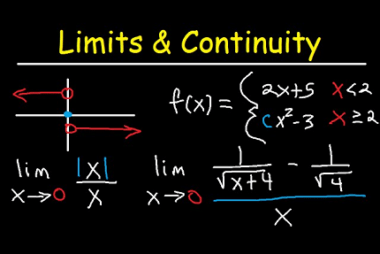
Differential Calculus Difference
Differential calculus is a branch of mathematics that deals with the study of rates of change and slopes of curves. It focuses on finding the derivative of a function, which is the instantaneous rate of change of the function at a particular point. The derivative gives us information about the steepness of a curve at…