Parametric equations of a circle
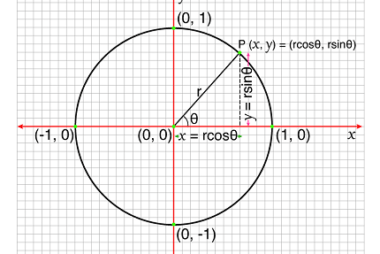
A circle with center (a,b) and radius r can be parameterized using the following parametric equations: x = a + r cos(t) y = b + r sin(t) where t is the parameter that ranges from 0 to 2π. These equations describe the position of any point on the circle in terms of its angle…