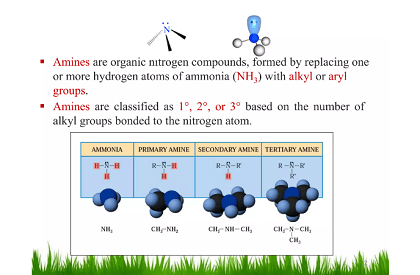
Amines are organic compounds that contain a nitrogen atom with a lone pair of electrons, which makes them weakly basic. They can be categorized as primary, secondary, or tertiary amines depending on the number of alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom.
In the JEE (Main+Advance) chemistry syllabus, amines are covered under the topic of Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen. Here are some of the key concepts that you should be familiar with:
- Preparation of Amines: Amines can be prepared by various methods such as reduction of nitro compounds, Gabriel synthesis, Hoffmann bromamide degradation, and reductive amination.
- Physical Properties of Amines: Amines have a higher boiling point than alkanes and alkenes of comparable molecular weight due to the presence of hydrogen bonding.
- Chemical Reactions of Amines: Amines can undergo various chemical reactions such as alkylation, acylation, and reaction with nitrous acid to form diazonium salts.
- Basicity of Amines: Amines are weakly basic due to the presence of the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom. The basicity increases with the number of alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom.
- Diazonium Salts: Diazonium salts are important intermediates in organic synthesis. They can be used for the preparation of various compounds such as phenols, aromatic amines, and azo dyes.
- Aromaticity of Amines: Aromatic amines are compounds in which the amino group is directly attached to an aromatic ring. They exhibit enhanced stability due to the delocalization of the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom.
- Polymers of Amines: Polyamides and polyurethanes are important polymers of amines. They have a wide range of applications in industry and everyday life.
It is important to have a strong understanding of the concepts mentioned above to excel in the JEE (Main+Advance) chemistry exam. Additionally, solving practice problems and previous years’ question papers can help you prepare effectively.
History of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines
The Joint Entrance Examination (JEE) is an engineering entrance exam conducted in India for admission to various undergraduate engineering programs in prestigious institutes such as the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs), National Institutes of Technology (NITs), and other government-funded technical institutions. The JEE (Main+Advance) chemistry syllabus includes the topic of Amines under the broader topic of Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen.
The JEE was first introduced in the year 2002 as a single entrance exam for admission to the IITs. Prior to that, each IIT conducted its entrance exam separately. In 2012, a major change was introduced, and the JEE was split into two separate exams: JEE (Main) and JEE (Advanced).
JEE (Main) is a screening exam conducted to shortlist candidates for JEE (Advanced). The exam is conducted twice a year in online mode, and the syllabus covers topics from Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics. The JEE (Main) chemistry syllabus includes Amines as a part of Organic Chemistry.
JEE (Advanced) is the second stage of the exam and is conducted once a year in offline mode. The exam is designed to test the in-depth knowledge of the candidates in the subjects of Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics. The JEE (Advanced) chemistry syllabus includes Organic Chemistry in great detail, and Amines is one of the important topics.
Over the years, the JEE (Main+Advance) chemistry syllabus has been revised to keep up with the changing trends in the field of engineering and technology. The syllabus for Amines has remained largely the same, with minor changes being made to keep the syllabus updated with the latest developments in the field of Organic Chemistry.
Today, JEE (Main+Advance) is one of the most competitive engineering entrance exams in India, and Amines is an important topic that aspirants need to master to excel in the chemistry section of the exam.
Nature of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines
Amines are organic compounds that contain a nitrogen atom with a lone pair of electrons. They are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary amines based on the number of alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom. Amines are an important topic in the JEE (Main+Advance) chemistry syllabus and are studied under the broader topic of Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen.
The nature of amines can be understood in terms of their physical and chemical properties. Here are some important points about the nature of amines:
- Physical Properties: Amines have a higher boiling point than alkanes and alkenes of comparable molecular weight. This is due to the presence of hydrogen bonding between the nitrogen and hydrogen atoms of neighboring molecules.
- Basicity: Amines are weakly basic due to the presence of the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom. The basicity increases with the number of alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom.
- Chemical Properties: Amines can undergo various chemical reactions such as alkylation, acylation, and reaction with nitrous acid to form diazonium salts. Amines can also react with carboxylic acids to form amides.
- Diazonium Salts: Diazonium salts are important intermediates in organic synthesis. They can be used for the preparation of various compounds such as phenols, aromatic amines, and azo dyes.
- Aromaticity: Aromatic amines are compounds in which the amino group is directly attached to an aromatic ring. They exhibit enhanced stability due to the delocalization of the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom.
- Polymers: Polyamides and polyurethanes are important polymers of amines. They have a wide range of applications in industry and everyday life.
In summary, amines are a versatile class of organic compounds with important physical and chemical properties. Mastery of the nature of amines is essential for success in the JEE (Main+Advance) chemistry exam.
