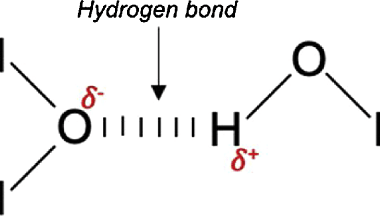
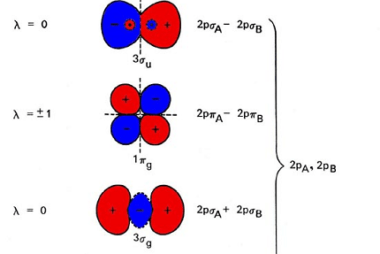
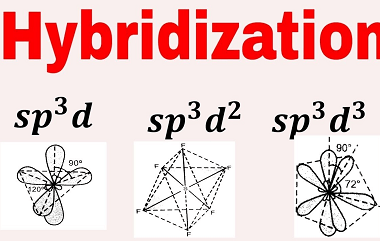
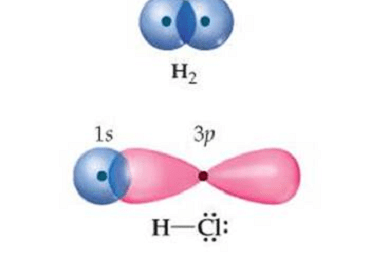
Hydrogen bond
A hydrogen bond is a type of intermolecular force that occurs between a hydrogen atom bonded to an electronegative atom, such as nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine, and another electronegative atom. The hydrogen atom has a partial positive charge due to the electron-withdrawing effect of the more electronegative atom, while the other atom has a partial…