Electromagnetic induction and alternating currents
Here’s a crash course on the NEET (National Eligibility cum Entrance Test) Physics syllabus topic of Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents:
- Introduction to Electromagnetic Induction:
- Understand the concept of electromagnetic induction, which states that a changing magnetic field induces an electromotive force (EMF) in a conductor.
- Learn about Faraday’s laws of electromagnetic induction, which describe the relationship between the induced EMF and the rate of change of magnetic field.
- Magnetic Flux and Faraday’s Law:
- Define magnetic flux as the product of the magnetic field strength and the area through which it passes.
- Discuss Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, which states that the magnitude of the induced EMF is proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux.
- Lenz’s Law:
- Explore Lenz’s law, which states that the direction of the induced current in a conductor is such that it opposes the change that produced it.
- Understand the concept of conservation of energy and how Lenz’s law is related to it.
- Eddy Currents:
- Learn about eddy currents, which are circulating currents induced in a conductor when it is exposed to a changing magnetic field.
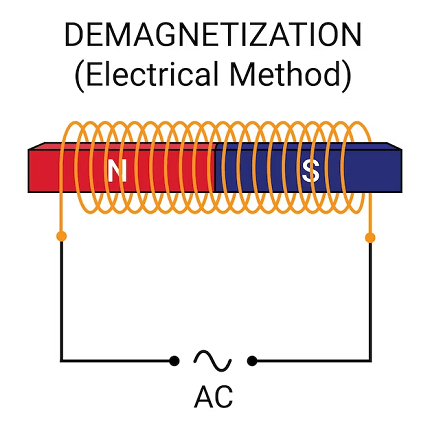
- Discuss the applications and effects of eddy currents, such as in electromagnetic braking and induction heating.
- Self-Induction and Mutual Induction:
- Understand self-induction, where the changing current in a coil induces an EMF in the same coil.
- Explore mutual induction, which occurs when the changing current in one coil induces an EMF in an adjacent coil.
- Alternating Current (AC):
- Introduce the concept of alternating current, which periodically reverses its direction.
- Discuss the advantages of AC over DC (direct current) and its applications in power generation and transmission.
- AC Circuit Analysis:
- Study the mathematical representation of AC using sinusoidal functions, peak value, root mean square (RMS) value, and frequency.
- Learn about impedance, reactance, and resistance in AC circuits and how they affect the flow of current.
- AC Circuits with Resistors, Inductors, and Capacitors:
- Analyze AC circuits with resistors, inductors, and capacitors in series and parallel configurations.
- Understand the concepts of inductive reactance and capacitive reactance and their respective formulas.
- Power in AC Circuits:
- Discuss the concept of power in AC circuits, including active power (real power), reactive power, and apparent power.
- Learn about power factor and power factor correction in AC circuits.
- Transformers:
- Study the principles of transformers, which are devices used to step up or step down the voltage in AC circuits.
- Understand the transformer’s construction, working principle, and the transformer equation.
Make sure to practice solving numerical problems and work on understanding the underlying concepts for a better grasp of the topic.
What is Required NEET PHYSICS SYLLABUS Electromagnetic induction and alternating currents
The NEET Physics syllabus for Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents covers the following topics:
- Electromagnetic Induction:
- Faraday’s laws of electromagnetic induction.
- Lenz’s law and conservation of energy.
- Self-induction and mutual induction.
- Eddy currents and their applications.
- Alternating Currents:
- AC circuits and AC current.
- Mathematical representation of AC using sinusoidal functions.
- Peak value, RMS value, and average value of AC current and voltage.
- Reactance and impedance in AC circuits.
- Power in AC circuits, power factor, and power factor correction.
- Resonance in AC circuits.
- Transformers and their working principles.
It’s important to note that the above topics are a general guideline, and the exact weightage of each subtopic may vary in the NEET Physics exam. Therefore, it’s essential to refer to the official NEET syllabus and exam pattern provided by the National Testing Agency (NTA) or the relevant exam authority to get precise information on the syllabus and distribution of marks.
Additionally, it’s recommended to consult reliable NEET preparation books, study materials, and previous years’ question papers to get a comprehensive understanding of the topics and to practice solving questions related to electromagnetic induction and alternating currents.
How is Required NEET PHYSICS SYLLABUS Electromagnetic induction and alternating currents
The topic of Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents is an important part of the NEET Physics syllabus. It carries a significant weightage in the exam and requires a good understanding of the underlying concepts and problem-solving skills. Here’s how the topic is typically covered in the NEET Physics exam:
- Conceptual Understanding:
- Students are expected to have a clear understanding of Faraday’s laws of electromagnetic induction and Lenz’s law.
- They should comprehend the relationship between changing magnetic fields and the induction of electromotive force (EMF) in conductors.
- Knowledge of self-induction and mutual induction is crucial, along with the ability to apply these concepts in different scenarios.
- Understanding the principles and applications of eddy currents is also important.
- Mathematical Analysis:
- Students should be able to analyze and solve problems related to electromagnetic induction using mathematical formulas and equations.
- They should be familiar with the mathematical representation of alternating currents using sinusoidal functions and the associated parameters such as peak value, RMS value, and frequency.
- Calculating reactance, impedance, and power in AC circuits is another key aspect of the syllabus.
- Circuit Analysis and Applications:
- Students should be able to analyze and solve problems related to AC circuits with resistors, inductors, and capacitors in series and parallel configurations.
- They should understand the behavior of different circuit elements in AC circuits, including inductive reactance, capacitive reactance, and resistance.
- Knowledge of power factor, power factor correction, and resonance in AC circuits is required.
