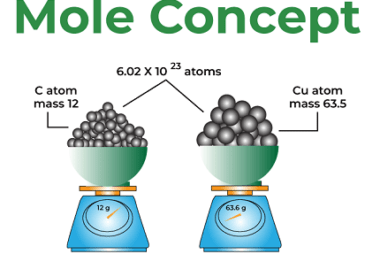
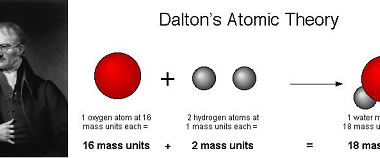
Molality and Normality
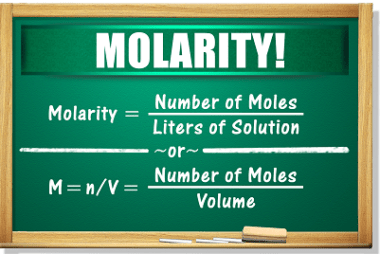
Molality and Normality are both measures of concentration used in chemistry. Molality (symbol: m) is defined as the number of moles of solute per kilogram of solvent. It is expressed in units of moles per kilogram (mol/kg). Molality is a useful measure of concentration when temperature changes occur because it is not dependent on temperature,…