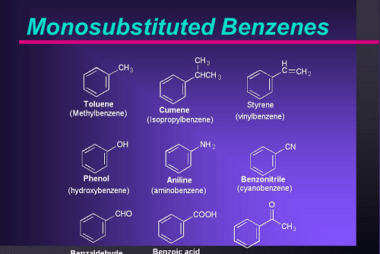
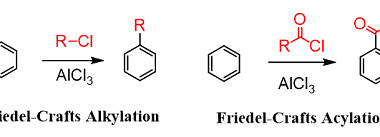
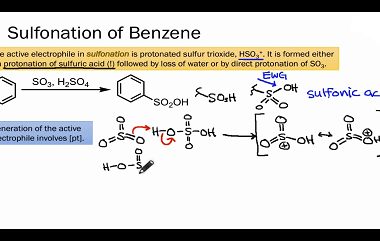
Effect of directing groups (monosubstituted benzene) in these reactions
The effect of directing groups in reactions of monosubstituted benzene depends on the type of reaction being considered. In summary, directing groups play an important role in the reactivity and selectivity of reactions involving monosubstituted benzene. What is Required Effect of directing groups (monosubstituted benzene) in these reactions The effect of directing groups in reactions…