Optics
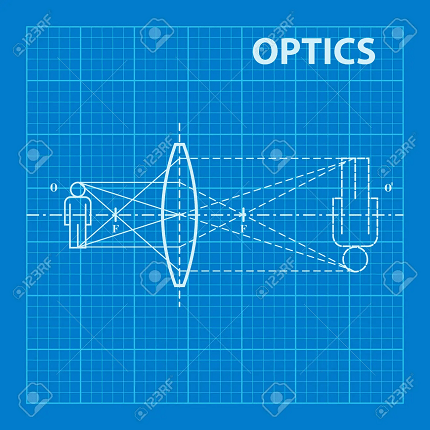
Optics is a branch of physics that deals with the study of light and its behavior. It focuses on the properties of light, its interaction with matter, and the formation of images. Optics plays a crucial role in understanding various phenomena related to vision, lenses, mirrors, and the behavior of light in different media.
The field of optics can be broadly categorized into two main branches:
- Geometrical Optics: Geometrical optics studies the behavior of light in terms of rays and assumes that light travels in straight lines. It focuses on the principles of reflection, refraction, and the formation of images by mirrors and lenses. Geometrical optics is particularly useful for understanding the basic properties of light and image formation.
- Physical Optics: Physical optics, also known as wave optics, treats light as a wave phenomenon. It deals with the wave nature of light, interference, diffraction, and polarization. Physical optics provides a more detailed and comprehensive understanding of light behavior by considering the wave properties of light.
The study of optics has practical applications in various fields, including:
- Optics in Medicine: Optics is essential in the field of medicine for techniques such as microscopy, endoscopy, laser surgery, and imaging technologies like optical coherence tomography (OCT).
- Optics in Communications: Fiber optics, which uses thin strands of glass or plastic to transmit light signals, is widely used in telecommunications for high-speed data transmission.
- Optics in Astronomy: Optics plays a crucial role in astronomical observations. Telescopes, lenses, mirrors, and spectroscopy techniques are used to gather and analyze light from celestial objects.
- Optics in Engineering: Optics is employed in engineering disciplines for various purposes, including designing optical systems, developing optical sensors, and analyzing light interactions in materials.
- Optics in Photography: Understanding the behavior of light is essential for capturing and manipulating images in photography.
Overall, the study of optics provides a foundation for understanding how light interacts with the world around us and enables the development of technologies and applications that utilize light in diverse fields.
The syllabus for NEET (National Eligibility cum Entrance Test) Physics includes a variety of topics in optics. Here is an overview of the integrated course NEET Physics syllabus for optics:
- Reflection of Light:
- Laws of reflection
- Reflection from plane mirrors
- Spherical mirrors (concave and convex)
- Mirror formula and magnification
- Image formation by mirrors
- Sign convention for mirrors
- Refraction of Light:
- Laws of refraction
- Refraction through a rectangular glass slab
- Refraction at spherical surfaces
- Refraction by lenses (concave and convex)
- Lens formula and magnification
- Image formation by lenses
- Power of a lens
- Sign convention for lenses
- Total Internal Reflection:
- Critical angle and total internal reflection
- Applications of total internal reflection (optical fibers, prism, etc.)
- Dispersion and Spectra:
- Refraction and dispersion of light
- Dispersion by a prism
- Spectrum of white light
- Formation of rainbow
- Optical Instruments:
- Human eye and its defects
- Correction of eye defects (myopia, hyperopia, presbyopia)
- Microscopes and astronomical telescopes
- Compound microscope
- Astronomical telescope
- Wave Optics:
- Huygens’ principle
- Young’s double-slit experiment
- Interference of light
- Conditions for constructive and destructive interference
- Coherent and incoherent sources of light
- Diffraction of light
- Single-slit diffraction
- Polarization:
- Polarization of light
- Polaroids and Malus’ law
- Brewster’s law
- Optical Phenomena in Nature:
- Scattering of light
- Tyndall effect
- Polarization by scattering
- Atmospheric refraction
It is important to note that the NEET Physics syllabus may vary slightly from year to year. It is always advisable to refer to the official NEET syllabus or consult the latest information provided by the conducting authority for the most accurate and up-to-date syllabus.
