Group 15 of the periodic table consists of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), and bismuth (Bi). Both nitrogen and phosphorus form oxides and oxoacids.
Oxides of Nitrogen:
- Nitrogen Monoxide or Nitric Oxide (NO)
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2)
- Nitrous Oxide (N2O)
- Dinitrogen Trioxide (N2O3)
- Dinitrogen Tetroxide (N2O4)
- Dinitrogen Pentoxide (N2O5)
Oxoacids of Phosphorus:
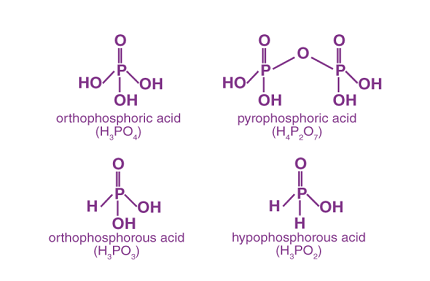
- Phosphoric Acid (H3PO4)
- Phosphorous Acid (H3PO3)
- Hypophosphorous Acid (H3PO2)
- Meta-Phosphoric Acid (HPO3)
- Pyrophosphoric Acid (H4P2O7)
- Orthophosphorous Acid (H3PO2)
What is Required p-Block Elements Group 15 Oxides of Nitrogen and Oxoacids of phosphorus
The p-block elements in Group 15 of the periodic table, namely nitrogen and phosphorus, exhibit the formation of oxides and oxoacids.
Nitrogen oxides are a group of gases that are formed as a result of the combustion of fossil fuels and other industrial processes. Nitrogen oxides can lead to the formation of acid rain, smog, and other environmental issues. The most common oxides of nitrogen are nitrogen monoxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2), which are important intermediates in the formation of other nitrogen oxides. Nitrous oxide (N2O) is another important oxide of nitrogen that is used as an anesthetic gas and in rocket propulsion systems.
Phosphorus oxides are compounds that are formed by the reaction of phosphorus with oxygen. The most important phosphorus oxide is phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5), which is a white, crystalline solid that is used as a desiccant and as a reagent in organic chemistry. Phosphorus also forms several oxoacids, which are acids that contain oxygen and phosphorus. Some of the most important oxoacids of phosphorus include phosphoric acid (H3PO4), phosphorous acid (H3PO3), and hypophosphorous acid (H3PO2). These oxoacids are used in a variety of industrial processes, including the production of fertilizers and detergents.
When is Required p-Block Elements Group 15 Oxides of Nitrogen and Oxoacids of phosphorus
The formation of oxides and oxoacids of Group 15 p-block elements, namely nitrogen and phosphorus, occurs when these elements react with oxygen.
Nitrogen oxides are formed during the combustion of fossil fuels, and also during lightning strikes and microbial activities in the soil. They are also used in the manufacturing of fertilizers and in the production of nitric acid.
Phosphorus oxides are formed when phosphorus reacts with oxygen. The most common and important phosphorus oxide is phosphorus pentoxide, which is used as a reagent in organic chemistry and as a desiccant.
Oxoacids of phosphorus are formed when phosphorus reacts with oxygen and water. They are important in various industrial applications, such as the production of fertilizers and detergents.
In summary, the formation of oxides and oxoacids of Group 15 p-block elements occurs during various natural and industrial processes, when these elements react with oxygen and/or water.
Where is Required p-Block Elements Group 15 Oxides of Nitrogen and Oxoacids of phosphorus
Group 15 of the periodic table consists of nitrogen, phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, and bismuth, and these elements are generally referred to as p-block elements.
Nitrogen is found in the atmosphere as nitrogen gas, which makes up about 78% of the Earth’s atmosphere. Nitrogen oxides are formed during various natural and industrial processes, such as lightning strikes, forest fires, and fossil fuel combustion. Nitrogen oxides also contribute to the formation of acid rain, smog, and other environmental issues.
