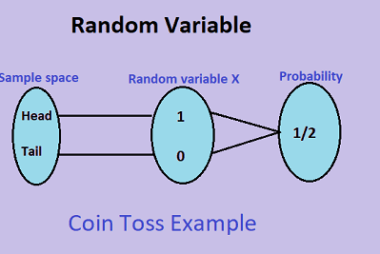
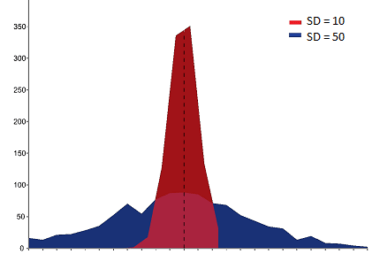
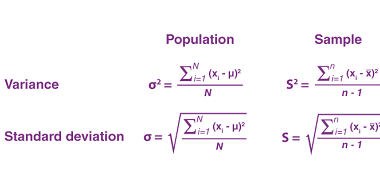Mean and variance of the random variable
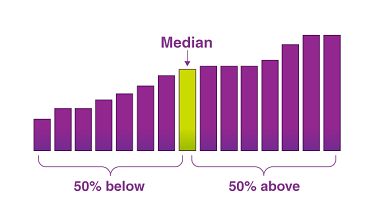
The mean of a random variable is also known as its expected value. It is a measure of the central tendency of the distribution of the random variable. The expected value of a discrete random variable X with possible values x1, x2, …, xn and corresponding probabilities P(X = x1), P(X = x2), …, P(X…