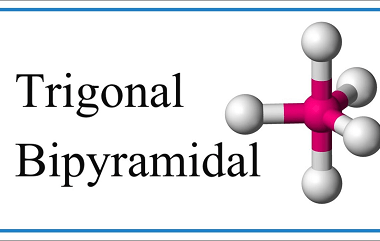
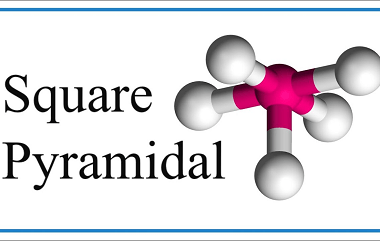
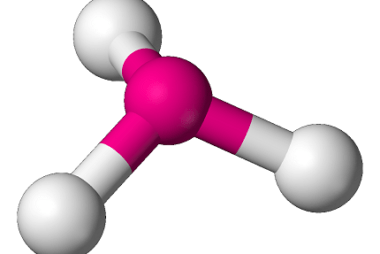
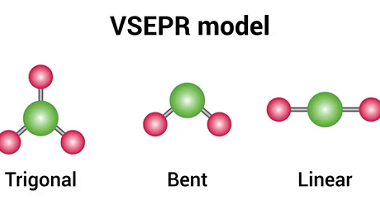
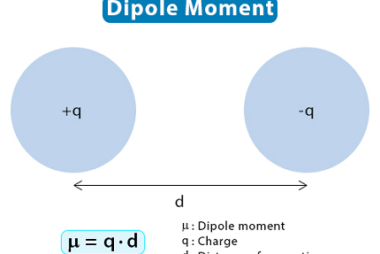
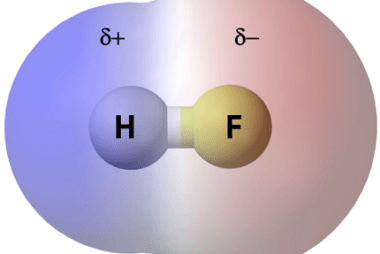
Tetrahedral and Octahedral
Tetrahedral and octahedral are two geometric shapes commonly found in chemistry and crystallography. Tetrahedral refers to a shape with four sides, each of which is a triangle. The tetrahedron is a regular solid with four identical equilateral triangles as its faces, and it is often used to describe the molecular geometry of compounds with four…