Enthalpy
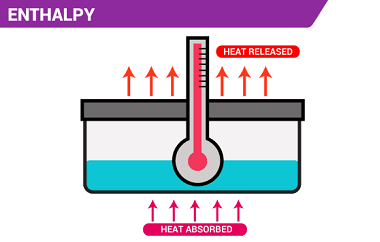
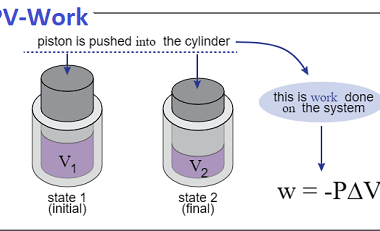
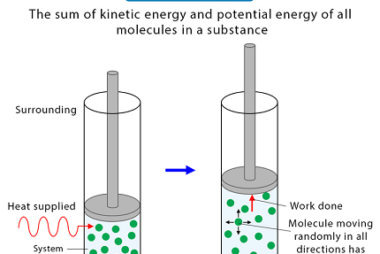
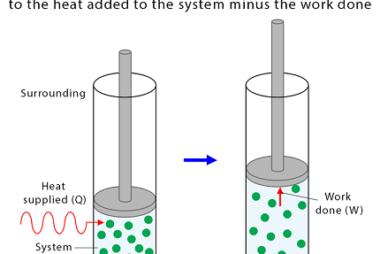
Enthalpy (H) is a thermodynamic property that describes the total heat content of a system at constant pressure. It is defined as the sum of the internal energy (U) of the system and the product of the pressure (P) and volume (V) of the system: H = U + PV Enthalpy is a state function,…