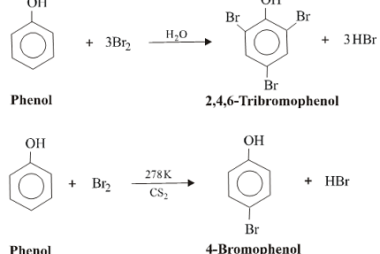
Halogenation
Halogenation of phenols involves the substitution of one or more hydrogen atoms on the phenolic ring with a halogen atom such as chlorine, bromine or iodine. The reaction is typically carried out in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst such as iron(III) chloride or aluminum trichloride to increase the electrophilicity of the halogen. The…