Alkylation is a chemical reaction in which an alkyl group (a group of carbon and hydrogen atoms) is added to a molecule. This process is commonly used in organic chemistry to introduce new alkyl groups to a molecule in order to modify its properties or reactivity.
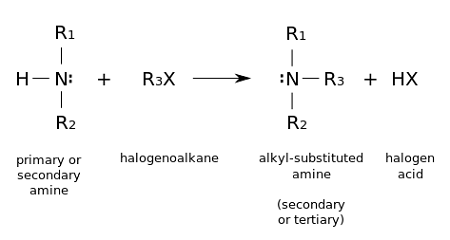
Alkylation reactions can be carried out using a variety of reagents and conditions. One common method involves the use of an alkyl halide, such as methyl iodide or ethyl bromide, as the alkylating agent. These reactive molecules can be used to add an alkyl group to a variety of nucleophiles, such as amines, alcohols, or carboxylic acids.
Another common method of alkylation involves the use of alkyl metal reagents, such as organolithium or Grignard reagents. These highly reactive species can be used to add an alkyl group to a variety of electrophilic substrates, such as ketones, esters, or nitriles.
Alkylation reactions can be used in a variety of applications, including the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and polymers. However, alkylation reactions can also be problematic due to the potential for side reactions and the formation of unwanted products. Careful control of reaction conditions and choice of reagents is often required to achieve the desired selectivity and yield.
What is Required Amines Alkylation
Amines alkylation refers to the addition of an alkyl group to an amine molecule. In order to carry out this reaction, a suitable alkylating agent and a source of heat or a catalyst are typically required.
One common method of amines alkylation involves the use of an alkyl halide, such as methyl iodide or ethyl bromide, as the alkylating agent. The amine and the alkyl halide are typically mixed together in a suitable solvent, such as ether or THF, and heated to promote the reaction. Alternatively, a base catalyst such as sodium hydroxide or potassium carbonate may be used to facilitate the reaction.
Another method of amines alkylation involves the use of an alkyl sulfonate, such as methyl or ethyl sulfonate, as the alkylating agent. This method is often used for the alkylation of primary amines, which can be difficult to alkylate using alkyl halides.
Amines alkylation reactions are widely used in organic synthesis, particularly in the preparation of pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals. However, the selectivity and yield of these reactions can be influenced by a number of factors, such as the steric hindrance of the amine substrate and the choice of alkylating agent and catalyst. Careful optimization of these reaction parameters is often required to achieve the desired outcome.
When is Required Amines Alkylation
Amines alkylation is a widely used reaction in organic chemistry and is commonly employed in the synthesis of a wide range of compounds, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials. Amines alkylation can be used to introduce alkyl groups onto nitrogen-containing molecules, which can be important for modulating the properties of these compounds.
One common application of amines alkylation is in the synthesis of amine-containing drugs, such as antidepressants, antihistamines, and antipsychotics. In many cases, the addition of an alkyl group to the amine can improve the pharmacological properties of the drug, such as its potency, solubility, and bioavailability.
Amines alkylation can also be used in the synthesis of agrochemicals, such as herbicides, fungicides, and insecticides. For example, the addition of an alkyl group to the amine in a pesticide molecule can increase its stability and persistence in the environment, improving its effectiveness as a crop protectant.
In addition, amines alkylation is commonly used in the synthesis of materials, such as polymers and surfactants. The addition of alkyl groups to amine-containing monomers or surfactants can improve their solubility and processability, as well as their ability to interact with other molecules or surfaces.
Overall, amines alkylation is an important reaction in organic synthesis and has a wide range of applications in various fields of chemistry.
Where is Required Amines Alkylation
Amines alkylation is a widely used reaction in organic chemistry and can be carried out in a variety of laboratory and industrial settings. This reaction is often employed in the synthesis of drugs, agrochemicals, and materials, which have a wide range of applications in industry and daily life.
In laboratory settings, amines alkylation can be carried out using standard synthetic techniques and equipment, such as refluxing, stirring, and heating. Typically, the reaction is carried out in a suitable solvent, such as ether, THF, or DMF, and requires the use of a suitable alkylating agent, such as an alkyl halide or alkyl sulfonate, and a source of heat or catalyst.
In industrial settings, amines alkylation may be carried out on a larger scale using specialized equipment and processes. For example, the reaction may be carried out in a continuous flow reactor, which allows for rapid and efficient reaction control and separation of products. Alternatively, the reaction may be carried out in a batch reactor, which allows for larger-scale production of the desired compounds.
Amines alkylation is used in a variety of industries, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science. The resulting products may be used in a wide range of applications, such as medicines, crop protectants, and consumer products.
How is Required Amines Alkylation
Amines alkylation is the chemical process of adding an alkyl group, such as a methyl or ethyl group, to an amine molecule. The alkylation process can be carried out through a variety of methods, depending on the desired outcome and the type of amine being used.
One common method of amines alkylation involves the use of an alkyl halide as the alkylating agent. The amine and the alkyl halide are mixed together in a suitable solvent, such as ether or THF, and heated to promote the reaction. A base catalyst, such as sodium hydroxide or potassium carbonate, may also be used to facilitate the reaction.
Another method of amines alkylation involves the use of an alkyl sulfonate, such as methyl or ethyl sulfonate, as the alkylating agent. This method is often used for the alkylation of primary amines, which can be difficult to alkylate using alkyl halides.