- Students should also be familiar with the principles and working of transformers and their applications in stepping up or stepping down voltages.
To excel in this topic, it’s crucial to practice solving a variety of numerical problems and understand the underlying concepts thoroughly. Consulting NEET-specific study materials, textbooks, and previous years’ question papers will provide a good foundation for the exam. Regular revision and mock tests can help identify areas that need improvement and enhance overall performance in the NEET Physics exam.
Case Study on NEET PHYSICS SYLLABUS Electromagnetic induction and alternating currents
Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents in NEET Physics Syllabus
Let’s consider the case of Rajesh, a NEET aspirant preparing for the Physics section of the exam. Rajesh is focusing on the topic of Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents, which is an essential part of the NEET Physics syllabus. Let’s delve into Rajesh’s study approach and how he tackles this topic.
- Understanding the Concepts: Rajesh begins by thoroughly understanding the fundamental concepts of electromagnetic induction. He studies Faraday’s laws of electromagnetic induction, which describe the relationship between changing magnetic fields and the induction of EMF. He grasps Lenz’s law, which explains the direction of induced currents opposing the change in magnetic flux.
- Learning Through Visuals: Rajesh finds visual aids such as diagrams, animations, and videos to be helpful in understanding electromagnetic induction and AC concepts. He watches educational videos and refers to interactive simulations to visualize the effects of changing magnetic fields on induced currents and the behavior of AC circuits.
- Practice with Numerical Problems: Rajesh understands that problem-solving is crucial to master this topic. He solves a variety of numerical problems related to electromagnetic induction and AC circuits. By practicing calculations involving reactance, impedance, power factor, and transformers, Rajesh develops his problem-solving skills and becomes more confident in tackling similar questions in the NEET exam.
- Connecting Theory with Real-Life Applications: To enhance his understanding, Rajesh explores real-life applications of electromagnetic induction and AC circuits. He learns about transformers used in power distribution, induction heating, and electromagnetic braking systems. Understanding these applications not only reinforces his conceptual knowledge but also provides practical relevance to the topic.
- Revision and Mock Tests: Rajesh recognizes the importance of regular revision. He creates concise notes and summarizes the key concepts, formulas, and equations related to electromagnetic induction and AC circuits. He revisits these notes frequently to reinforce his understanding.
Additionally, Rajesh takes mock tests and solves previous years’ NEET Physics question papers. This practice helps him familiarize himself with the exam pattern, time management, and question types specific to the topic of electromagnetic induction and AC circuits. By analyzing his performance in these tests, Rajesh identifies areas that require further improvement and focuses his efforts accordingly.
- Seeking Clarification: Throughout his preparation, Rajesh actively seeks clarification whenever he encounters doubts or struggles with certain concepts. He reaches out to his teachers, peers, or online platforms to gain a clearer understanding of the topic. This proactive approach helps him address any gaps in knowledge and ensures a strong foundation in electromagnetic induction and AC circuits.
By following this comprehensive study approach, Rajesh builds a solid understanding of electromagnetic induction and AC circuits within the NEET Physics syllabus. With consistent practice, revision, and seeking clarification whenever needed, he prepares himself to confidently tackle questions related to this topic in the NEET exam.
White paper on NEET PHYSICS SYLLABUS Electromagnetic induction and alternating currents
Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents: Principles, Applications, and Future Perspectives
Abstract: This white paper provides an in-depth exploration of the concepts, principles, applications, and future perspectives of electromagnetic induction and alternating currents. It offers a comprehensive understanding of this topic, highlighting its significance in various fields such as electrical engineering, power generation, and communication systems. The paper also discusses emerging trends and advancements in electromagnetic induction and alternating currents, providing insights into potential areas of research and development.
- Introduction:
- Overview of electromagnetic induction and the historical development of the concept.
- Introduction to alternating currents and their importance in modern technology.
- Significance of electromagnetic induction and alternating currents in various industries.
- Fundamental Concepts:
- Faraday’s laws of electromagnetic induction and their implications.
- Lenz’s law and its role in determining the direction of induced currents.
- Self-induction and mutual induction: principles and applications.
- Mathematical Analysis of Alternating Currents:
- Mathematical representation of alternating currents using sinusoidal functions.
- Parameters of AC circuits: peak value, RMS value, frequency, and phase.
- Impedance, reactance, and resistance in AC circuits.
- AC Circuit Analysis:
- Series and parallel configurations of resistors, inductors, and capacitors in AC circuits.
- Analysis of power in AC circuits: active power, reactive power, and apparent power.
- Power factor, power factor correction, and their significance.
- Applications of Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents:
- Power generation and distribution systems: transformers and their principles.
- Induction motors and generators: working principles and applications.
- Communication systems: electromagnetic waves and modulation techniques.
- Induction heating, electromagnetic braking, and other practical applications.
- Advancements and Future Perspectives:
- Emerging trends and advancements in electromagnetic induction and AC technology.
- High-frequency applications: wireless power transfer and electromagnetic radiation.
- Smart grid systems and renewable energy integration.
- Role of electromagnetic induction in emerging technologies such as electric vehicles and wireless charging.
- Conclusion:
- Summary of the key concepts and applications of electromagnetic induction and alternating currents.
- Importance of continued research and innovation in this field.
- Future prospects and potential areas of growth in electromagnetic induction and AC technology.
This white paper aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of electromagnetic induction and alternating currents, highlighting their significance in various sectors. It serves as a valuable resource for researchers, engineers, and students interested in this field, offering insights into current applications and future directions. By exploring the principles and advancements of electromagnetic induction and AC technology, we can unlock new opportunities and contribute to the progress of diverse industries.