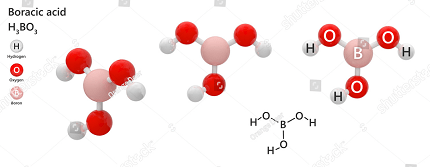
Orthoboric acid, also known as boracic acid or H3BO3, is a white, crystalline, weak acid that belongs to Group 13 of the periodic table. It is composed of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen atoms, with a chemical formula of H3BO3.
Orthoboric acid is commonly used in the production of boron compounds, as a mild antiseptic, and as a flame retardant. It is also used as a component in various industrial processes, such as the manufacture of glass, ceramics, and enamels.
In its solid form, orthoboric acid has a melting point of 169 °C (336 °F) and a boiling point of 300 °C (572 °F). It is soluble in water and has a weak acidic taste. When heated, it decomposes to form water and boron trioxide (B2O3).
Orthoboric acid is considered to be relatively safe for human use when used in appropriate concentrations, although ingestion of large amounts may cause gastrointestinal irritation. It is also considered to be non-toxic to aquatic life and the environment in general.
What is Required p-Block Elements Group 13 Orthoboric acid
The p-Block elements are the elements belonging to groups 13 to 18 of the periodic table. Group 13 elements include boron (B), aluminum (Al), gallium (Ga), indium (In), and thallium (Tl).
Orthoboric acid, which has the chemical formula H3BO3, is a compound that contains boron, which is a Group 13 element. It is formed by the reaction of boron oxide (B2O3) with water, and it can also be produced by the reaction of borax (Na2B4O7) with a strong acid such as hydrochloric acid (HCl).
Orthoboric acid is an important compound in the chemistry of boron, which is a metalloid element in Group 13 of the periodic table. Boron and its compounds have a wide range of applications in industry, medicine, and agriculture. For example, boron compounds are used as catalysts, flame retardants, and in the production of fiberglass, ceramics, and semiconductors. Boron is also an essential micronutrient for plants, and boron-containing compounds are used in some medical treatments, such as for arthritis and cancer.
In summary, orthoboric acid is a compound that contains boron, a Group 13 element, and it is an important compound in the chemistry of boron and its applications in industry, medicine, and agriculture.
When is Required p-Block Elements Group 13 Orthoboric acid
Orthoboric acid, which is a compound containing boron, a Group 13 element, can be used in a variety of applications due to its unique chemical and physical properties. Some of the applications of orthoboric acid are:
- Glass production: Orthoboric acid is used as a flux in the production of glass. It helps to reduce the melting point of the glass and improve its chemical stability.
- Antiseptic: Orthoboric acid can be used as a mild antiseptic to treat minor cuts and wounds. It has antifungal and antibacterial properties and can help to prevent infections.
- Flame retardant: Orthoboric acid is used as a flame retardant in the production of textiles, plastics, and other materials. It helps to reduce the flammability of these materials and make them safer to use.
- Insecticide: Orthoboric acid can be used as an insecticide to control pests such as ants, cockroaches, and termites. It works by disrupting the digestive system of the insects and is considered to be a low-toxicity option for pest control.
- Nuclear industry: Orthoboric acid is used in the nuclear industry as a neutron absorber. It helps to control the rate of nuclear reactions and prevent nuclear accidents.
In summary, orthoboric acid, a compound containing boron, a Group 13 element, can be used in a variety of applications such as glass production, antiseptic, flame retardant, insecticide, and in the nuclear industry.
Where is Required p-Block Elements Group 13 Orthoboric acid
Orthoboric acid, which contains boron, a Group 13 element, can be found in various places and products. Some examples include:
- In the earth’s crust: Boron is a naturally occurring element that can be found in the earth’s crust. Orthoboric acid can be produced by the reaction of boron oxide with water, which can be obtained from boron-rich minerals and ores.
- Glass production: Orthoboric acid is used as a flux in the production of glass. It is added to the raw materials used to make glass to lower the melting point and improve the chemical stability of the final product.
- Antiseptic: Orthoboric acid can be found in some antiseptic products such as eyewashes and skin lotions. It is used to treat minor cuts and wounds and has antifungal and antibacterial properties.
- Flame retardant: Orthoboric acid can be found in some textiles, plastics, and other materials as a flame retardant. It helps to reduce the flammability of these materials and make them safer to use.
- Insecticide: Orthoboric acid can be found in some insecticide products used to control pests such as ants, cockroaches, and termites. It works by disrupting the digestive system of the insects and is considered to be a low-toxicity option for pest control.
- Nuclear industry: Orthoboric acid is used in the nuclear industry as a neutron absorber. It can be found in nuclear reactors to control the rate of nuclear reactions and prevent nuclear accidents.
In summary, orthoboric acid, which contains boron, a Group 13 element, can be found in the earth’s crust, glass products, antiseptics, flame retardants, insecticides, and the nuclear industry.
Nomenclature of p-Block Elements Group 13 Orthoboric acid
The systematic name of Group 13 Orthoboric acid is trihydroxidoboron. However, it is more commonly known as boracic acid or orthoboric acid, which comes from its chemical structure and properties.
In the IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) nomenclature system, the name of the compound is derived from the prefix “borate” followed by the oxidation state of the boron atom in parentheses, and then the name of the counter ion. For example, the sodium salt of orthoboric acid would be named as sodium trihydroxidoborate(III) or sodium borate(III).
