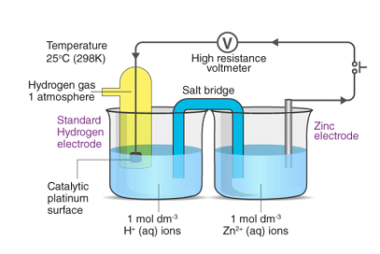
Nernst equation
The Nernst equation is an important formula in electrochemistry that relates the concentration of ions in a solution to the potential difference across a membrane or electrode. The equation is named after German chemist Walther Nernst, who formulated it in 1889. The Nernst equation is given as: E = E° – (RT/nF) * ln(Q) where:…