The extraction of crude metal from concentrated ores involves several steps that depend on the nature of the ore and the metal to be extracted. Here is a general process for extracting crude metal from concentrated ores:
- Crushing and grinding: The concentrated ore is first crushed and ground into a fine powder.
- Roasting or calcination: The powdered ore is then subjected to a high-temperature process known as roasting or calcination. This process involves heating the ore in the presence of air or oxygen, which causes it to react and release any volatile impurities, leaving behind the metal oxide.
- Reduction: The metal oxide is then reduced to the metal by a suitable reducing agent. This can be done using one of several methods, including:
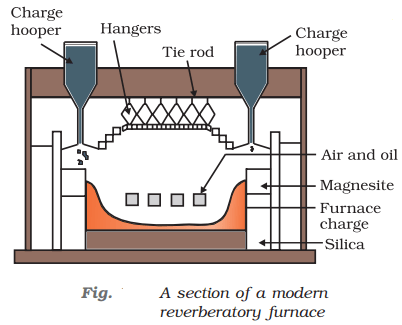
- Smelting: The metal oxide is heated with a reducing agent such as coke or charcoal in a furnace. The metal melts and collects at the bottom of the furnace, while any impurities are left behind as slag.
- Electrolysis: In this process, an electric current is passed through a solution of the metal salt, causing the metal to be deposited on the cathode.
- Hydrogen reduction: Some metals, such as iron, can be reduced using hydrogen gas at high temperatures.
- Refining: The crude metal obtained by reduction may still contain impurities, so it is refined to remove any remaining impurities. This can be done using one of several methods, including:
- Electrolytic refining: The crude metal is dissolved in an electrolyte and an electric current is passed through the solution, causing the pure metal to be deposited on the cathode.
- Distillation: This method is used for metals with low boiling points, such as zinc and mercury. The crude metal is heated, and the pure metal vaporizes and is condensed and collected.
- Zone refining: This method is used for metals with high melting points, such as silicon and germanium. A small region of the metal is melted and moved along the length of the ingot, leaving behind the impurities.
These are the basic steps involved in extracting crude metal from concentrated ores. However, the specific process used may vary depending on the nature of the ore and the metal to be extracted.
What is Required Isolation of Metals Extraction of crude metal from concentrated ores
The required isolation of metals extraction of crude metal from concentrated ores is the process of extracting pure metals from concentrated ores through a series of chemical and physical processes. It involves separating the metal from the rest of the ore, which may include various impurities and unwanted elements.
To achieve this, the concentrated ore is first treated with chemical agents and/or heat to remove the unwanted materials, leaving behind a metal-rich compound. This compound is then subjected to further processing, which involves various techniques such as roasting, smelting, and refining to extract the pure metal.
The isolation of metals is an important process as it allows us to obtain pure metals that are necessary for a wide range of applications, including construction, electronics, and transportation. In addition, pure metals are often required in industries such as aerospace and medicine, where even minor impurities can have significant consequences.
Overall, the required isolation of metals extraction of crude metal from concentrated ores is a complex process that requires careful planning and execution to ensure that the extracted metal is of high purity and quality.
Who is Required Isolation of Metals Extraction of crude metal from concentrated ores
“Required Isolation of Metals Extraction of crude metal from concentrated ores” is not a person. It is a process that involves a series of chemical and physical steps to extract pure metals from concentrated ores. The process involves various techniques such as crushing, grinding, roasting, smelting, and refining to extract the pure metal. The objective of the process is to separate the metal from the rest of the ore, which may include various impurities and unwanted elements. The isolation of metals is an important process as it allows us to obtain pure metals that are necessary for a wide range of applications in various industries.
When is Required Isolation of Metals Extraction of crude metal from concentrated ores
The required isolation of metals extraction of crude metal from concentrated ores is carried out whenever there is a need to extract a specific metal from its concentrated ore. This may be required for various reasons, such as meeting the demand for a particular metal, obtaining a higher purity metal for specific applications, or recovering valuable metals from waste materials.
The process of extraction is carried out when the concentration of the metal in the ore is high enough to make extraction economically viable. The specific timing for the process may vary depending on several factors, including the type of metal, the quality of the ore, and the market demand for the metal.
In general, the required isolation of metals extraction of crude metal from concentrated ores is an ongoing process that is carried out by mining companies and metal producers worldwide. The demand for metals is constantly growing due to their wide range of applications, which means that the process of extracting metals from concentrated ores will continue to be necessary for the foreseeable future.
Where is Required Isolation of Metals Extraction of crude metal from concentrated ores
The required isolation of metals extraction of crude metal from concentrated ores is typically carried out in specialized facilities, such as mines, smelters, and refineries. The location of these facilities may vary depending on the location of the ore deposits, market demand, and other factors.
Mining companies typically operate mines where the concentrated ores are extracted from the earth using various methods such as open-pit mining or underground mining. Once the ore is extracted, it is transported to specialized facilities such as smelters or concentrators, where the required isolation of metals extraction process takes place.
Smelting facilities are used to extract the metal from the concentrated ore through high-temperature processes such as roasting and smelting. These facilities may be located near the mines or may be located in other regions where the infrastructure, such as transportation and energy supply, is available.
Refining facilities are used to further purify the extracted metal by removing any remaining impurities. These facilities are typically located close to the smelters, and they may use various techniques such as electrolysis, distillation, or zone refining.
