Laws of Motion
The Laws of Motion are a fundamental concept in physics, and they are an important part of the NEET (National Eligibility cum Entrance Test) syllabus. The Laws of Motion were formulated by Sir Isaac Newton and describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting upon it. Here is a crash course on the Laws of Motion for NEET physics:
- Newton’s First Law of Motion (Law of Inertia):
- An object at rest tends to stay at rest, and an object in motion tends to stay in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an external force.
- Inertia is the property of an object to resist changes in its state of motion. The first law explains the concept of inertia.
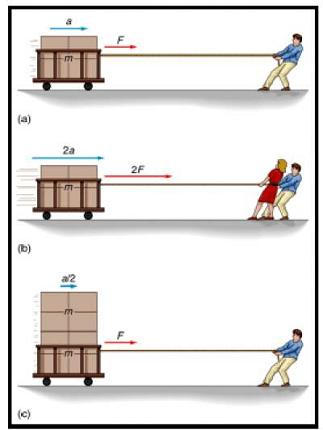
- Newton’s Second Law of Motion:
- The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass.
- Mathematically, F = ma, where F is the net force applied to the object, m is the mass of the object, and a is the acceleration produced.
- Newton’s Third Law of Motion (Law of Action-Reaction):
- For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
- This law states that whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first object.
- Applications of Newton’s Laws of Motion:
- Friction: Frictional forces oppose the motion or tendency of motion between objects in contact.
- Tension: Tension is the pulling force transmitted through a string, rope, or cable.
- Normal Force: The normal force is the force exerted by a surface to support the weight of an object resting on it.
- Circular Motion: The net force required to maintain circular motion is called centripetal force.
- Gravitational Force: The force of attraction between two objects with mass is called the gravitational force.
- Free Body Diagrams:
- Free body diagrams are used to analyze the forces acting on an object in a given situation. They help in visualizing and solving problems related to Newton’s Laws of Motion.
It’s important to study these laws thoroughly, understand their applications, and practice solving problems related to them to perform well in the NEET physics section. Remember to focus on the concepts, principles, and their mathematical representations to gain a strong foundation in the Laws of Motion.
What is Required NEET PHYSICS SYLLABUS Laws of Motion
The NEET physics syllabus covers the Laws of Motion as part of the broader topic of “Mechanics.” Here are the specific subtopics related to the Laws of Motion included in the NEET physics syllabus:
- Laws of Motion:
- Newton’s First Law of Motion (Law of Inertia)
- Newton’s Second Law of Motion
- Newton’s Third Law of Motion (Law of Action-Reaction)
- Momentum and impulse
- Conservation of linear momentum and its applications
- Equilibrium of concurrent forces
- Static and kinetic friction
- Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion:
- Centripetal force and centrifugal force
- Banked curves
It’s important to note that while the Laws of Motion are a key topic, the NEET physics syllabus covers other topics as well. Some of the other major topics in the NEET physics syllabus include:
- Physical World and Measurement
- Kinematics
- Work, Energy, and Power
- Rotational Motion
- Gravitation
- Properties of Bulk Matter
- Thermodynamics
- Behavior of Perfect Gas and Kinetic Theory
- Oscillations and Waves
- Electrostatics
- Current Electricity
- Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism
- Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents
- Electromagnetic Waves
- Optics
- Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation
- Atoms and Nuclei
- Electronic Devices
It is crucial to study and understand all the topics mentioned in the NEET physics syllabus to perform well in the exam. Make sure to refer to the official NEET syllabus or consult your study materials for a comprehensive understanding of the topics and subtopics included.
Where is Required NEET PHYSICS SYLLABUS Laws of Motion
The Laws of Motion are a fundamental concept in physics and are typically found under the topic of “Mechanics” in most physics curricula, including the NEET physics syllabus. The Laws of Motion are usually covered as a part of the broader study of motion and forces. In the NEET physics syllabus, you can find the Laws of Motion under the section titled “Dynamics.”
The topic of “Dynamics” includes the study of the laws governing the motion of objects, the forces acting on them, and their interactions. Specifically, within the Dynamics section, you will find the Laws of Motion, which include Newton’s First Law of Motion (Law of Inertia), Newton’s Second Law of Motion, and Newton’s Third Law of Motion (Law of Action-Reaction).
