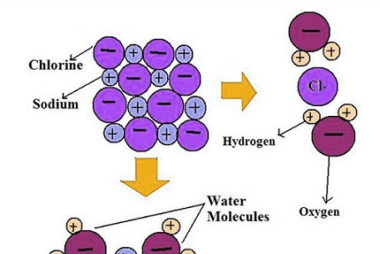
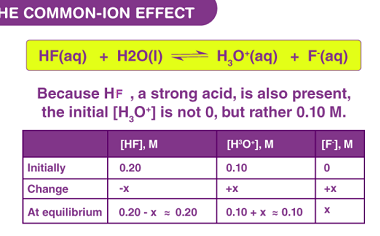
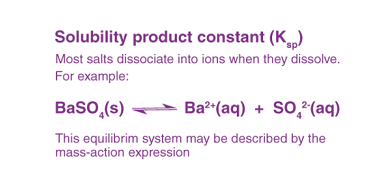
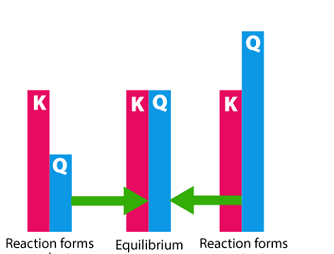
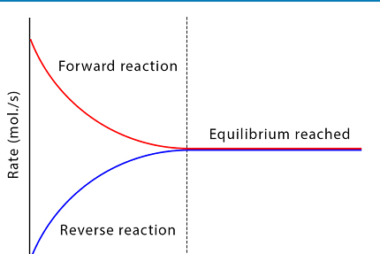
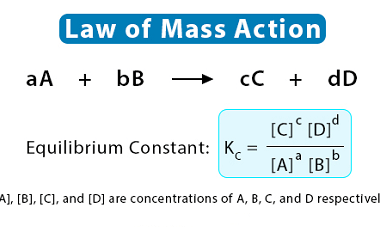
Hydrolysis of salts
Hydrolysis of salts is a chemical reaction in which a salt reacts with water to produce an acidic or basic solution. The nature of the salt and the pH of the resulting solution depend on the cation and anion present in the salt. If the cation is derived from a strong base and the anion…