In the traditional naming system, orthoboric acid is named based on the element boron and the suffix “-ic acid.” The prefix “ortho-” is used to indicate that the acid has three hydroxyl groups attached to the boron atom. Therefore, orthoboric acid is also known as boracic acid, which refers to the acid derived from boron.
Overall, the most commonly used name for this compound is orthoboric acid, which is widely recognized and accepted in both the scientific and commercial fields.
How is Required p-Block Elements Group 13 Orthoboric acid
Orthoboric acid is a compound that can be produced by the reaction of boron oxide (B2O3) with water. The chemical equation for this reaction is:
B2O3 + 3H2O → 2H3BO3
This reaction produces orthoboric acid (H3BO3) as the main product. The reaction is exothermic, meaning that heat is released during the reaction.
In industry, orthoboric acid can also be produced by the reaction of borax (Na2B4O7) with a strong acid such as hydrochloric acid (HCl). The reaction can be represented by the following equation:
Na2B4O7 + 2HCl + 5H2O → 4H3BO3 + 2NaCl
This reaction produces orthoboric acid (H3BO3) and sodium chloride (NaCl) as the main products.
Orthoboric acid is a white, crystalline solid that is soluble in water and has a weak acidic taste. It is commonly used in a variety of applications due to its unique chemical and physical properties, such as its ability to act as a mild antiseptic, flux in glass production, flame retardant, insecticide, and neutron absorber in the nuclear industry.
Case Study on p-Block Elements Group 13 Orthoboric acid
Here is a case study on the use of orthoboric acid, a compound containing boron, a Group 13 element, in the production of glass:
Case Study: Orthoboric Acid in Glass Production
Background:
Glass is a widely used material in various applications such as windows, lenses, mirrors, and packaging. The production of glass involves melting a mixture of raw materials, including silica, soda ash, and limestone, at high temperatures. However, the high melting point of silica can make the production process difficult and energy-intensive. To reduce the melting point of silica and improve the chemical stability of the final product, a fluxing agent such as orthoboric acid can be added to the raw materials.
Challenge:
A glass manufacturer is looking to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of their production process. They are exploring the use of orthoboric acid as a fluxing agent to reduce the melting point of silica and improve the chemical stability of the final product.
Solution:
The glass manufacturer decides to add orthoboric acid to their raw materials to act as a fluxing agent. Orthoboric acid can reduce the melting point of silica and other raw materials, allowing them to be melted at lower temperatures. This not only saves energy but also reduces the wear and tear on the production equipment. In addition, orthoboric acid can improve the chemical stability of the final product by reducing the amount of impurities that can cause cloudiness and other defects in the glass.
Results:
By using orthoboric acid as a fluxing agent, the glass manufacturer was able to reduce the melting point of the raw materials and produce high-quality glass with improved chemical stability. This resulted in a more efficient and cost-effective production process, with lower energy costs and less wear and tear on the production equipment. The use of orthoboric acid also improved the quality of the final product, which increased customer satisfaction and improved the company’s reputation.
Conclusion:
Orthoboric acid, a compound containing boron, a Group 13 element, can be used as a fluxing agent in glass production to reduce the melting point of raw materials and improve the chemical stability of the final product. By using orthoboric acid, glass manufacturers can produce high-quality glass more efficiently and cost-effectively, resulting in improved customer satisfaction and a better reputation for the company.
White paper on Group 13 Orthoboric acid
Here is a white paper on the properties and applications of orthoboric acid, a compound containing boron, a Group 13 element:
Introduction:
Orthoboric acid (H3BO3), also known as boracic acid, is a compound containing boron, a Group 13 element. It is a white, crystalline solid that is soluble in water and has a weak acidic taste. Orthoboric acid is commonly used in a variety of applications due to its unique chemical and physical properties.
Properties:
Orthoboric acid has a molecular weight of 61.83 g/mol and a melting point of 170.9°C. It has a density of 1.435 g/cm³ and a boiling point of 300°C. Orthoboric acid is a weak acid with a pKa of 9.2, meaning that it is less acidic than most other acids. It is non-flammable and non-toxic, making it a safe compound to handle and use.
Applications:
- Glass Production: Orthoboric acid is commonly used as a fluxing agent in the production of glass. It reduces the melting point of silica and other raw materials, allowing them to be melted at lower temperatures. This not only saves energy but also reduces the wear and tear on the production equipment. In addition, orthoboric acid can improve the chemical stability of the final product by reducing the amount of impurities that can cause cloudiness and other defects in the glass.
- Antiseptic: Orthoboric acid has mild antiseptic properties and can be used as a topical treatment for minor skin irritations, such as cuts and burns. It can also be used as an eye wash to treat conjunctivitis and other eye infections.
- Flame Retardant: Orthoboric acid is used as a flame retardant in various applications, including textiles, plastics, and wood. It acts as a char-forming agent that slows down the spread of flames and reduces the amount of smoke and toxic gases released during a fire.
- Insecticide: Orthoboric acid is used as an insecticide to control pests such as ants, cockroaches, and termites. It works by disrupting the insect’s digestive system and causing dehydration.
- Neutron Absorber: Orthoboric acid is used in the nuclear industry as a neutron absorber. It can be used to control nuclear reactions and prevent accidents.
Conclusion:
Orthoboric acid, a compound containing boron, a Group 13 element, has a wide range of applications due to its unique chemical and physical properties. It is commonly used as a fluxing agent in glass production, a mild antiseptic, a flame retardant, an insecticide, and a neutron absorber in the nuclear industry. Orthoboric acid’s versatility and safety make it a valuable compound in many industries.
