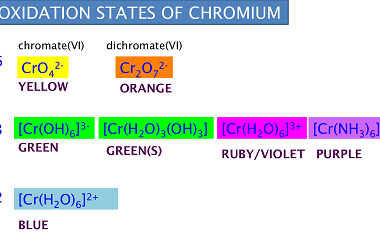
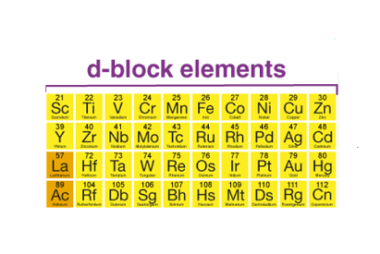
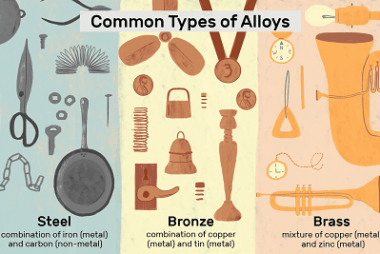
Manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery-gray metal that is widely distributed in the Earth’s crust. Manganese is an essential trace element that is involved in many biological processes, including bone formation, metabolism, and the antioxidant defense system. Manganese is commonly used in…