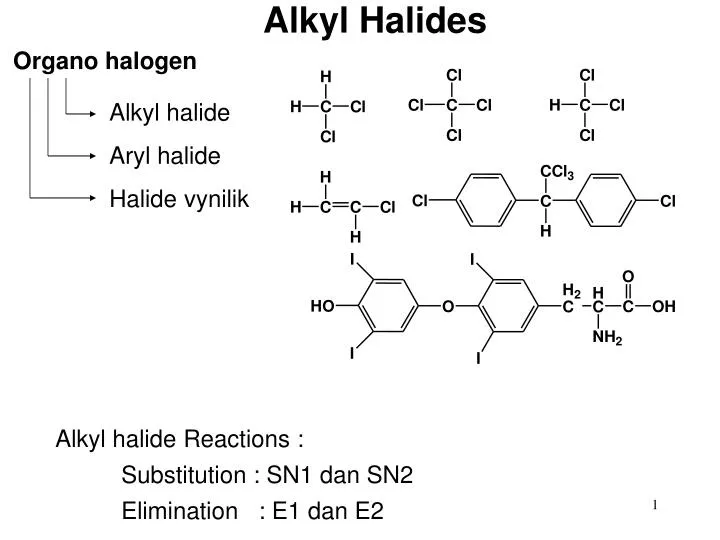
Alkyl halides, also known as haloalkanes or alkyl halides, are organic compounds that contain a halogen atom bonded to a carbon atom in an alkyl group. They are commonly used as starting materials in organic synthesis reactions.
Here are some important topics related to alkyl halides that are typically covered in JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate courses:
- Nomenclature: The IUPAC rules for naming alkyl halides involve identifying the longest carbon chain containing the halogen atom and numbering the chain so that the halogen atom has the lowest possible number.
- Physical properties: Alkyl halides have higher boiling points and densities compared to their parent alkanes due to the polar nature of the C-X bond. They are also relatively insoluble in water but soluble in non-polar solvents.
- Preparation: Alkyl halides can be prepared by several methods, including the addition of halogens to alkenes or alkynes, the substitution of a hydroxyl group in an alcohol with a halogen, and the free radical halogenation of alkanes.
- Reactions: Alkyl halides undergo various reactions, such as nucleophilic substitution, elimination, and addition reactions. The choice of reaction pathway depends on the nature of the nucleophile or base and the type of alkyl halide.
- Stereochemistry: Alkyl halides can exhibit stereoisomerism due to the presence of chiral carbon atoms or double bonds. The stereochemistry of the reactants and products must be considered when predicting the outcome of a reaction.
- Uses: Alkyl halides are used in a variety of industrial applications, such as as solvents, refrigerants, and pesticides. They are also used as starting materials in the synthesis of many important organic compounds, such as pharmaceuticals and plastics.
It is important to have a thorough understanding of the properties and reactions of alkyl halides, as they are commonly encountered in organic chemistry reactions.
History of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Alkyl Halides
The study of alkyl halides has been an important part of organic chemistry since the early 19th century. In 1825, French chemist Eugene Soubeiran prepared the first known alkyl halide, ethyl chloride, by treating ethanol with hydrochloric acid. However, it wasn’t until the mid-19th century that the significance of alkyl halides in organic chemistry was fully appreciated.
In the 1850s, German chemist August Wilhelm von Hofmann made significant contributions to the study of alkyl halides. He discovered that alkyl halides could be converted to amines by reacting them with ammonia, a reaction known as the Hofmann degradation. He also developed the concept of substitution and elimination reactions in organic chemistry, which are fundamental to understanding the reactions of alkyl halides.
During the 20th century, the study of alkyl halides continued to grow and expand. In the 1920s, American chemist John Christian Warner discovered that alkyl halides could undergo free radical halogenation, a reaction that is widely used in industrial processes to this day.
In the 1950s and 60s, the study of stereochemistry and asymmetric synthesis led to important discoveries in the field of alkyl halides. The work of Nobel laureate Derek Barton, who developed the concept of conformational analysis, was particularly influential in this regard.
In more recent years, the study of alkyl halides has been closely tied to the field of organic synthesis, which involves using chemical reactions to create complex organic molecules from simpler starting materials. Alkyl halides are commonly used as starting materials in organic synthesis, and their properties and reactions are studied extensively in JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate courses in order to prepare students for careers in organic chemistry and related fields.
Importance of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Alkyl Halides
The study of alkyl halides is an important part of the JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in organic chemistry. Here are some of the key reasons why:
- Understanding of Organic Chemistry: Alkyl halides are a fundamental class of organic compounds, and their study provides a foundation for understanding many other organic reactions and functional groups. Students who master the concepts related to alkyl halides will be well-prepared to tackle more advanced topics in organic chemistry.
- Practical Applications: Alkyl halides are used in a wide variety of industrial applications, such as as solvents, refrigerants, and pesticides. They are also used as starting materials in the synthesis of many important organic compounds, such as pharmaceuticals and plastics. A strong understanding of alkyl halides is essential for students who plan to pursue careers in these fields.