In addition to these methods, there are many other approaches to amines alkylation, including the use of Grignard reagents, organolithium reagents, and diazonium salts, among others. The choice of alkylating agent and reaction conditions will depend on the specific amine being used and the desired outcome.
The alkylation of amines can be a challenging process due to the presence of nitrogen atoms, which can participate in a variety of side reactions. Therefore, careful optimization of reaction conditions, including the choice of solvent, temperature, and catalyst, is often required to achieve the desired outcome with high selectivity and yield.
Production of Amines Alkylation
Amines alkylation is an important industrial process, as it is used in the production of a wide range of chemicals, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials. The production of amines alkylation typically involves several steps, including the preparation of the starting materials, the reaction itself, and the purification and isolation of the desired product.
The starting materials for amines alkylation are typically the amine and the alkylating agent, such as an alkyl halide or alkyl sulfonate. These materials may be prepared in-house or purchased from chemical suppliers. Prior to the reaction, it is important to ensure that both the amine and the alkylating agent are of high purity and suitable for the desired application.
The reaction itself may be carried out using a variety of techniques and equipment, depending on the desired scale of production. For example, the reaction may be carried out in a batch reactor, which allows for larger-scale production, or in a continuous flow reactor, which allows for precise control over reaction conditions and faster reaction times.
After the reaction, the product must be purified and isolated from any unreacted starting materials or side products. This may involve a variety of techniques, including extraction, distillation, chromatography, or crystallization. The choice of purification method will depend on the properties of the product and the desired purity level.
Overall, the production of amines alkylation is a complex process that requires careful planning, optimization, and execution to ensure high yields and purity levels. As with any chemical process, safety is also a key concern, and appropriate measures must be taken to ensure the safety of personnel and the environment.
Case Study on Amines Alkylation
One example of amines alkylation is the synthesis of methylamine, an important building block in the production of a variety of chemicals, including pharmaceuticals, pesticides, and surfactants.
The synthesis of methylamine involves the alkylation of ammonia with methanol in the presence of a catalyst. The reaction is typically carried out at elevated temperatures and pressures, and requires careful control over reaction conditions to ensure high selectivity and yield.
One common method of synthesizing methylamine involves the use of a fluidized bed reactor. In this process, ammonia and methanol are fed into a reactor vessel containing a catalyst bed. The catalyst is typically a mixture of alumina and copper oxide, which promotes the formation of methylamine while minimizing the formation of byproducts.
As the reactants flow through the catalyst bed, they undergo a series of reactions, ultimately leading to the formation of methylamine. The resulting product is then purified and isolated using distillation or other techniques.
The synthesis of methylamine is a complex process that requires careful attention to reaction conditions, catalyst choice, and purification methods. In addition, safety is a key concern, as the reaction involves the use of flammable and toxic chemicals. Therefore, appropriate measures must be taken to ensure the safety of personnel and the environment.
In conclusion, amines alkylation plays an important role in the synthesis of a wide range of chemicals, including methylamine. The production of methylamine requires careful planning, optimization, and execution to ensure high yields and purity levels, as well as the safety of personnel and the environment.
White paper on Amines Alkylation
Introduction:
Amines alkylation is an important chemical process that involves the addition of an alkyl group to an amine molecule. This reaction has significant industrial applications, including the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials. The purpose of this white paper is to provide an overview of amines alkylation, including its mechanism, types, applications, and challenges.
Mechanism:
The mechanism of amines alkylation involves the addition of an alkyl group to the nitrogen atom of an amine molecule. The reaction may be carried out using a variety of alkylating agents, including alkyl halides, alkyl sulfonates, and Grignard reagents, among others. The reaction typically requires the use of a catalyst or base to promote the reaction and may be carried out under a variety of conditions, including elevated temperatures and pressures.
Types:
There are several types of amines alkylation, including primary, secondary, and tertiary alkylation. Primary alkylation involves the addition of an alkyl group to a primary amine, while secondary alkylation involves the addition of an alkyl group to a secondary amine. Tertiary alkylation involves the addition of an alkyl group to a tertiary amine. In addition, amines alkylation may be carried out using a variety of alkylating agents and reaction conditions, depending on the desired outcome and the specific amine being used.
Applications:
Amines alkylation has significant industrial applications, including the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials. For example, amines alkylation is used in the production of antidepressants, such as fluoxetine and venlafaxine, as well as in the production of pesticides, such as chlorpyrifos and imidacloprid. Amines alkylation is also used in the production of materials, such as surfactants, resins, and polymers.
Challenges:
Amines alkylation can be a challenging process, as the nitrogen atom in the amine molecule can participate in a variety of side reactions, including formation of quaternary ammonium salts or the formation of unwanted byproducts. In addition, the choice of alkylating agent and reaction conditions can have a significant impact on the selectivity and yield of the reaction. Therefore, careful optimization of reaction conditions and the use of suitable catalysts or bases are often required to achieve the desired outcome with high selectivity and yield.
Conclusion:
Amines alkylation is an important chemical process with significant industrial applications. The reaction involves the addition of an alkyl group to an amine molecule and may be carried out using a variety of alkylating agents and reaction conditions. However, the process can be challenging due to the presence of nitrogen atoms in the amine molecule and the potential for side reactions. Therefore, careful optimization of reaction conditions and the use of suitable catalysts or bases are often required to achieve the desired outcome with high selectivity and yield.
