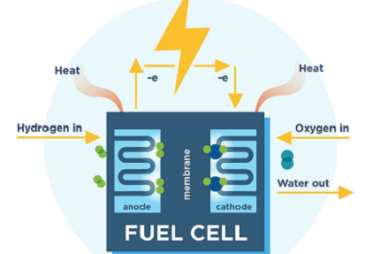
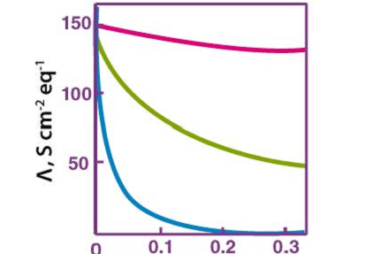
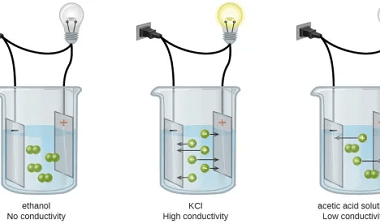
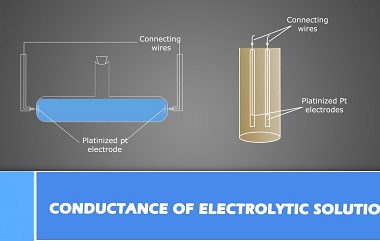
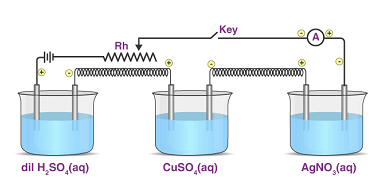
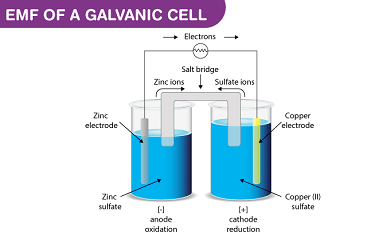
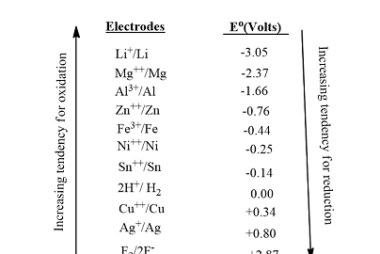
Corrosion
Corrosion is the gradual degradation of a material due to a chemical reaction with its environment. It is a natural process that occurs in materials such as metals, ceramics, and polymers, and can lead to the loss of mechanical strength, structural integrity, and even aesthetic appearance of the material. Corrosion can occur in many different…