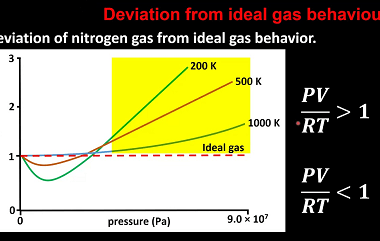
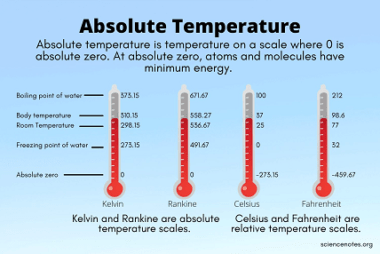
Kinetic theory of gases
The kinetic theory of gases is a model that explains the behavior of gases in terms of the motion of their individual particles. The theory is based on the following assumptions: From these assumptions, the kinetic theory of gases explains several properties of gases, such as: Overall, the kinetic theory of gases provides a useful…