Importance of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines
Amines are an important topic in the JEE (Main+Advance) chemistry syllabus and are studied under the broader topic of Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen. Here are some reasons why amines are important in the JEE (Main+Advance) exam:
- Amines are widely used in industry for the production of a variety of products such as dyes, polymers, pharmaceuticals, and agrochemicals. Therefore, a thorough understanding of the chemistry of amines is essential for a career in chemical engineering or related fields.
- Amines are weakly basic due to the presence of the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom. The basicity of amines is important in understanding the reactivity and selectivity of various chemical reactions involving amines. Therefore, a thorough understanding of the nature of amines is essential for success in the JEE (Main+Advance) exam.
- Diazonium salts, which are important intermediates in organic synthesis, are derived from amines. The chemistry of diazonium salts is extensively studied in the JEE (Main+Advance) exam. Diazonium salts are used for the preparation of various compounds such as phenols, aromatic amines, and azo dyes.
- Aromatic amines, which are a subclass of amines, are important due to their enhanced stability and their role in the synthesis of various compounds. The aromaticity of amines is important in understanding the chemistry of heterocyclic compounds, which are widely used in medicinal chemistry.
- Polyamides and polyurethanes, which are important polymers derived from amines, have a wide range of applications in industry and everyday life. Therefore, a thorough understanding of the chemistry of amines is important for a career in materials science or related fields.
In summary, amines are an important topic in the JEE (Main+Advance) chemistry syllabus due to their wide range of applications in industry and their importance in understanding the reactivity and selectivity of various chemical reactions. Mastery of the chemistry of amines is essential for success in the JEE (Main+Advance) exam and for a career in chemical engineering, materials science, or related fields.
System of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines
The JEE (Main+Advance) chemistry syllabus covers the topic of amines under the broader topic of Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen. Here is an overview of the system of the JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines:
- Classification of Amines: Amines are classified into primary, secondary, and tertiary amines based on the number of alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom.
- Preparation of Amines: Amines can be prepared by various methods such as reduction of nitro compounds, Gabriel phthalimide synthesis, and Hofmann bromamide reaction.
- Physical Properties of Amines: The physical properties of amines, such as boiling point and solubility, depend on the size of the alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom.
- Basicity of Amines: Amines are weakly basic due to the presence of the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom. The basicity of amines increases with the number of alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom.
- Chemical Reactions of Amines: Amines can undergo various chemical reactions such as alkylation, acylation, and reaction with nitrous acid to form diazonium salts. Amines can also react with carboxylic acids to form amides.
- Diazonium Salts: Diazonium salts are important intermediates in organic synthesis. They can be used for the preparation of various compounds such as phenols, aromatic amines, and azo dyes.
- Aromaticity of Amines: Aromatic amines are compounds in which the amino group is directly attached to an aromatic ring. They exhibit enhanced stability due to the delocalization of the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom.
- Polymers Derived from Amines: Polyamides and polyurethanes are important polymers derived from amines. They have a wide range of applications in industry and everyday life.
In summary, the JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines covers the classification, preparation, physical properties, basicity, chemical reactions, diazonium salts, aromaticity, and polymers derived from amines. Mastery of this topic is essential for success in the JEE (Main+Advance) exam and for a career in chemical engineering, materials science, or related fields.
Conclusion of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines
In conclusion, amines are an important topic in the JEE (Main+Advance) chemistry syllabus and are studied under the broader topic of Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen. Amines have a wide range of applications in industry and everyday life, making their study essential for a career in chemical engineering, materials science, or related fields.
The JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines covers the classification, preparation, physical properties, basicity, chemical reactions, diazonium salts, aromaticity, and polymers derived from amines. Mastery of this topic is essential for success in the JEE (Main+Advance) exam and for a career in the field of chemistry.
Overall, amines are an important class of organic compounds that play a significant role in organic synthesis, medicinal chemistry, and materials science. A thorough understanding of the chemistry of amines is essential for success in the JEE (Main+Advance) exam and for a successful career in the field of chemistry.
Overview of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines
The JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines is a part of the chemistry syllabus that focuses on the study of organic compounds containing nitrogen. Amines are a class of organic compounds that contain a nitrogen atom bonded to one or more alkyl or aryl groups. This topic is important because amines have a wide range of applications in industry, medicine, and everyday life.
The JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines covers various aspects of amines such as their classification based on the number of alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom, preparation methods, physical properties, basicity, chemical reactions, diazonium salts, aromaticity, and polymers derived from amines. Understanding these aspects of amines is crucial for success in the JEE (Main+Advance) exam and for a career in the field of chemistry.
In summary, the JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines provides students with a comprehensive understanding of amines and their importance in the field of chemistry. It covers various topics related to amines and provides students with the knowledge and skills necessary for success in the JEE (Main+Advance) exam and for a career in the field of chemistry.
