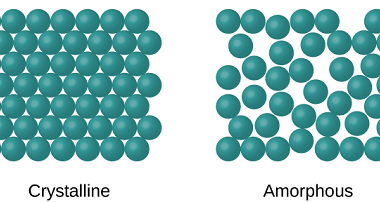
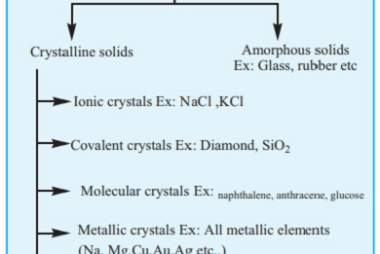
Point defects
In materials science, point defects refer to localized irregularities in the arrangement of atoms or ions within a crystal lattice structure. These defects can occur naturally during the growth of a crystal, or they can be intentionally introduced through various processes such as irradiation, doping, or mechanical deformation. There are several types of point defects,…