- Relevance to JEE Exam: The JEE (Main+Advanced) exam places a significant emphasis on organic chemistry, and alkyl halides are a commonly tested topic. Students who have a thorough understanding of the properties and reactions of alkyl halides will be better equipped to perform well on the exam.
- Foundation for Further Study: For students who plan to pursue advanced studies in organic chemistry, a strong understanding of alkyl halides is essential. The concepts related to alkyl halides are often built upon in more advanced courses, and students who master these concepts early on will be well-prepared for further study.
In summary, the study of alkyl halides is an essential component of the JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in organic chemistry. A thorough understanding of this topic will provide students with a strong foundation for future studies and careers in organic chemistry and related fields.
Benefits of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Alkyl Halides
The JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in alkyl halides provides numerous benefits for students. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Understanding of Organic Chemistry: The study of alkyl halides is an essential component of the JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in organic chemistry. A thorough understanding of alkyl halides provides students with a strong foundation for understanding other organic reactions and functional groups.
- Mastery of Concepts: By studying alkyl halides, students gain a mastery of important concepts such as nomenclature, physical properties, preparation methods, and reaction mechanisms. This knowledge is essential for performing well on the JEE (Main+Advanced) exam and for pursuing advanced studies in organic chemistry.
- Practical Applications: Alkyl halides have a wide range of industrial applications, such as solvents, refrigerants, and pesticides. Students who have a strong understanding of alkyl halides will be well-prepared for careers in these fields.
- Problem-Solving Skills: The study of alkyl halides requires students to develop strong problem-solving skills, as they must be able to apply their knowledge of reaction mechanisms to predict the outcomes of various reactions.
- Foundation for Advanced Study: For students who plan to pursue advanced studies in organic chemistry, a thorough understanding of alkyl halides is essential. The concepts related to alkyl halides are often built upon in more advanced courses, and students who master these concepts early on will be well-prepared for future studies.
In summary, the JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in alkyl halides provides numerous benefits for students, including a strong foundation in organic chemistry, mastery of important concepts, practical applications, development of problem-solving skills, and preparation for advanced studies.
Conclusion of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Alkyl Halides
The JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in alkyl halides is a critical component of the organic chemistry curriculum. It provides students with a thorough understanding of the properties and reactions of alkyl halides, which are essential for pursuing advanced studies in organic chemistry or careers in related fields.
By studying alkyl halides, students gain mastery of important concepts such as nomenclature, physical properties, preparation methods, and reaction mechanisms. They also develop strong problem-solving skills as they apply their knowledge of reaction mechanisms to predict the outcomes of various reactions.
In addition to its academic benefits, the study of alkyl halides has practical applications in a wide range of industries, including solvents, refrigerants, and pesticides. A strong understanding of alkyl halides is essential for students who plan to pursue careers in these fields.
Overall, the JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in alkyl halides provides students with a strong foundation in organic chemistry, practical skills, and preparation for advanced studies. It is a critical component of the JEE (Main+Advanced) exam, and students who master the concepts related to alkyl halides will be well-prepared to tackle more advanced topics in organic chemistry and excel on the exam.
Overview of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Alkyl Halides
The JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in alkyl halides is a critical component of the organic chemistry curriculum. This course covers the study of alkyl halides, which are organic compounds that contain a halogen atom (such as chlorine, bromine, or iodine) bonded to an alkyl group (a chain of carbon and hydrogen atoms).
The course covers important concepts related to alkyl halides, including nomenclature, physical properties, preparation methods, and reaction mechanisms. Students learn how to predict the outcomes of various reactions involving alkyl halides, and develop strong problem-solving skills.
The study of alkyl halides has practical applications in a wide range of industries, including solvents, refrigerants, and pesticides. A strong understanding of alkyl halides is essential for students who plan to pursue careers in these fields.
In addition to its practical applications, the study of alkyl halides is an essential component of the JEE (Main+Advanced) exam. The exam places a significant emphasis on organic chemistry, and alkyl halides are a commonly tested topic. Students who have a thorough understanding of the properties and reactions of alkyl halides will be better equipped to perform well on the exam.
Overall, the JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in alkyl halides provides students with a strong foundation in organic chemistry, practical skills, and preparation for advanced studies. It is a critical component of the JEE (Main+Advanced) exam, and students who master the concepts related to alkyl halides will be well-prepared to tackle more advanced topics in organic chemistry and excel on the exam.
Types of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Alkyl Halides
The JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in alkyl halides covers several types of alkyl halides. Some of the most important types include:
- Primary alkyl halides: These are alkyl halides in which the halogen atom is bonded to a primary carbon atom, which is bonded to only one other carbon atom.
- Secondary alkyl halides: These are alkyl halides in which the halogen atom is bonded to a secondary carbon atom, which is bonded to two other carbon atoms.
- Tertiary alkyl halides: These are alkyl halides in which the halogen atom is bonded to a tertiary carbon atom, which is bonded to three other carbon atoms.