Types of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines
The JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines covers several types of amines based on the number of alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom. Here are the three main types of amines:
- Primary Amines: Primary amines are a type of amine in which the nitrogen atom is bonded to one alkyl or aryl group and two hydrogen atoms. They have the general formula RNH2, where R is an alkyl or aryl group. Primary amines are basic in nature and can form salts with acids.
- Secondary Amines: Secondary amines are a type of amine in which the nitrogen atom is bonded to two alkyl or aryl groups and one hydrogen atom. They have the general formula R2NH, where R is an alkyl or aryl group. Secondary amines are less basic than primary amines and can also form salts with acids.
- Tertiary Amines: Tertiary amines are a type of amine in which the nitrogen atom is bonded to three alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula R3N, where R is an alkyl or aryl group. Tertiary amines are weakly basic and cannot form salts with acids.
In addition to these types of amines, the JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines also covers other topics related to amines such as their physical properties, chemical reactions, and applications in industry and everyday life. Mastery of these topics is essential for success in the JEE (Main+Advance) exam and for a career in the field of chemistry.
Application of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines
The JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines has a wide range of applications in various fields. Here are some of the applications of amines:
- Pharmaceuticals: Amines are widely used in the pharmaceutical industry to produce drugs. For example, anesthetics, antidepressants, and antihistamines all contain amines.
- Agriculture: Amines are used in agriculture as pesticides, fungicides, and herbicides. These compounds are used to protect crops from insects, fungi, and weeds.
- Polymer Industry: Amines are used in the polymer industry to produce polyurethane foam, epoxy resins, and nylon. These compounds have high tensile strength, durability, and resistance to heat.
- Textile Industry: Amines are used in the textile industry to produce dyes and pigments. Amines react with other chemicals to form colored compounds that can be used to dye textiles.
- Water Treatment: Amines are used in water treatment to remove carbon dioxide and other impurities. They react with the impurities to form compounds that can be removed from the water.
- Petroleum Industry: Amines are used in the petroleum industry to remove impurities from crude oil. They react with the impurities to form compounds that can be easily removed.
Overall, the JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines has many applications in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, agriculture, polymer industry, textile industry, water treatment, and petroleum industry. Understanding the chemistry of amines is crucial for success in these fields and for a successful career in chemistry.
Nomenclature of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines
The nomenclature of amines is based on the name of the alkyl or aryl group attached to the nitrogen atom. Here are the rules for nomenclature of amines:
- Primary amines are named by adding the suffix -amine to the name of the alkyl or aryl group. For example, CH3NH2 is methylamine.
- Secondary amines are named by adding the prefix N- to the name of the alkyl or aryl group attached to the nitrogen atom, followed by the suffix -amine. For example, (CH3)2NH is N,N-dimethylamine.
- Tertiary amines are named by adding the prefix N,N-dialkyl or N,N-diaryl to the name of the amine. For example, (CH3)3N is trimethylamine.
- If the amine is a substituent in a larger molecule, it is named as an amino group (-NH2) and given a location number to indicate its position in the molecule. For example, in the molecule CH3NHCH2CH2OH, the amino group is attached to the second carbon atom and is named as 2-aminoethanol.
- If there are two or more amino groups in the molecule, they are named using prefixes such as di-, tri-, tetra-, etc. For example, if the molecule contains two amino groups, it is named as diamine.
It is important to note that in the case of aromatic amines, the amino group is named as aniline, and the substituents attached to the aromatic ring are named according to the usual rules of substituent nomenclature.
Career Opportunities of JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines
A degree in JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines can lead to a variety of career opportunities in fields such as research, medicine, agriculture, and manufacturing. Here are some of the career opportunities available for those with a degree in JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines:
- Pharmaceutical research and development: Amines play an important role in the development of new drugs, and those with a degree in JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines can work in the pharmaceutical industry in roles such as research scientist, process chemist, or drug development specialist.
- Chemical manufacturing: Amines are used in a variety of chemical manufacturing processes, and those with a degree in JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines can work in roles such as process engineer, production chemist, or quality control analyst.
- Agriculture and food industry: Amines are used as pesticides and herbicides in the agriculture industry, and they are also used in the production of food additives. Those with a degree in JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines can work in roles such as research scientist or product development specialist.
- Environmental science: Amines are used in water treatment processes to remove impurities, and they are also used in air pollution control. Those with a degree in JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines can work in roles such as environmental chemist or pollution control engineer.
- Medical research: Amines are used in a variety of medical applications, including anesthesia, cancer treatment, and pain relief. Those with a degree in JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines can work in medical research roles such as biochemist or medical researcher.
- Teaching and academia: Those with a degree in JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines can also pursue careers in academia as professors, lecturers, or researchers.
Overall, a degree in JEE (Main+Advance) Intermediate Course Amines can open up a variety of career opportunities in many different fields, and there is a high demand for professionals with this expertise.
