Viscosity
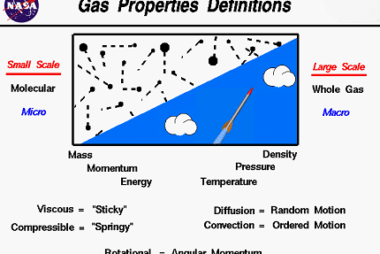
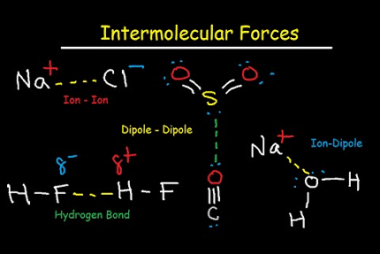
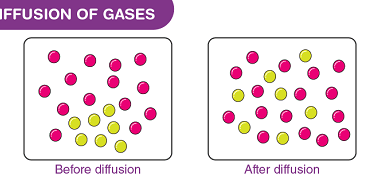
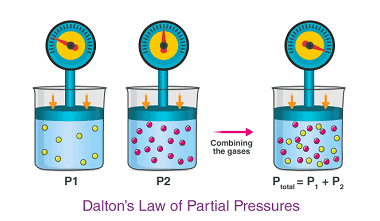
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow. In simpler terms, it is the internal friction between different layers of fluid as they move past each other. Viscosity is commonly measured in units of poise or centipoise, and is dependent on factors such as temperature, pressure, and composition of the fluid. Fluids with…