Phosphorus is found in various minerals, such as apatite, and in living organisms, such as DNA and bones. Phosphorus is also an important component of fertilizers and is used in various industrial applications. Phosphorus oxides, such as phosphorus pentoxide, are used as reagents in organic chemistry and as desiccants. Oxoacids of phosphorus, such as phosphoric acid, are used in the production of fertilizers, detergents, and other industrial processes.
In summary, nitrogen and phosphorus, which are the main elements involved in the formation of oxides and oxoacids of Group 15 p-block elements, are found in various natural and industrial sources, including the atmosphere, minerals, living organisms, and various chemical processes.
How is Required p-Block Elements Group 15 Oxides of Nitrogen and Oxoacids of phosphorus
The formation of oxides and oxoacids of Group 15 p-block elements, nitrogen and phosphorus, occurs through various chemical reactions.
Nitrogen oxides are formed during the combustion of fossil fuels, in which nitrogen gas in the air reacts with oxygen gas. The high temperatures and pressures of the combustion process cause the nitrogen and oxygen to react, forming nitrogen oxides such as NO and NO2. Nitrogen oxides can also be formed through microbial activities in the soil and by lightning strikes in the atmosphere.
Phosphorus oxides are formed when phosphorus reacts with oxygen gas. The most common and important phosphorus oxide is phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5), which is formed when white phosphorus (P4) is burned in excess oxygen. Phosphorus pentoxide reacts with water to form phosphoric acid (H3PO4) and other oxoacids of phosphorus.
Oxoacids of phosphorus, such as phosphoric acid, are formed by the reaction of phosphorus oxides with water. Phosphoric acid is formed when phosphorus pentoxide reacts with water, and this reaction is highly exothermic. Phosphoric acid can also be formed by the oxidation of phosphorus with nitric acid or by the reaction of phosphorus with concentrated sulfuric acid.
In summary, the formation of oxides and oxoacids of Group 15 p-block elements occurs through various chemical reactions involving nitrogen, phosphorus, oxygen, and water. These reactions can occur naturally, such as through microbial activities and lightning strikes, or through industrial processes, such as fossil fuel combustion and the production of fertilizers and other chemicals.
Nomenclature of p-Block Elements Group 15 Oxides of Nitrogen and Oxoacids of phosphorus
The nomenclature of p-Block Elements Group 15 oxides of nitrogen and oxoacids of phosphorus follows certain naming conventions based on the oxidation states and the number of oxygen atoms present in the compounds.
Nitrogen oxides are named according to the oxidation state of nitrogen. For example, nitrogen oxide with oxidation state +1 is named as nitrous oxide (N2O) and with oxidation state +2 is named as nitrogen dioxide (NO2).
Oxoacids of phosphorus are named according to the number of oxygen atoms attached to the phosphorus atom. For example, when phosphorus is bonded with three oxygen atoms, the compound is called phosphoric acid (H3PO4), and when it is bonded with two oxygen atoms, the compound is called phosphorous acid (H3PO3).
The prefixes hypo- and per- are used to indicate lower or higher oxidation states, respectively. For example, hypophosphorous acid (H3PO2) contains one less oxygen atom than phosphorous acid (H3PO3), while perchloric acid (HClO4) contains one more oxygen atom than chloric acid (HClO3).
In summary, the nomenclature of p-Block Elements Group 15 oxides of nitrogen and oxoacids of phosphorus follows a systematic naming convention based on the oxidation state and the number of oxygen atoms attached to the central atom.
Case Study on p-Block Elements Group 15 Oxides of Nitrogen and Oxoacids of phosphorus
One of the most significant applications of p-Block Elements Group 15 oxides of Nitrogen and Oxoacids of phosphorus is in the field of agriculture as fertilizers. Let’s take a look at a case study that illustrates the use of these compounds in agriculture.
Case Study: Use of p-Block Elements Group 15 oxides in agriculture
Nitrogen and phosphorus are two essential nutrients required for plant growth and development. Nitrogen is required for the formation of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins, while phosphorus is required for various cellular processes, such as energy transfer and DNA synthesis. In many cases, the availability of nitrogen and phosphorus in soil is limited, and as a result, plants cannot grow to their full potential.