It is important to study and understand the Laws of Motion thoroughly as they provide the foundation for understanding and analyzing various aspects of motion, forces, and equilibrium.
Case Study on NEET PHYSICS SYLLABUS Laws of Motion
Projectile Motion
One of the topics that involve the Laws of Motion in the NEET physics syllabus is projectile motion. Let’s consider the case of a projectile, such as a ball, being thrown horizontally from the top of a cliff.
Scenario: A ball is thrown horizontally with an initial velocity of 10 m/s from the top of a cliff that is 20 meters high. The acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 m/s². We need to determine the time it takes for the ball to hit the ground and its horizontal displacement.
Solution:
- Analyzing the vertical motion: Since the ball is thrown horizontally, there is no initial vertical velocity (vy = 0 m/s). The only force acting on the ball is the force of gravity, which causes it to accelerate downward.
Using the second equation of motion for vertical motion: h = (1/2)gt²
Here, h is the vertical displacement (20 m) and g is the acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s²).
20 = (1/2)(9.8)t²
Simplifying the equation: t² = 20 / (1/2)(9.8) t² = 40 / 9.8 t ≈ √(40 / 9.8) t ≈ √4.08 t ≈ 2.02 s
Therefore, it takes approximately 2.02 seconds for the ball to hit the ground.
- Analyzing the horizontal motion: Since the ball is thrown horizontally, the initial horizontal velocity (vx) remains constant throughout the motion. The horizontal displacement (x) can be calculated using the equation:
x = vx × t
Here, vx is the initial horizontal velocity (10 m/s), and t is the time calculated in the previous step (2.02 s).
x = 10 m/s × 2.02 s x ≈ 20.2 m
Therefore, the horizontal displacement of the ball is approximately 20.2 meters.
This case study demonstrates the application of the Laws of Motion, specifically in the context of projectile motion. By considering the principles of vertical and horizontal motion, we were able to calculate the time of flight and horizontal displacement of the projectile. Understanding the Laws of Motion is crucial for solving such problems in the NEET physics exam.
White paper on NEET PHYSICS SYLLABUS Laws of Motion
White Paper on the Laws of Motion
Abstract: This white paper provides a comprehensive overview of the Laws of Motion, which form the foundation of classical mechanics. Developed by Sir Isaac Newton, these laws describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting upon it. Understanding the Laws of Motion is crucial in various scientific disciplines, including physics, engineering, and astronomy. This paper explores each law in detail, discussing their applications, implications, and mathematical formulations. Additionally, it highlights the significance of the Laws of Motion in modern scientific research and technological advancements.
- Introduction:
- Background and historical context of the Laws of Motion
- Significance and relevance of the Laws of Motion in science and technology
- Newton’s First Law of Motion (Law of Inertia):
- Definition and explanation of inertia
- Application of the first law in everyday situations
- Examples illustrating the concept of inertia
- Newton’s Second Law of Motion:
- Mathematical formulation: F = ma
- Relationship between force, mass, and acceleration
- Calculation of forces and accelerations in different scenarios
- Examples of applying the second law to solve problems
- Newton’s Third Law of Motion (Law of Action-Reaction):
- Understanding action-reaction pairs
- Balanced and unbalanced forces
- Applications of the third law in various phenomena
- Real-world examples showcasing action-reaction forces
- Applications of the Laws of Motion:
- Friction and its impact on motion
- Tension in strings and cables
- Normal force and equilibrium
- Circular motion and centripetal force
- Gravitational force and planetary motion
- Momentum and impulse
- Advanced Concepts and Extensions:
- Extended applications of the Laws of Motion in modern physics
- Relativistic effects and the laws of motion
- Quantum mechanical interpretations of the laws
- Impact and Relevance:
- Role of the Laws of Motion in technological advancements
- Influence on fields such as aerospace engineering, robotics, and biomechanics
- Examples of real-world applications and innovations based on the laws
- Conclusion:
- Summary of the Laws of Motion and their significance
- Encouragement for further research and exploration in the field
This white paper serves as a comprehensive resource for understanding the Laws of Motion, their applications, and their importance in various scientific and technological domains. It aims to inspire further exploration and research in classical mechanics, fostering innovation and advancements in related fields.