- Allylic and benzylic halides: These are alkyl halides in which the halogen atom is bonded to a carbon atom that is adjacent to either an allylic (double bond on a carbon atom adjacent to the alkyl group) or benzylic (aromatic ring adjacent to the alkyl group) carbon atom.
- Vinyl halides: These are alkyl halides in which the halogen atom is bonded to a carbon atom that is part of a vinyl group (a carbon-carbon double bond).
- Aryl halides: These are alkyl halides in which the halogen atom is bonded to a carbon atom that is part of an aromatic ring.
Each type of alkyl halide has unique physical and chemical properties, and reacts differently in various reactions. Students who study these different types of alkyl halides will gain a thorough understanding of their properties and reactions, which is essential for performing well on the JEE (Main+Advanced) exam and for pursuing advanced studies in organic chemistry.
Application of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Alkyl Halides
The JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in alkyl halides has numerous applications in various industries. Some of the most common applications include:
- Solvents: Alkyl halides are commonly used as solvents in a variety of industrial processes, such as cleaning and degreasing.
- Refrigerants: Some alkyl halides are used as refrigerants, such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs).
- Pesticides: Alkyl halides are used in the production of pesticides, such as insecticides and herbicides.
- Pharmaceuticals: Alkyl halides are used in the production of certain pharmaceuticals, such as anesthetics and antiseptics.
- Polymers: Alkyl halides are used in the production of polymers, such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
- Organic synthesis: Alkyl halides are widely used in organic synthesis reactions to introduce alkyl groups into various molecules.
- Catalysis: Some alkyl halides can be used as catalysts in chemical reactions.
A thorough understanding of alkyl halides is essential for students who plan to pursue careers in any of these fields or related industries. The JEE (Main+Advanced) intermediate course in alkyl halides provides students with the necessary knowledge and skills to work with alkyl halides in a variety of applications, making it an important component of the JEE (Main+Advanced) exam and for pursuing advanced studies in organic chemistry.
Nomenclature of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Alkyl Halides
The nomenclature of alkyl halides follows the rules established by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). The IUPAC nomenclature system for alkyl halides involves identifying the parent chain, identifying the substituent group (in this case, the halogen), and numbering the carbon atoms in the chain.
Here are the basic steps to name alkyl halides using IUPAC nomenclature:
- Identify the parent chain: The parent chain is the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms that contains the halogen atom. This chain is numbered starting from the end nearest to the halogen atom.
- Identify the halogen substituent: The halogen substituent is named as a prefix to the parent chain name. The prefixes used for halogens are “fluoro-” for fluorine, “chloro-” for chlorine, “bromo-” for bromine, and “iodo-” for iodine.
- Number the carbon atoms in the parent chain: The carbon atoms in the parent chain are numbered sequentially, starting from the end closest to the halogen substituent. If there are multiple halogens, the numbering should begin with the halogen that comes first in alphabetical order.
- Specify the location of the halogen substituent: The location of the halogen substituent is specified by using the number of the carbon atom that it is attached to, followed by a hyphen and the prefix for the halogen.
- Name any additional substituents: If there are additional substituents present, they are named using the appropriate prefixes and located by number.
- Combine the names of the substituents and parent chain: The names of the halogen substituent and any additional substituents are listed in alphabetical order, followed by the name of the parent chain.
Overall, the nomenclature of alkyl halides can be complex, but it is important for students to master this skill in order to perform well on the JEE (Main+Advanced) exam and to pursue advanced studies in organic chemistry.
Career Opportuities of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Alkyl Halides
JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Alkyl Halides is a part of the chemistry curriculum for students preparing for engineering entrance exams in India. Alkyl halides are organic compounds that contain a halogen atom (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, or iodine) bonded to a carbon atom in an alkyl group.
Here are some career opportunities for students who have studied alkyl halides as a part of their JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course:
- Chemical industry: The chemical industry is a major employer of chemists, and the knowledge of alkyl halides is essential for those working in this field. Chemists can work in research and development, quality control, and production departments of chemical companies.
- Pharmaceuticals: Pharmaceuticals also employ chemists who have a deep understanding of organic chemistry, including alkyl halides. They work in research and development, quality control, and production departments.
- Petrochemicals: Petrochemicals are chemicals that are derived from petroleum or natural gas. Alkyl halides are used in the production of many petrochemicals, and chemists who have knowledge of alkyl halides can work in this industry.
- Teaching and research: Students who are passionate about chemistry can pursue a career in teaching and research. They can work as professors, research scientists, or laboratory technicians in academic institutions.
- Environmental science: Alkyl halides are used in many industrial processes that can have an impact on the environment. Environmental scientists who understand the properties of alkyl halides can work to develop solutions to environmental problems caused by these chemicals.
- Forensic science: Forensic scientists use their knowledge of chemistry to analyze evidence in criminal investigations. Alkyl halides can be used as trace evidence in some cases, and a deep understanding of their properties can be valuable in forensic investigations.
In conclusion, the knowledge of alkyl halides gained through the JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course can open up various career opportunities in the chemical industry, pharmaceuticals, petrochemicals, teaching and research, environmental science, and forensic science.