principle in electrical physics and is applicable in a wide range of scenarios.
Ohm’s Law can be applied in various contexts, including:
- Simple DC Circuits: Ohm’s Law is commonly used to analyze and calculate the behavior of direct current (DC) circuits. It helps determine the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit.
- AC Circuits: Ohm’s Law can also be applied to alternating current (AC) circuits, although in AC circuits, impedance (a combination of resistance and reactance) is used instead of resistance. However, in circuits with purely resistive components (without capacitors or inductors), Ohm’s Law remains valid.
- Electronic Components: Ohm’s Law is used to understand and analyze the behavior of electronic components such as resistors, where the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance is crucial for proper circuit design and analysis.
- Circuit Design and Troubleshooting: Ohm’s Law is an essential tool for designing electrical circuits and calculating the values of resistors or determining the appropriate current and voltage levels in a circuit. It is also used in troubleshooting electrical problems by analyzing voltage drops and current flows.
Overall, Ohm’s Law is a fundamental principle in electrical engineering and is widely applicable in various electrical and electronic systems, providing a foundation for understanding and analyzing the behavior of electric circuits.
Where is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Ohms law
Ohm’s Law is a fundamental concept in electrical physics and is applicable in various contexts and settings. It is not confined to a specific physical location but rather represents a principle or relationship that applies to the behavior of electric circuits.
You can apply Ohm’s Law in different places, including:
- Electrical Circuits: Ohm’s Law is commonly used in analyzing and understanding the behavior of electrical circuits, whether they are simple circuits, complex systems, or integrated circuits.
- Electronic Devices: Ohm’s Law is relevant to electronic devices that involve the flow of electric current, such as computers, smartphones, televisions, and any other device that relies on electric circuits for operation.
- Power Systems: Ohm’s Law is applicable in power systems, such as electrical grids, where it helps determine the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in transmission lines and distribution networks.
- Laboratories and Experimentation: Ohm’s Law is often employed in laboratories when conducting experiments related to electricity and circuits. It is used to make predictions, analyze data, and validate experimental results.
- Electrical Engineering and Design: Ohm’s Law is utilized in electrical engineering and design processes, where it plays a crucial role in circuit analysis, component selection, and system design.
In summary, Ohm’s Law is not located in a physical place but rather describes a principle that can be applied in various settings involving the behavior of electric circuits, devices, and systems.
How is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Ohms law
Ohm’s Law describes the relationship between voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R) in an electrical circuit. It states that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage across it and inversely proportional to the resistance of the conductor.
Mathematically, Ohm’s Law can be expressed in three different forms:
- V = I * R: This equation relates voltage (V) to current (I) and resistance (R). It states that the voltage across a conductor is equal to the product of the current flowing through it and the resistance of the conductor.
- I = V / R: This equation relates current (I) to voltage (V) and resistance (R). It states that the current flowing through a conductor is equal to the ratio of the voltage across it to the resistance of the conductor.
- R = V / I: This equation relates resistance (R) to voltage (V) and current (I). It states that the resistance of a conductor is equal to the ratio of the voltage across it to the current flowing through it.
These equations can be used to calculate any one of the three variables (voltage, current, or resistance) if the other two are known. Ohm’s Law provides a fundamental relationship that allows us to understand and analyze the behavior of electric circuits, design systems, and troubleshoot electrical problems.
It’s important to note that Ohm’s Law assumes that the conductor being considered obeys Ohm’s Law, meaning that its resistance remains constant regardless of the voltage or current. This assumption holds true for most metallic conductors under normal operating conditions.
Nomenclature of AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Ohms law
The nomenclature used for Ohm’s Law is generally straightforward and follows standard conventions in physics and electrical engineering. The key variables and symbols used in Ohm’s Law are:
V: Voltage (measured in volts, V) I: Current (measured in amperes, A) R: Resistance (measured in ohms, Ω)
The equation itself, V = I * R, represents the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance. The nomenclature is consistent across different sources and contexts.
It’s important to note that while the nomenclature for Ohm’s Law is generally standardized, different educational institutions or publications may use slightly different notations or symbols. However, the fundamental concept and relationship expressed by Ohm’s Law remain the same regardless of the specific nomenclature used.
