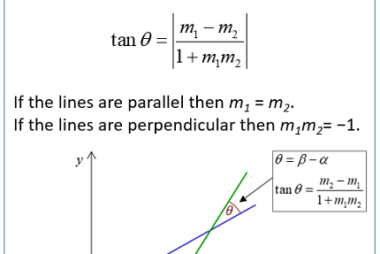
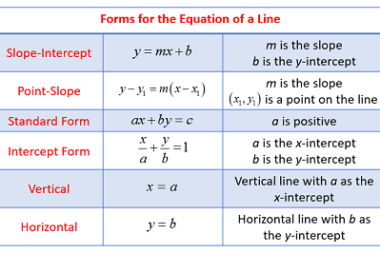
Distance of a point from a line
To find the distance between a point and a line in analytical geometry, you can use the formula: distance = |ax + by + c| / √(a^2 + b^2) where a, b, and c are constants that represent the coefficients of the equation of the line in the form of ax + by + c…