What is Required NEET-PHYSICS-SYLLABUS Optics
The NEET Physics syllabus for optics includes various topics that are essential for the exam. Here is a list of the specific topics related to optics that are required for NEET:
- Reflection of Light:
- Laws of reflection
- Reflection from plane mirrors
- Spherical mirrors (concave and convex)
- Mirror formula and magnification
- Image formation by mirrors
- Refraction of Light:
- Laws of refraction
- Snell’s law
- Refraction through a rectangular glass slab
- Refraction at spherical surfaces
- Refraction by lenses (concave and convex)
- Lens formula and magnification
- Image formation by lenses
- Power of a lens
- Total Internal Reflection:
- Critical angle and total internal reflection
- Applications of total internal reflection (e.g., optical fibers)
- Dispersion and Spectra:
- Refraction and dispersion of light
- Dispersion by a prism
- Formation of spectra and rainbow
- Optical Instruments:
- Human eye and its defects
- Correction of eye defects (myopia, hyperopia, presbyopia)
- Microscopes
- Astronomical telescopes
- Wave Optics:
- Huygens’ principle
- Young’s double-slit experiment
- Interference of light
- Conditions for constructive and destructive interference
- Diffraction of light
- Single-slit diffraction
- Polarization:
- Polarization of light
- Polaroids and Malus’ law
- Brewster’s law
It is important to note that the NEET syllabus may vary slightly from year to year. Therefore, it is recommended to refer to the official NEET syllabus or consult the latest information provided by the conducting authority to ensure you have the most accurate and up-to-date syllabus for optics in NEET Physics.
When is Required NEET-PHYSICS-SYLLABUS Optics
Optics is an important topic within the NEET Physics syllabus, and it is crucial to cover it thoroughly to prepare for the exam. Optics is typically covered in the “Ray Optics and Optical Instruments” and “Wave Optics” sections of the NEET Physics syllabus. These topics are part of the broader “Optics” unit.
The NEET exam does not specify a specific time period or duration for studying optics. However, it is advisable to allocate an appropriate amount of time to understand the concepts, practice problem-solving, and gain proficiency in applying the principles of optics.
To effectively cover the optics portion of the NEET Physics syllabus, it is recommended to follow a structured study plan. Allocate sufficient time to learn and understand the fundamental concepts, study the relevant theories and formulas, and practice solving a variety of numerical problems and conceptual questions related to optics. Additionally, make use of textbooks, reference materials, online resources, and practice papers to enhance your preparation.
Remember to integrate your optics study with other topics in the NEET Physics syllabus to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the subject. Allocating regular study sessions and practicing consistently will help you build a strong foundation in optics and maximize your performance in the NEET exam.
Where is Required NEET-PHYSICS-SYLLABUS Optics
The topic of optics is included in the NEET Physics syllabus. NEET (National Eligibility cum Entrance Test) is a national-level medical entrance examination conducted in India. The syllabus for NEET is set by the National Testing Agency (NTA) and covers various subjects, including Physics.
In the NEET Physics syllabus, optics is typically covered under two main sections:
- Ray Optics and Optical Instruments:
- Reflection of light by spherical mirrors (concave and convex)
- Refraction and laws of refraction
- Refraction by lenses (concave and convex)
- Lens formula and magnification
- Power of a lens
- Image formation by mirrors and lenses
- Combination of thin lenses in contact
- Microscopes and astronomical telescopes
- Human eye and its defects
- Correction of eye defects (myopia, hyperopia, presbyopia)
- Wave Optics:
- Huygens’ principle
- Young’s double-slit experiment
- Interference of light
- Conditions for constructive and destructive interference
- Diffraction of light
- Single-slit diffraction
- Polarization of light
- Brewster’s law
These topics cover the fundamental principles and applications of optics that are relevant for the NEET Physics exam.
It is important to note that the NEET syllabus may be subject to slight variations from year to year. To obtain the most accurate and up-to-date information regarding the NEET Physics syllabus and the inclusion of optics, it is advisable to refer to the official NEET website or consult the latest information provided by the conducting authority, which is the NTA.
