The modern periodic law states that the properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers. This means that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physical properties.
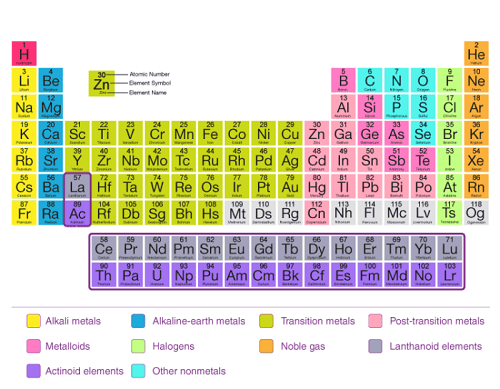
The present form of the periodic table is based on the modern periodic law and is arranged in order of increasing atomic number. The periodic table consists of rows called periods and columns called groups. Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties, while elements in the same period have similar electron configurations.
The periodic table is divided into several categories, including metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. Metals are located on the left side and middle of the periodic table, and they have properties such as high thermal conductivity, high electrical conductivity, and luster. Nonmetals are located on the right side of the periodic table, and they have properties such as low thermal conductivity, low electrical conductivity, and non-luster. Metalloids are located along the diagonal line between the metals and nonmetals and have properties intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals.
The modern periodic table has helped scientists predict the properties of new elements and understand the behavior of known elements. It has also provided a framework for organizing and studying the properties of elements, which has led to many advances in chemistry and other fields.
What is Required Modern periodic law and the present form of periodic table
The modern periodic law and the present form of the periodic table are both essential for understanding and organizing the properties of elements.
The modern periodic law provides a fundamental principle for understanding how the properties of elements are related to their atomic structure. It states that the properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers, which means that elements with similar electronic configurations exhibit similar chemical and physical properties.
The present form of the periodic table, based on the modern periodic law, is an arrangement of the elements in order of increasing atomic number. The periodic table is divided into periods (rows) and groups (columns), with elements in the same group having similar chemical properties.
The present form of the periodic table also helps to predict the properties of new elements, and it has been used to discover and synthesize new elements that were not known before. Additionally, the periodic table provides a useful framework for studying the properties of elements, including their reactivity, bonding, and electronic configurations.
In summary, the modern periodic law and the present form of the periodic table are both required for understanding the properties of elements and their behavior in chemical reactions. They provide a foundation for the study of chemistry and other related fields, and have contributed to many advances in science and technology.
Who is Required Modern periodic law and the present form of periodic table
The modern periodic law and the present form of the periodic table were developed by several scientists over time, building on the work of previous researchers.
The modern periodic law was first proposed by the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, who noticed a periodic repetition of chemical and physical properties when he arranged the known elements in order of increasing atomic weight. Later, the English physicist Henry Moseley demonstrated in 1913 that the periodicity of properties could be explained by the atomic number rather than atomic weight, leading to the modern periodic law.
The present form of the periodic table is based on the modern periodic law and was developed by various scientists, including Glenn T. Seaborg, who proposed the actinide and lanthanide series in the 1940s, and Neil Bartlett, who synthesized the first noble gas compound in 1962.
The periodic table has been revised and updated over time to accommodate new discoveries and data, and it remains an active area of research and study for chemists and other scientists.
In summary, the modern periodic law and the present form of the periodic table were developed by several scientists over time, with Mendeleev being the first to propose the periodic law and subsequent researchers contributing to the development and refinement of the periodic table.
When is Required Modern periodic law and the present form of periodic table
The modern periodic law was first proposed by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, and it states that the properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers. This fundamental principle was later refined by the English physicist Henry Moseley in 1913, who demonstrated that the periodicity of properties could be explained by the atomic number rather than atomic weight.
The present form of the periodic table, which is based on the modern periodic law, was developed over time by various scientists, and it continues to be revised and updated as new elements are discovered and new data becomes available.
The periodic table as we know it today has gone through several stages of development and refinement, with the first recognized periodic table being published by Mendeleev in 1869. Over the years, the periodic table has been expanded to include new elements and modified to reflect changes in our understanding of atomic structure and properties.
In summary, the modern periodic law was proposed in 1869, and the present form of the periodic table is the result of decades of research and refinement by various scientists, building on the work of Mendeleev and others.
Where is Required Modern periodic law and the present form of periodic table
The modern periodic law and the present form of the periodic table are concepts and models used in the field of chemistry, which is a branch of physical science.
The modern periodic law is a fundamental principle that describes the periodic repetition of properties of elements based on their atomic structure. This principle is applied to the organization and study of the elements in the periodic table, which is a graphical representation of the periodic law.
