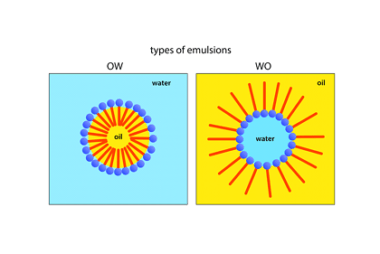
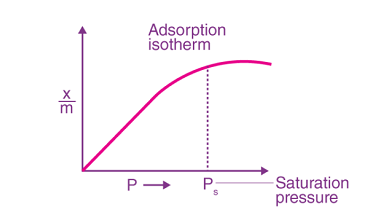
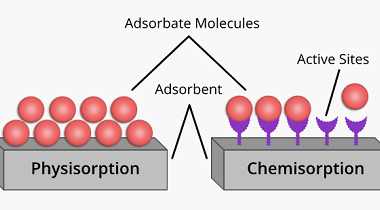
Surfactants and micelles (only definitions and examples)
Surfactants are compounds that reduce the surface tension between two different substances, typically between a liquid and a gas or between two immiscible liquids. The word “surfactant” is a contraction of “surface active agent.” Surfactants have a hydrophilic (water-loving) head and a hydrophobic (water-repelling) tail, which allows them to interact with both water and oil.…