How is Required NEET-PHYSICS-SYLLABUS Optics
The topic of optics is an important part of the NEET Physics syllabus. To effectively cover the required optics content for NEET, it is recommended to follow a systematic approach. Here are some steps to help you prepare:
- Understand the Concepts: Start by gaining a solid understanding of the basic concepts and principles of optics. This includes topics such as reflection, refraction, image formation, lens formula, interference, diffraction, and polarization. Refer to your textbooks, lecture notes, and other reliable resources to grasp the underlying principles.
- Study Material: Utilize appropriate study materials that cover the NEET Physics syllabus. There are several NEET preparation books and online resources available that specifically focus on NEET Physics and provide comprehensive coverage of optics. Ensure that the study material you choose is aligned with the NEET syllabus.
- Make Notes: Create concise and organized notes while studying optics. Summarize important formulas, concepts, and key points. These notes will serve as a quick reference during revision.
- Practice Numerical Problems: Optics involves numerical problem-solving. Practice a wide range of numerical problems related to optics to strengthen your problem-solving skills. This will help you understand the application of concepts and formulas in solving different types of questions.
- Solve Previous Year Question Papers: Solve previous year question papers and sample papers specifically for optics. This will familiarize you with the pattern of questions asked in NEET and help you identify areas that require further practice and understanding.
- Take Mock Tests: Regularly take mock tests focused on optics to assess your knowledge and gauge your exam preparedness. Mock tests will also help you improve your time management skills and build exam confidence.
- Seek Clarification: If you encounter any difficulties or have doubts while studying optics, seek clarification from your teachers, mentors, or online communities. Clearing your doubts will ensure a thorough understanding of the subject.
Remember to integrate your optics study with other topics in the NEET Physics syllabus to have a holistic preparation. Devote regular and consistent study sessions to optics, allocate time for revision, and monitor your progress through regular assessments. With effective planning and dedicated effort, you can successfully cover the required optics content for NEET Physics.
Nomenclature of NEET-PHYSICS-SYLLABUS Optics
The NEET Physics syllabus does not provide specific nomenclature for individual topics within the optics section. However, the optics portion of the NEET Physics syllabus can be categorized into two main sections: “Ray Optics and Optical Instruments” and “Wave Optics.” These sections encompass various subtopics that are essential to cover for the exam.
Here is a breakdown of the optics section in NEET Physics syllabus with subtopics:
- Ray Optics and Optical Instruments:
- Reflection of light
- Spherical mirrors (concave and convex)
- Mirror formula and magnification
- Refraction of light
- Laws of refraction
- Refraction through a rectangular glass slab
- Refraction at spherical surfaces
- Lenses (concave and convex)
- Lens formula and magnification
- Power of a lens
- Image formation by mirrors and lenses
- Combination of thin lenses in contact
- Optical instruments: Microscopes and astronomical telescopes
- Human eye and its defects
- Correction of eye defects (myopia, hyperopia, presbyopia)
- Wave Optics:
- Huygens’ principle
- Young’s double-slit experiment
- Interference of light
- Conditions for constructive and destructive interference
- Diffraction of light
- Single-slit diffraction
- Polarization of light
- Brewster’s law
While the NEET Physics syllabus does not provide specific nomenclature for each topic, it is important to cover all the subtopics mentioned above to have a comprehensive understanding of optics for the exam. Refer to your study materials, textbooks, and practice papers that are aligned with the NEET syllabus to ensure you cover all the necessary content for optics.
Case Study on NEET-PHYSICS-SYLLABUS Optics
Case Study: Laser Eye Surgery and Optics
Background: John, a 30-year-old individual, has been wearing glasses since childhood due to myopia (nearsightedness). He is considering undergoing laser eye surgery to correct his vision and eliminate the need for glasses or contact lenses. Laser eye surgery, also known as refractive surgery, is a procedure that uses lasers to reshape the cornea, thus altering its focusing power.
Case Scenario: John schedules a consultation with an ophthalmologist who specializes in laser eye surgery. During the consultation, the ophthalmologist explains the optics behind laser eye surgery and discusses the specific procedure known as LASIK (Laser-Assisted in Situ Keratomileusis).
Optical Principles:
- Refraction: The ophthalmologist explains the concept of refraction, which is the bending of light as it passes through different media. In the case of the eye, refraction occurs at the cornea and the lens. The cornea is primarily responsible for focusing light onto the retina.