To overcome this problem, various fertilizers containing p-Block Elements Group 15 oxides of nitrogen and phosphorus are used in agriculture. One such example is ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3), which is a common nitrogen-based fertilizer. Ammonium nitrate contains nitrogen in the form of ammonium ions (NH4+) and nitrate ions (NO3-), which are readily taken up by plants and used for their growth and development.
Another example of a fertilizer containing p-Block Elements Group 15 oxides is triple superphosphate (Ca(H2PO4)2), which is a common phosphorus-based fertilizer. Triple superphosphate contains phosphorus in the form of orthophosphate ions (H2PO4-), which are readily taken up by plants and used for their growth and development.
Both of these fertilizers have significantly improved the agricultural yield by providing plants with the essential nutrients required for their growth and development. However, excessive use of these fertilizers can also have negative consequences, such as the pollution of water bodies due to the runoff of excess fertilizers.
In summary, p-Block Elements Group 15 oxides of nitrogen and phosphorus play a crucial role in the field of agriculture as fertilizers. The use of these compounds has significantly improved agricultural yield by providing plants with the essential nutrients required for their growth and development. However, it is important to use these fertilizers judiciously to avoid negative consequences such as water pollution.
White paper on p-Block Elements Group 15 Oxides of Nitrogen and Oxoacids of phosphorus
Introduction:
p-Block Elements Group 15 oxides of Nitrogen and Oxoacids of phosphorus are an important class of inorganic compounds with significant applications in various fields such as agriculture, medicine, and industry. Nitrogen and phosphorus are two of the most abundant elements on earth, and their oxides and oxoacids play a crucial role in various biochemical processes.
Properties and Applications of Nitrogen Oxides:
Nitrogen oxides are a family of inorganic compounds that contain nitrogen and oxygen. These compounds exhibit a wide range of properties and have several applications in various fields.
One of the most important nitrogen oxides is nitric oxide (NO), which is a colorless gas with a slightly sweet odor. Nitric oxide is an important signaling molecule in the human body, where it regulates various physiological processes such as blood pressure, inflammation, and neurotransmission. It also plays a role in the immune system, where it helps to fight against bacterial and viral infections.
Another important nitrogen oxide is nitrogen dioxide (NO2), which is a reddish-brown gas with a pungent odor. Nitrogen dioxide is a highly reactive compound that can cause respiratory problems, especially in people with pre-existing respiratory conditions such as asthma. It is also a major contributor to air pollution and is responsible for the formation of acid rain.
Nitrogen oxides also have several industrial applications, such as in the production of nitric acid, which is used in the manufacture of fertilizers, explosives, and dyes.
Properties and Applications of Oxoacids of Phosphorus:
Oxoacids of phosphorus are a family of inorganic compounds that contain phosphorus, oxygen, and hydrogen. These compounds exhibit a wide range of properties and have several applications in various fields.
One of the most important oxoacids of phosphorus is phosphoric acid (H3PO4), which is a colorless, odorless, and crystalline solid. Phosphoric acid is widely used in the manufacture of fertilizers, detergents, and food and beverages. It is also used as a rust inhibitor and as an etchant in the electronics industry.
Another important oxoacid of phosphorus is phosphorous acid (H3PO3), which is a colorless, crystalline solid with a pungent odor. Phosphorous acid is used as a reducing agent in the chemical industry and as a fungicide in agriculture.
Conclusion:
p-Block Elements Group 15 oxides of Nitrogen and Oxoacids of phosphorus are an important class of inorganic compounds with diverse applications in various fields. Nitrogen oxides play a crucial role in various physiological processes in the human body and have several industrial applications. Oxoacids of phosphorus are widely used in the manufacture of fertilizers, detergents, and food and beverages, and also have important applications in the electronics industry and in agriculture. The properties and applications of these compounds make them an important area of research, and further studies in this field are necessary to understand their behavior and potential applications in the future.
