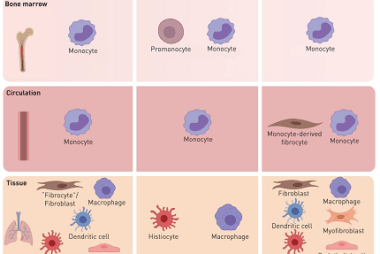
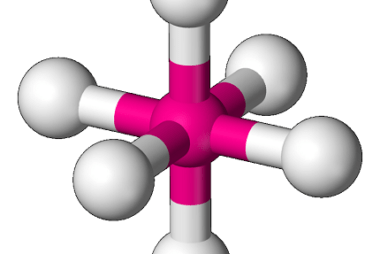
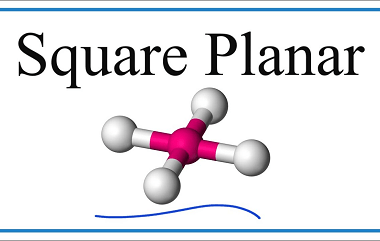
Metal carbonyls
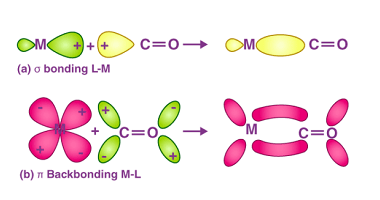
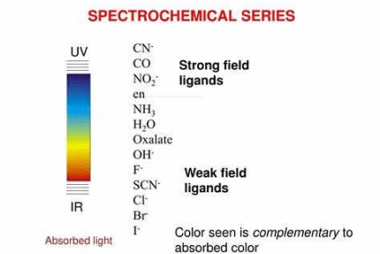
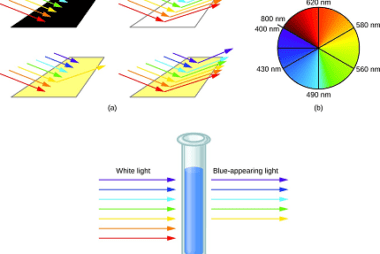
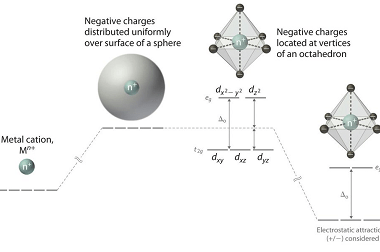
Metal carbonyls are compounds that consist of metal atoms coordinated to one or more carbon monoxide (CO) molecules. They are important in organometallic chemistry and have many industrial applications, particularly as catalysts in chemical reactions. The most well-known metal carbonyl is probably iron pentacarbonyl (Fe(CO)5), which is a colorless, volatile liquid that is used as…