- Myopia: The ophthalmologist explains that myopia is a condition where the eyeball is elongated or the cornea is too steep, causing light to focus in front of the retina instead of directly on it. This results in distant objects appearing blurry. Glasses or contact lenses correct myopia by introducing a diverging lens that compensates for the excessive focusing power of the eye.
- LASIK Procedure: The ophthalmologist describes the LASIK procedure, which involves two main steps: a. Flap Creation: A microkeratome or femtosecond laser is used to create a thin corneal flap, which is lifted to expose the underlying corneal tissue. b. Corneal Reshaping: An excimer laser is used to remove a precise amount of corneal tissue to reshape the cornea. This alters the cornea’s curvature, thereby correcting the refractive error.
- Post-Surgery Correction: The ophthalmologist discusses how the laser removes tissue from the central cornea to flatten its curvature in myopia. This allows light entering the eye to focus directly on the retina, resulting in clearer vision without the need for corrective lenses.
Benefits and Considerations: The ophthalmologist explains the potential benefits of laser eye surgery, such as reduced dependence on glasses or contact lenses, improved visual acuity, and enhanced quality of life. However, they also discuss the importance of a comprehensive pre-operative evaluation to determine the suitability of the patient for the procedure. Factors such as corneal thickness, corneal shape, and overall eye health play a role in assessing the candidacy for surgery.
Conclusion: In this case study, John explores the optics behind laser eye surgery as he considers undergoing the LASIK procedure to correct his myopia. Understanding the principles of refraction, myopia, and corneal reshaping helps John make an informed decision regarding the surgery. The case study highlights the application of optics in ophthalmology and demonstrates how advancements in laser technology have revolutionized vision correction procedures.
White paper on NEET-PHYSICS-SYLLABUS Optics
Title: Advancements in Optics: Transforming Science and Technology
Abstract: This white paper explores the field of optics, focusing on its advancements and transformative impact on various domains of science and technology. Optics, the study of light and its behavior, has played a pivotal role in understanding the fundamental properties of light, developing cutting-edge technologies, and revolutionizing numerous industries. This paper highlights key advancements in optics, ranging from fundamental research to practical applications, and discusses their implications for fields such as communication, medicine, manufacturing, and astronomy. By examining the latest innovations in optics, this white paper aims to provide insights into the exciting possibilities and future prospects in this rapidly evolving field.
- Introduction:
- Overview of optics as a scientific discipline
- Importance of optics in understanding light and its properties
- Brief history of optics and its evolution
- Fundamentals of Optics:
- Overview of the wave-particle duality of light
- Laws of reflection and refraction
- Concepts of interference, diffraction, and polarization
- Wavefront shaping and control
- Optical Technologies and Applications: 3.1. Optics in Communication: – Fiber optics and high-speed data transmission – Optical networking and telecommunications – Photonic devices and components3.2. Optics in Medicine and Biotechnology: – Optical imaging techniques (e.g., microscopy, endoscopy, OCT) – Laser surgery and therapeutic applications – Optical biosensing and diagnostics3.3. Optics in Manufacturing and Materials Science: – Laser processing and micromachining – Precision metrology and optical inspection – Nanophotonics and photonic materials3.4. Optics in Astronomy and Space Science: – Telescope technology and observations – Spectroscopy and astronomical imaging – Exoplanet detection and characterization
- Emerging Trends and Future Prospects:
- Advances in computational optics and machine learning
- Nano-optics and plasmonics
- Quantum optics and quantum information processing
- Integrated photonics and on-chip optical devices
- Challenges and Opportunities:
- Limitations and current challenges in optics
- Potential applications in emerging fields (e.g., quantum computing, biophotonics)
- Collaborative efforts and interdisciplinary research
- Conclusion:
- Recap of key advancements in optics
- Importance of continued research and innovation
- Potential impact on society, economy, and scientific progress
- References:
- Citations and resources for further reading
This white paper serves as a comprehensive overview of the advancements in optics, highlighting its transformative impact across various disciplines. By exploring the latest research and technological developments, it aims to inspire further exploration and collaboration in the field, driving innovation and shaping the future of optics and its applications.