Integrated Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Chemical Kinetics
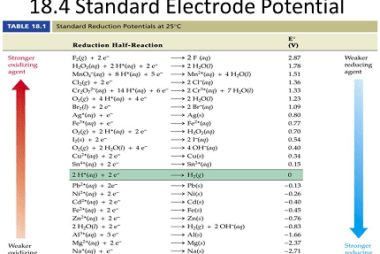
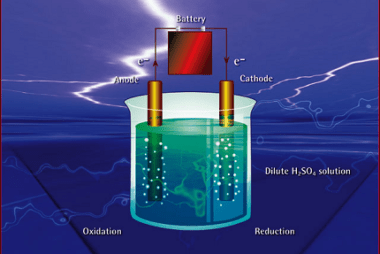
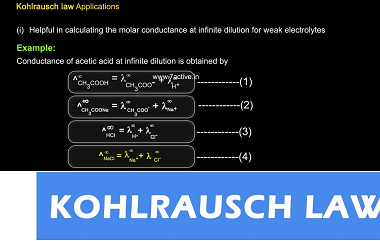
Chemical Kinetics Chemical kinetics is the branch of chemistry that deals with the study of the rates at which chemical reactions occur and the factors that influence these rates. It focuses on understanding the mechanisms by which reactants transform into products and the factors that affect the speed of these reactions. Key concepts in chemical…