Case Study on AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Ohms law
Here’s a hypothetical case study demonstrating the application of Ohm’s Law in analyzing an electrical circuit:
Case Study: Residential Circuit Analysis
Scenario: You are an electrical engineer tasked with analyzing a residential electrical circuit to ensure proper voltage and current levels for safety and functionality.
Information:
- The circuit consists of a 120-volt power supply.
- A 60-watt incandescent light bulb is connected to the circuit.
- The resistance of the light bulb can be determined using Ohm’s Law.
Step 1: Determine the current flowing through the circuit. Using Ohm’s Law (V = I * R), we can rearrange the formula to solve for current (I): I = V / R
The voltage (V) is 120 volts, and we need to determine the resistance (R) of the light bulb.
Step 2: Calculate the resistance of the light bulb. Given that the power (P) of the light bulb is 60 watts, we can use the formula for power (P = V^2 / R) and rearrange it to solve for resistance (R): R = V^2 / P
Substituting the values, we have: R = (120^2) / 60
Calculating this, we find: R = 240 ohms
Step 3: Calculate the current flowing through the circuit. Now that we know the resistance (R) of the light bulb, we can calculate the current (I) flowing through the circuit: I = V / R I = 120 / 240 I = 0.5 amperes (A)
Step 4: Analyze the circuit. Based on the calculations, we find that the current flowing through the circuit is 0.5 amperes. This information can be used to assess the circuit’s safety and functionality. We can check if the current is within the rated limits of the circuit components and ensure that it does not exceed the capacity of the wires or other elements in the circuit.
By applying Ohm’s Law, we were able to determine the resistance of the light bulb and calculate the current flowing through the circuit. This analysis helps ensure the circuit’s proper functioning and assists in maintaining electrical safety standards.
White paper on AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Ohms law
However, I can provide you with an outline or structure that you can use as a starting point to create your own white paper on Ohm’s Law. You can then conduct further research, gather data, and expand on each section to create a comprehensive document. Here is a suggested structure for a white paper on Ohm’s Law:
- Introduction
- Briefly introduce the concept of Ohm’s Law and its significance in electrical physics and engineering.
- Provide an overview of the purpose and scope of the white paper.
- Background and History
- Explain the historical context of Ohm’s Law, including its discovery by Georg Simon Ohm and its development over time.
- Discuss the fundamental principles and concepts underlying Ohm’s Law.
- Statement of Ohm’s Law
- Present the mathematical representation of Ohm’s Law: V = I * R.
- Explain the meaning of each variable (voltage, current, and resistance) and their units of measurement.
- Understanding Voltage, Current, and Resistance
- Define voltage, current, and resistance in detail.
- Discuss the properties and characteristics of each variable, including their relationship to electric circuits.
- Applications of Ohm’s Law
- Explain the practical applications of Ohm’s Law in various fields, such as electrical engineering, electronics, circuit design, and troubleshooting.
- Provide examples of how Ohm’s Law is used to calculate current, voltage, and resistance in different circuit configurations.
- Limitations and Assumptions
- Discuss the assumptions and limitations of Ohm’s Law, such as the assumption of linearity and constant temperature.
- Explain situations in which Ohm’s Law may not be directly applicable or requires modifications.
- Experimental Verification and Validation
- Describe experimental methods used to verify and validate Ohm’s Law.
- Present examples of experiments and measurements that demonstrate the accuracy and applicability of Ohm’s Law.
- Practical Implications and Importance
- Discuss the practical importance of Ohm’s Law in designing and analyzing electrical circuits.
- Explain how Ohm’s Law enables engineers to determine circuit behavior, calculate power consumption, select appropriate components, and ensure safety.
- Conclusion
- Summarize the key points discussed in the white paper.
- Emphasize the significance of Ohm’s Law in the field of electrical engineering and its continued relevance in modern applications.
- References
- Provide a list of references and sources used to gather information and support the content of the white paper.
Remember to conduct thorough research, cite relevant sources, and provide accurate and reliable information throughout the white paper.