The present form of the periodic table, based on the modern periodic law, is a tabular arrangement of the elements in order of increasing atomic number. It consists of rows and columns that are used to organize the elements based on their properties.
The periodic table is an important tool used by chemists to study the behavior of elements and their interactions with other substances. It is used in a wide range of applications, including materials science, pharmaceuticals, environmental science, and many other fields.
In summary, the modern periodic law and the present form of the periodic table are concepts used in the field of chemistry, and they are used to organize and study the properties of elements and their behavior in chemical reactions.
How is Required Modern periodic law and the present form of periodic table
The modern periodic law and the present form of the periodic table are closely related and are used together to organize and understand the properties of elements.
The modern periodic law states that the properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers, which means that elements with similar electronic configurations exhibit similar chemical and physical properties. This principle is applied to the organization of the elements in the periodic table.
The present form of the periodic table is a graphical representation of the modern periodic law, and it is arranged in order of increasing atomic number. The periodic table is divided into periods (rows) and groups (columns), with elements in the same group having similar chemical properties. The elements in the periodic table are also arranged according to their electron configurations, which helps to predict their chemical and physical properties.
The periodic table is used to identify and predict the behavior of elements in chemical reactions, as well as to design and synthesize new materials with specific properties. It is a fundamental tool used in the study of chemistry and is used in many other scientific and technological fields.
In summary, the modern periodic law and the present form of the periodic table are used together to organize and understand the properties of elements. The periodic table is a graphical representation of the modern periodic law, and it is a fundamental tool used in the study of chemistry and other fields.
Case Study on Modern periodic law and the present form of periodic table
One example of how the modern periodic law and the present form of the periodic table have been used is in the discovery and study of new elements.
In 2016, four new elements were added to the periodic table: nihonium (Nh), moscovium (Mc), tennessine (Ts), and oganesson (Og). The discovery of these elements was made possible by advancements in technology, which allowed scientists to synthesize the elements in the laboratory and study their properties.
The properties of these new elements were predicted based on their positions in the periodic table, using the modern periodic law. For example, nihonium and moscovium are both predicted to be highly reactive metals with properties similar to other elements in their respective groups.
The present form of the periodic table was also used to determine the names and symbols of the new elements. The names and symbols were chosen based on a set of guidelines established by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), which oversees the naming and discovery of new elements.
Overall, the discovery and study of new elements is just one example of how the modern periodic law and the present form of the periodic table are used in modern chemistry research. By organizing and understanding the properties of elements, these tools allow scientists to predict and design new materials with specific properties, and to deepen our understanding of the fundamental principles of the natural world.
White paper on Modern periodic law and the present form of periodic table
Introduction
The modern periodic law and the present form of the periodic table are fundamental concepts in chemistry that have played a central role in the organization and understanding of the properties of elements. In this white paper, we will discuss the historical development of the periodic table, the modern periodic law, and its relevance in modern chemistry research.
Historical Development of the Periodic Table
The first periodic table was developed by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869. Mendeleev organized the known elements at that time according to their atomic weights and properties, and arranged them in a table with rows and columns. He noticed that elements with similar properties appeared at regular intervals, and he proposed that this was due to a periodic repetition of properties based on their atomic weights.
Over time, the periodic table was refined and expanded to include new elements and reflect changes in our understanding of atomic structure and properties. In 1913, Henry Moseley proposed a modification to the periodic table based on the atomic number of elements, which provided a more accurate basis for the periodicity of properties.
Modern Periodic Law
The modern periodic law, proposed by Mendeleev and refined by Moseley, states that the properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers. This principle explains the periodic repetition of properties observed in the periodic table and provides a basis for predicting the properties of new elements.
The modern periodic law is based on the electronic structure of atoms, specifically the arrangement of electrons in energy levels or shells. The number of electrons in the outermost shell, or valence shell, determines the chemical behavior and properties of an element.
Present Form of the Periodic Table
The present form of the periodic table is a graphical representation of the modern periodic law. The elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, and the table is divided into rows (periods) and columns (groups).
Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties due to their similar electronic configurations, and the table can be used to predict the behavior and properties of elements in chemical reactions. The periodic table is also used in the design and synthesis of new materials with specific properties.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the modern periodic law and the present form of the periodic table are fundamental concepts in chemistry that have played a central role in the organization and understanding of the properties of elements. The periodic table has evolved over time, reflecting advances in our understanding of atomic structure and properties. The modern periodic law provides a basis for predicting the properties of new elements and understanding the behavior of elements in chemical reactions. The periodic table remains a central tool in modern chemistry research, used in fields such as materials science, pharmaceuticals, and environmental science.