Overall, the required isolation of metals extraction of crude metal from concentrated ores may occur in different locations depending on the specific process and the availability of the necessary infrastructure and resources.
How is Required Isolation of Metals Extraction of crude metal from concentrated ores
The required isolation of metals extraction of crude metal from concentrated ores is a complex process that involves various steps, both physical and chemical, to extract pure metals from concentrated ores. The following are the general steps involved in the extraction process:
- Crushing and Grinding: The concentrated ore is first crushed and ground to reduce its particle size.
- Concentration: The crushed ore is then subjected to a process called concentration, which involves separating the metal from the rest of the ore. This can be achieved through various techniques such as gravity separation, magnetic separation, or froth flotation.
- Roasting: Some concentrated ores may require roasting, which involves heating the ore in the presence of oxygen. This process can help remove unwanted impurities such as sulfur and carbon, leaving behind a metal oxide.
- Smelting: The metal oxide is then subjected to a process called smelting, which involves heating it to high temperatures in the presence of a reducing agent. This converts the metal oxide to its pure metal form.
- Refining: The pure metal obtained from smelting may still contain impurities that need to be removed. The metal is refined through processes such as electrolysis, distillation, or zone refining to obtain a high-purity metal.
- Casting or Forming: The final step involves casting or forming the pure metal into the desired shape or form.
Overall, the required isolation of metals extraction of crude metal from concentrated ores is a complex and multi-step process that requires specialized knowledge and equipment. The specific techniques used may vary depending on the type of ore and the metal being extracted.
Case Study on Isolation of Metals Extraction of crude metal from concentrated ores
One example of the required isolation of metals extraction of crude metal from concentrated ores is the extraction of copper from its concentrated ore, which is typically chalcopyrite (CuFeS2). The following is a brief case study of the extraction process:
- Crushing and Grinding: The chalcopyrite ore is first crushed and ground to reduce its particle size.
- Concentration: The crushed ore is then subjected to a process called froth flotation, which involves adding water and chemicals to the ore to form a slurry. Air is then bubbled through the slurry, causing the copper sulfide particles to float to the surface and form a froth. This froth is then skimmed off and dried, resulting in a concentrated copper sulfide mineral called copper concentrate.
- Roasting: The copper concentrate is then roasted in a furnace at a high temperature to remove any remaining sulfur and convert the copper sulfide to copper oxide (CuO).
- Smelting: The copper oxide is then subjected to a process called smelting, which involves heating it in a furnace with a reducing agent such as coke (a form of coal) or charcoal. This reduces the copper oxide to its pure metal form and also produces a waste product called slag.
- Refining: The pure copper obtained from smelting may still contain impurities such as iron, sulfur, and other metals. The copper is refined through a process called electrolysis, which involves placing the pure copper in an electrolytic cell with an electrolyte solution and passing an electric current through it. This causes the impurities to separate and settle at the bottom of the cell, leaving behind pure copper.
- Casting or Forming: The final step involves casting the pure copper into the desired shape or form, such as copper wire, pipes, or sheets.
Overall, the extraction of copper from its concentrated ore is a complex process that involves multiple steps and specialized equipment. However, the resulting high-purity copper is an essential material used in a wide range of applications, including electrical wiring, plumbing, and industrial machinery.
White paper on Isolation of Metals Extraction of crude metal from concentrated ores
Introduction:
Isolation of metals extraction of crude metal from concentrated ores is a critical process in the mining and metallurgical industries. The extraction process involves various physical and chemical techniques to extract pure metals from concentrated ores. This white paper provides an overview of the extraction process, including the different techniques used, the equipment involved, and the environmental impact of the process.
Extraction Techniques:
There are various techniques used to extract metals from concentrated ores. The following are the most common techniques used:
- Froth Flotation: This is a physical separation technique that uses water and chemicals to create a slurry. Air is bubbled through the slurry, causing the metal-containing particles to float to the surface and form a froth. The froth is then collected and dried, resulting in a concentrated metal mineral.
- Smelting: This is a high-temperature process that involves heating the concentrated ore with a reducing agent, such as coke or charcoal, in a furnace. This converts the metal oxide to its pure metal form and also produces a waste product called slag.
- Electrolysis: This is an electrochemical process that involves passing an electric current through a solution containing the metal ions. This causes the metal ions to deposit onto the cathode, forming a pure metal.
Equipment Used:
The equipment used in the extraction process depends on the technique used. For example, froth flotation requires specialized flotation machines, while smelting requires furnaces and other high-temperature equipment. Electrolysis requires specialized electrolytic cells and power sources.
Environmental Impact:
The extraction of metals from concentrated ores can have a significant environmental impact. The use of chemicals in froth flotation can lead to water pollution, while the high temperatures used in smelting can result in air pollution. Electrolysis requires a significant amount of electricity, which can come from non-renewable sources and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the extraction of metals can result in the removal of large areas of land and destruction of habitats.
Conclusion:
The required isolation of metals extraction of crude metal from concentrated ores is a complex and multi-step process that requires specialized knowledge and equipment. The specific techniques used may vary depending on the type of ore and the metal being extracted. The process can have a significant environmental impact, and therefore, it is essential to implement sustainable mining practices that minimize the impact on the environment.
