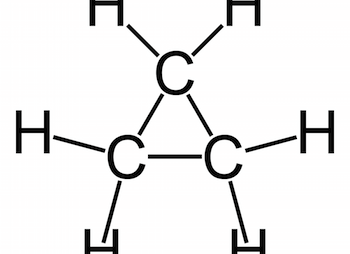
Their mono-functional
“Mono-functional” refers to something that has a single function or purpose. It is the opposite of “multi-functional,” which means that something can perform multiple functions. For example, a kitchen knife is a mono-functional tool, as it is designed specifically for cutting food. In contrast, a Swiss Army Knife is a multi-functional tool, as it can…